Discontinuation of Initial Antiretroviral Therapy in Clinical Practice: Moving Toward Individualized Therapy
- PMID: 26871881
- PMCID: PMC4770376
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000000849
Discontinuation of Initial Antiretroviral Therapy in Clinical Practice: Moving Toward Individualized Therapy
Abstract
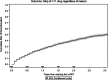
Background: Study aim was to estimate the rate and identify predictors of discontinuation of first combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) in recent years.
Methods: Patients who initiated first cART between January 2008 and October 2014 were included. Discontinuation was defined as stop of at least 1 drug of the regimen, regardless of the reason. All causes of discontinuation were evaluated and 3 main endpoints were considered: toxicity, intolerance, and simplification. Predictors of discontinuation were examined separately for all 3 endpoints. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used for the outcome discontinuation of ≥ 1 drug regardless of the reason. Cox regression analysis was used to identify factors associated with treatment discontinuation because of the 3 reasons considered.
Results: A total of 4052 patients were included. Main reason for stopping at least 1 drug were simplification (29%), intolerance (21%), toxicity (19%), other causes (18%), failure (8%), planned discontinuation (4%), and nonadherence (2%). In a multivariable Cox model, predictors of discontinuation for simplification were heterosexual transmission (P = 0.007), being immigrant (P = 0.017), higher nadir lymphocyte T CD4 cell (P = 0.011), and higher lymphocyte T CD8 cell count (P = 0.025); for discontinuation due to intolerance: the use of statins (P = 0.029), higher blood glucose levels (P = 0.050). About toxicity: higher blood glucose levels (P = 0.010) and the use of zidovudine/lamivudine as backbone (P = 0.044).
Conclusions: In the late cART era, the main reason for stopping the initial regimen is simplification. This scenario reflects the changes in recommendations aimed to enhance adherence and quality of life, and minimize drug toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Gulick RM, Mellors JW, Havlir D, et al. Treatment with indinavir, zidovudine, and lamivudine in adults with human immunodeficiency virus infection and prior antiretroviral therapy. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:734–739. - PubMed
-
- Hammer SM, Squires KE, Hughes MD, et al. A controlled trial of two nucleoside analogues plus indinavir in persons with human immunodeficiency virus infection and CD4 cell counts of 200 per cubic millimeter or less. AIDS Clinical Trials Group 320 Study Team. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:725–733. - PubMed
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–860. - PubMed
-
- Li TS, Tubiana R, Katlama C, et al. Long-lasting recovery in CD4 T-cell function and viral-load reduction after highly active antiretroviral therapy in advanced HIV-1 disease. Lancet. 1998;351:1682–1686. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials