Pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions for reducing rocuronium bromide induced pain on injection in children and adults
- PMID: 26871982
- PMCID: PMC8741206
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009346.pub2
Pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions for reducing rocuronium bromide induced pain on injection in children and adults
Abstract
Background: Rocuronium bromide is a routinely used muscle relaxant in anaesthetic practice. Its use, however, is associated with intense pain on injection. While it is well established that rocuronium bromide injection causes pain in awake patients, anaesthetized patients also tend to show withdrawal movements of the limbs when this muscle relaxant is administered. Various strategies, both pharmacological and non-pharmacological, have been studied to reduce the incidence and severity of pain on rocuronium bromide injection. We wanted to find out which of the existing modalities was best to reduce pain on rocuronium injection.
Objectives: The objectives of this review were to assess the ability of both pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions to reduce or eliminate the pain that accompanies rocuronium bromide administration.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL 2013, Issue 7), MEDLINE via Ovid SP (1966 to July 2013) and EMBASE via Ovid SP (1980 to July 2013). We also searched specific websites. We reran the searches in February 2015 and will deal with the 11 studies of interest found through this search when we update the review.
Selection criteria: We included all randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared the use of any drug or a non-pharmacological method with control patients, or those receiving no treatment to reduce the severity of pain with rocuronium injection. Our primary outcome was pain on rocuronium bromide injection measured by a pain score assessment. Our secondary outcomes were rise in heart rate and blood pressure following administration of rocuronium and adverse events related to the interventions.
Data collection and analysis: We used the standardized methods for conducting a systematic review as described in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Two authors independently extracted details of trial methodology and outcome data from reports of all trials considered eligible for inclusion. We made all analyses on an intention-to-treat basis. We used a fixed-effect model where there was no evidence of significant heterogeneity between studies and a random-effects model if heterogeneity was likely.
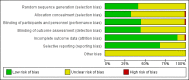
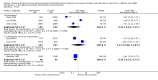
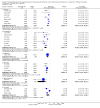
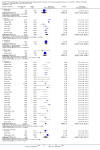
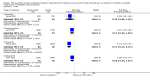
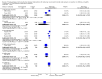
Main results: We included 66 studies with 7840 participants in the review, though most analyses were based on data from fewer participants. In total there are 17 studies awaiting classification. No studies were at a low risk of bias. We noted substantial statistical and clinical heterogeneity between trials. Most of the studies reported the primary outcome pain as assessed by verbal response from participants in an awake state but some trials reported withdrawal of the injected limb as a proxy for pain after induction of anaesthesia in response to rocuronium administration. Few studies reported adverse events and no study reported heart rate and blood pressure changes after administration of rocuronium. Lidocaine was the most commonly studied intervention drug, used in 29 trials with 2256 participants. The risk ratio (RR) of pain on injection if given lidocaine compared to placebo was 0.23 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.17 to 0.31; I² = 65%, low quality of evidence). The RR of pain on injection if fentanyl and remifentanil were given compared to placebo was 0.42 (95% CI 0.26 to 0.70; I² = 79%, low quality of evidence) and (RR 0.10, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.26; I² = 74%, low quality of evidence), respectively. Pain on injection of intervention drugs was reported with the use of lidocaine and acetaminophen in one study. Cough was reported with the use of fentanyl (one study), remifentanil (five studies, low quality evidence) and alfentanil (one study). Breath holding and chest tightness were reported with the use of remifentanil in two studies (very low quality evidence) and one study (very low quality evidence), respectively. The overall rate of complications was low.
Authors' conclusions: The evidence to suggest that the most commonly investigated pharmacological interventions reduce pain on injection of rocuronium is of low quality due to risk of bias and inconsistency. There is low or very low quality evidence for adverse events, due to risk of bias, inconsistency and imprecision of effect. We did not compare the various interventions with one another and so cannot comment on the superiority of one intervention over another. Complications were reported more often with use of opioids.
Conflict of interest statement
Hemanshu Prabhakar: none known
Gyaninder Pal Singh: none known
Zulfiqar Ali: none known
Mani Kalaivani: none known
Martha Smith: none known
Figures








Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009346
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Continuous intravenous perioperative lidocaine infusion for postoperative pain and recovery in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 4;6(6):CD009642. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009642.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29864216 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD010216. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010216.pub7. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jan 8;1:CD010216. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010216.pub8. PMID: 36384212 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Prediction of emergence agitation using withdrawal reaction following rocuronium injection in preschool-aged patients undergoing inguinal herniorrhaphy: a preliminary exploratory observational trial.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018 Jan 26;14:189-194. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S154264. eCollection 2018. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018. PMID: 29416346 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of different doses of rocuronium for general anesthesia on thyroid surgery.Gland Surg. 2021 Dec;10(12):3241-3251. doi: 10.21037/gs-21-618. Gland Surg. 2021. PMID: 35070884 Free PMC article.
-
A new rocuronium formulation not causing vascular pain in a flexor reflex model of anesthetized rats.J Anesth. 2018 Dec;32(6):806-812. doi: 10.1007/s00540-018-2557-x. Epub 2018 Sep 21. J Anesth. 2018. PMID: 30242475
-
The safety of high-dose rocuronium bromide in general anesthesia for spinal surgery and its effects on muscle relaxation.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Jul 15;13(7):8110-8117. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34377294 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of Antipyretic Analgesics administration intravenously for Preventing Rocuronium-Associated Pain/Withdrawal Response: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2020 Apr 20;20(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12871-020-00990-3. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020. PMID: 32312228 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
Abdusoglu 2011 {published data only}
-
- Abdusoglu MN, Ozkocak I, Yurtlu BS, Hanci V, Okyay RD, Ayoglu H. A subhypnotic dose of ketamine reduces pain associated with injection of propofol and rocuronium. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2011;28(3):229‐30. [PUBMED: 21157354] - PubMed
Ahmad 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ahmad N, Choy CY, Aris EA, Balan S. Preventing the withdrawal response associated with rocuronium injection: a comparison of fentanyl with lidocaine. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2005;100(4):987‐90. [PUBMED: 15781511] - PubMed
Akkaya 2008 {published data only}
-
- Akkaya T, Toygar P, Bedirili N, Yazicioglu D, Gumus H. Effects of pretreatment with lidocaine or ketamine on injection pain and withdrawal movements of rocuronium. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences 2008;38(6):577‐82. [CN‐00708630]
Alanoglu 2007 {published data only}
-
- Alanoglu Z, Yilmaz AA, Yilmaz D, Eker E, Asik I, Alkis N. A comparison of the use of lidocaine or tramadol for the prevention of pain during rocuronium injection. Anesteziyoloji ve Reanimasyon Uzmanları Derneği 2007;15(1):34‐7. [CN ‐ 00641870]
Asida 2009 {published data only}
-
- Asida SM, Megalla SA, Korany A. Effect of fentanyl, lidocaine or ketorolac on prevention of pain during rocuronium injection. Egyptian Journal of Anaesthesia 2009;25(1):31‐40.
Ayoglu 2007 {published data only}
Baek 2008 {published data only}
Borgeat 1997 {published data only}
-
- Borgeat A, Kwiatkowski D, Ruetsch YA. Spontaneous movements associated with rocuronium injection: the effects of prior administration of fentanyl. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 1997;9(8):650‐2. [PUBMED: 9438893] - PubMed
Byun 2005 {published data only}
-
- Byun JH, Kim JS, Park SW, Kang WJ. The effect of metoclopramide or lidocaine pretreatment on pain during rocuronium injection. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2005;49(1):35‐9.
Cheong 2000 {published data only}
-
- Cheong KF, Wong WH. Pain on injection of rocuronium: influence of two doses of lidocaine pretreatment. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2000;84(1):106‐7. [PUBMED: 10740559] - PubMed
Cheong 2003 {published data only}
-
- Cheong SH, Kim SY, Lee KM, Choe YK, Kim YJ, Park JW, et al. The effect of pretreatment with ketamine on vascular pain due to intravenous rocuronium injection in pediatric patients. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2003;45(4):447‐50.
Choi 2005 {published data only}
-
- Choi JH, Hwang JH, Shin YS. Comparison of the quantitative effect of ketamine on the vascular pain associated with intravenous rocuronium administration. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2005;49(1):30‐4.
Choi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Choi HG, Kim DS, Chang TH, Kim SH, Kim KH, Ryu SJ. Appropriate dosage of 8.4% sodium bicarbonate for preventing injection pain of rocuronium during anesthetic induction. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2006;51(2):162‐6.
Choi 2008 {published data only}
Dogru 2002 {published data only}
-
- Dogru K, Tosun Z, Yildiz K, Guler G, Sirri Kotanoglu M, Boyaci A. The effect of 2 % lidocaine pretreatment on rocuronium injection pain: a randomised, double blinded trial. Türk Anesteziyoloji ve Reanimasyon Cemiyeti Mecmuası 2002;30(8):350‐2.
Ertugrul 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ertugrul F. A comparison of the efficacies of different pretreatment drugs in resolving injection pain of rocuronium. Journal of International Medical Research 2006;34(6):665‐70. [PUBMED: 17294999] - PubMed
Eun 2005 {published data only}
-
- Eun SS, An TH. The comparison of the effects of ondansetron, lidocaine and tramadol for the prevention of pain on injection of rocuronium. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2005;48(1):20‐3.
Han 2003 {published data only}
-
- Han DW, Koo BN, Hwang SI, Shin YS, Kim KJ. Rocuronium injection pain is attenuated by NaHCO3. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2003;45(6):697‐701.
Han 2007 {published data only}
-
- Han DW, Koo BN, Choi SH, Lee JS, Shin YS, Sharma M, et al. Neutralized rocuronium (pH 7.4) before administration prevents injection pain in awake patients: a randomized prospective trial. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2007;19(6):418‐23. [PUBMED: 17967669] - PubMed
Hwang 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hwang SH, Jeon YH, Baek WY. The prevention of rocuronium injection pain by lidocaine pretreatment. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2003;45(4):451‐5.
Ikram 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ikram M, Ishaque M, Masood N, Abbas A. Effects of pre‐treatment with lidocaine on pain of rocuronium injection and withdrawal movements of the arm. APMC 2008;2(2):113‐6.
Jeon 2010 {published data only}
-
- Jeon Y, Baek S‐U, Park SS, Kim SO, Baek W‐Y, Yeo J‐S. Effect of pretreatment with acetaminophen on withdrawal movements associated with injection of rocuronium: a prospective randomized, double blind, placebo controlled study. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2010;59(1):13‐6. [PUBMED: 20651992] - PMC - PubMed
Jung 2005 {published data only}
-
- Jung SM, Kim SH, Lim YS, Kwon HU, Kang PS, Park CW. The effect of sodium bicarbonate or lidocaine mixed with rocuronium on withdrawal movement in pediatric patients. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2005;48(5):514‐9.
Jung 2005a {published data only}
-
- Jung SS, Lee JN, Yoon SH. Comparison of prevention effect of lidocaine pretreatment on pain and withdrawal associated with injection of rocuronium. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2005;49(2):131‐5.
Jung 2005b {published data only}
-
- Jung SM, Ko NY, Lim YS, Kang PS, Kwon HU. Comparison of premixed NaHCO3 and lidocaine on rocuronium injection pain. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2005;48(5):483‐8.
Kaya 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kaya G, Memis D, Turan A, Karamanlioglu B, Seker S, Pamukcu Z. Comparison of dexmedetomidine with lidocaine in the prevention of rocuronium injection pain. Türk Anesteziyoloji ve Reanimasyon Cemiyeti Mecmuası 2004;32(5):344‐8.
Kelsaka 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kelsaka E, Baris S, Kefeli H, Mehel A, Karakaya D, Kocamanoglu S, et al. Comparison of ondansetron and lidocaine in preventing of rocuronium injection pain. Ondokuz Mayis Universitesi Tip Dergisi 2002;19(3):163‐7.
Ki 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ki HS, So KY, Chung CD. The dose‐dependent analgesic effect of ondansetron for pain on injection of rocuronium in adults. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2005;48(2):145‐8.
Kilicaslan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kilicaslan A, Topal A, Erol A, Tavlan A. The prevention of pain from injection of rocuronium by diphenhydramine. Arastirma Yazisi Selçuk Üniversitesi. Tip Dergisi 2010;26(2):128‐31.
Kim 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kim KS, Chae YJ, Park SY, Cho HB, Kim JS. The effect of pretreatment with lidocaine for the withdrawal movement associated with the injection of rocuronium in children. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2002;43:572‐4.
Kim 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kim SJ, Lee HY, An TH. Comparison of withdrawal responses associated with temperature and gender on the injection of rocuronium. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2004;47(3):331‐5.
Kim 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kim KS, Kim YS, Jeon WJ, Yeon JH. Prevention of withdrawal associated with the injection of rocuronium in adults and children. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2006;18(5):334‐8. [PUBMED: 16905077] - PubMed
Kim 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kim JY, Kim JY, Kim YB, Kwak HJ. Pretreatment with remifentanil to prevent withdrawal after rocuronium in children. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2007;98(1):120‐3. [PUBMED: 17065169] - PubMed
Kim 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kim JY, Kwak HJ, Kim JY, Park KS, Song JS. Prevention of rocuronium‐induced withdrawal movement in children: a comparison of remifentanil with alfentanil. Pediatric Anesthesia 2008;18(3):245‐50. [PUBMED: 18230068] - PubMed
Kim 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kim JH, Kim JH, Han SH, Hwang JW, Oh AY. Alfentanil is comparable to remifentanil in preventing withdrawal movement following rocuronium injection. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2009;21(1):9‐12. [PUBMED: 19232934] - PubMed
Kim 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kim YH, Go YK, Lee JU, Chung WS, Shin YS, Han KC, et al. Pretreatment with nafamostat mesilate, a kallikrein inhibitor, to decrease withdrawal response associated with rocuronium. Journal of Anesthesia 2010;24(4):549‐52. [PUBMED: 20499255] - PubMed
Kirpit 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kirpit P, Akcaboy ZN, Akcaboy EY, Gogus N. Comparison of the effects of lidocaine, ketamine and ephedrine in the prevention of injection site pain of rocuronium. Türk Anesteziyoloji ve Reanimasyon Cemiyeti Mecmuası 2010;38(6):428‐34.
Kwak 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kwak HJ, Lee WK, Kim DY, Kwak HS. Pain on injection of rocuronium: influence of two methods of lidocaine injection. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2004;46(6):675‐8.
Kwak 2010 {published data only}
Lee 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lee SK, Lee JM, Kim YM, Moon HS. Pain on injection of rocuronium: the effect of pretreatment of lidocaine, fentanyl and ondansetron. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2004;46(2):151‐4.
Lee 2009 {published data only}
Lee 2009b {published data only}
-
- Lee YC, Jang YH, Kim JM, Lee SG. Rapid injection of rocuronium reduces withdrawal movement on injection. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2009;21(6):427‐30. [PUBMED: 19833276] - PubMed
Lee 2009c {published data only}
-
- Lee JI, Lim SH, Lee SE, Kim YH, Lee JH, Lee KM. Priming technique can alleviate the withdrawal responses associated with intravenous administration of rocuronium. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2009;56(6):628‐33. - PubMed
Lee 2011 {published data only}
Liou 2003 {published data only}
-
- Liou JT, Hsu JC, Liu FC, Ching‐Wah Sum D, Lui PW. Pretreatment with small‐dose ketamine reduces withdrawal movements associated with injection of rocuronium in pediatric patients. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2003;97(5):1294‐7. [PUBMED: 14570640] - PubMed
Mahajan 2005 {published data only}
-
- Mahajan R, Batra YK, Kumar S. Pain on injection of rocuronium: influence of ketamine pretreatment. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 2005;52(1):111‐2. [PUBMED: 15625267] - PubMed
Mahajan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Mahajan C, Rath GP, Bithal PK, Prabhakar H, Yadav R, Dube SK. Local warming at injection site helps alleviate pain after rocuronium administration. Journal of Anesthesia 2010;24(6):845‐8. [PUBMED: 20737278] - PubMed
Memis 2002 {published data only}
-
- Memis D, Turan A, Karamanlioglu B, Sut N, Pamukcu Z. The prevention of pain from injection of rocuronium by ondansetron, lidocaine, tramadol, and fentanyl. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2002;94(6):1517‐20. [PUBMED: 12032018] - PubMed
Memis 2005 {published data only}
-
- Memis D, Turan A, Kaya G, Karamanlioglu B, Seker S. Preventing pain on injection of rocuronium: two doses of dexmedetomidine. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia 2005;52(4):437‐8. [PUBMED: 15814762] - PubMed
Oh 2007 {published data only}
-
- Oh AY, Seo KS, Goo EK, Park YO, Kim SJ, Kim JH. Prevention of withdrawal movement associated with injection of rocuronium in children: comparison of remifentanil, alfentanil and fentanyl. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2007;51(9):1190‐3. [PUBMED: 17711566] - PubMed
Park 2005 {published data only}
Park 2006 {published data only}
-
- Park SJ, Lee JY, Jee DL. The effect of rocuronium diluted with 0.9% NaCl on withdrawal response during injection in pediatric patient. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2006;51(2):157‐61.
Park 2011 {published data only}
-
- Park SH, Oh AY, Goo EK, Nahm FS, Min SW, Hwang JW, et al. A short period of inhalation induction with sevoflurane prevents rocuronium‐induced withdrawal in children. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2011;55(1):87‐91. [PUBMED: 21126238] - PubMed
Reddy 2001 {published data only}
-
- Reddy MS, Chen FG, Ng HP. Effect of ondansetron pretreatment on pain after rocuronium and propofol injection: a randomised, double‐blinded controlled comparison with lidocaine. Anaesthesia 2001;56(9):902‐5. [PUBMED: 11531681] - PubMed
Sharma 2010 {published data only}
Shevchenko 1999 {published data only}
-
- Shevchenko Y, Jocson JC, McRae VA, Stayer SA, Schwartz RE, Rehman M, et al. The use of lidocaine for preventing the withdrawal associated with the injection of rocuronium in children and adolescents. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1999;88(4):746‐8. [PUBMED: 10195516] - PubMed
Shin 2011a {published data only}
Shin 2011b {published data only}
Singh 2007 {published data only}
-
- Singh M, Chauhan H, Rath GP, Prabhakar H, Bithal PK, Dash HH. Effect of narcotic pretreatment on pain after rocuronium injection: a randomized, double‐blind controlled comparison with lidocaine. Journal of Anesthesia 2007;21(4):510‐2. [PUBMED: 18008122] - PubMed
Tuncali 2004 {published data only}
-
- Tuncali B, Karci A, Tuncali BE, Mavioglu O, Olguner CG, Ayhan S, et al. Dilution of rocuronium to 0.5 mg/ml with 0.9% NaCl eliminates the pain during intravenous injection in awake patients. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2004;99(3):740‐3. [PUBMED: 15333404] - PubMed
Turan 2003 {published data only}
-
- Turan A, Memis D, Karamanlioglu B, Sut N, Pamukcu Z. The prevention of pain from injection of rocuronium by magnesium sulphate, lidocaine, sodium bicarbonate, and alfentanil. Anaesthesia and Intensive Care 2003;31(3):277‐81. [PUBMED: 12879672] - PubMed
Wee 2004 {published data only}
-
- Wee SW, Lee HS, An TH, So GY, Lim KJ, Jung JD, et al. The dose dependent analgesic effect of lidocaine for pain on injection rocuronium. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2004;47(3):327‐30.
Yavascaoglu 2007 {published data only}
-
- Yavascaoglu B, Kaya FN, Ozcan B. Esmolol pretreatment reduces the frequency and severity of pain on injection of rocuronium. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2007;19(6):413‐7. [PUBMED: 17967668] - PubMed
Yoon 2010 {published data only}
-
- Yoon JR, Jeon Y, Yoo Y, Shin HJ, Ahn JH, Lim CH. The analgesic effect of remifentanil on prevention of withdrawal response associated with the injection of rocuronium in children: no evidence for a peripheral action. Journal of International Medical Research 2010;38:1795‐800. [PUBMED: 21309495] - PubMed
Yoon 2011 {published data only}
Zhang 2012 {published data only}
-
- Zhang Y, Xiang Y, Liu J. Prevention of pain on injection of rocuronium: a comparison of lidocaine with different doses of parecoxib. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2012;24(6):456‐9. [PUBMED: 22762978] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Kim 2008a {published data only}
-
- Kim SK, Kwon MA, Park JS. The amount of 8.4% sodium bicarbonate needed to neutralize the acidity of rocuronium so as to prevent injection pain. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2008;20(8):629‐30. [PUBMED: 19100942] - PubMed
Min 2011 {published data only}
-
- Min SK, Lee SY, Park KS, Yoo J, Chae YJ. Bolus effective dose of ketamine for preventing withdrawal movement on injection of rocuronium in paediatric patients. Journal of International Medical Research 2011;39:1408‐12. [PUBMED: 21986141] - PubMed
Shabana 2011 {published data only}
-
- Shabana AM, Nasr ES. Prevention of rocuronium injection pain in paediatrics: ketamine versus midazolam? A prospective randomized double blind study. Egyptian Journal of Anaesthesia 2011;27:141‐4.
Yoon 2010a {published data only}
-
- Yoon JY, Kim HK, Kwon JY, Shin SW, Kim KH, Kim WS, et al. EC(50) of remifentanil to prevent withdrawal movement associated with injection of rocuronium. Journal of Anesthesia 2010;24(2):182‐6. [PUBMED: 20127371] - PubMed
Zeidan 2006 {published data only}
-
- Zeidan A, Nahle N, Maaliki H, Baraka A. Cisatracurium or rocuronium versus rocuronium‐cisatracurium combination. Middle East Journal of Anesthesiology 2006;18(5):879‐86. [PUBMED: 17094524] - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Abu‐Halaweh 2013 {published data only}
-
- Abu‐Halaweh SA, Aloweidi AK, Qudaisat IY, Al‐Hussami MO, Atyat BS, Al‐Mustafa M, et al. Comparison of three methods of preventing rocuronium induced pain on injection using venous occlusion technique: a randomized prospective double blind controlled study. Middle East Journal of Anesthesiology 2013;22(1):87‐92. [PUBMED: 23833856] - PubMed
Abu‐Halaweh 2014 {published data only}
-
- Abu‐Halaweh SA, Aloweidi AK, Qudaisat IY, Al‐Hussami MO, Al Zaben KR, Abu‐Halaweh AS. Pretreatment with remifentanil, fentanyl, or lidocaine to prevent withdrawal after rocuronium using venous occlusion technique in children and adolescents: a prospective randomized placebo‐controlled double‐blind study. Journal of Anesthesia 2014;28:886‐90. [PUBMED: 24816536] - PubMed
Akcaboy 2012 {published data only}
-
- Akcaboy ZN, Akcaboy EY, Soyal OB, Turhan G, Gogus N. Can ephedrine pretreatment be effective in alleviating rocuronium injection pain?. Medical Principles and Practice 2012;21:323‐7. - PubMed
Ates 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ates G, Kose EA, Oz G, Apan A. Effect of paracetamol pretreatment on rocuronium‐induced injection pain: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled comparison with lidocaine. Journal of Clinical and Analytical Medicine 2014;5:507‐10.
Aydin 2014 {published data only}
-
- Aydın GB, Polat R, Ergil J, Sayın M, Caparlar CO. Comparison of randomized preemptive dexketoprofen trometamol or placebo tablets to prevent withdrawal movement caused by rocuronium injection. Journal of Anesthesia 2014;28:471‐4. [PUBMED: 24201413] - PubMed
Chiarella 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chiarella AB, Jolly DT, Huston CM, Clanechan AS. Comparison of four strategies to reduce the pain associated with intravenous administration of rocuronium. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2003;90(3):377‐9. [12594153] - PubMed
Cho 2014 {published data only}
Choi 2012 {published data only}
Honca 2013 {published data only}
-
- Honca M, Kulah BB, Purtuloglu T, Honca T, Camgoz Eryilmaz N, Ozkan U, et al. A comparison of tramadol, sufentanil, meperidine, and lidocaine in prevention of pain due to rocuronium injection. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences 2013;43:79‐83.
Hwang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Hwang SM, Oh MS, Lim SY. Effect of sodium bicarbonate or lidocaine mixed with rocuronium on withdrawal movement during rocuronium injection. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2004;46(2):160‐3.
Jeon 2013 {published data only}
Jung 2014 {published data only}
Kim 2013 {published data only}
-
- Kim E, Kim CH, Kim HK, Kwon JY, Lee do W, Kim HY. Effect of nitrous oxide inhalation on pain after propofol and rocuronium injection. Journal of Anesthesia 2013;27:868‐73. [PUBMED: 23982855] - PubMed
Lee 2009a {published data only}
-
- Lee SS, Yoon H. A comparison of the effect of lidocaine or sodium bicarbonate mixed with rocuronium on withdrawal movement, mean arterial pressure and heart rate during rocuronium injection. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2009;39(2):270‐8. [PUBMED: 19411798] - PubMed
Lim 2006 {published data only}
-
- Lim CS, Shin YS. The effects of remifentanil pretreatment on rocuronium injection pain and cardiovascular response during anesthetic induction. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology 2006;50(6):637‐41.
Prasanna 2005 {published data only}
-
- Prasanna M, Priya V, Divatia JV, Sareen R. Comparison between different strategies to reduce pain on intravenous injection of rocuronium. Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology 2005;21(1):59‐61.
Sari 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sari M, Iyilikci L, Bayindir S, Ellidokuz H, Gunerli A. Comparison of the effectiveness of pretreatment by fentanyl and remifentanil on rocuronium induced injection pain. Saudi Medical Journal 2008;29(3):374‐8. [PUBMED: 18327362] - PubMed
Additional references
Abbas 2009
-
- Abbas N, Tariq S, Khan AW, Murtaza G, Naqvi N, Khanzada A. To asses the effects of rocuronium pretreatment on succinylcholine induced fasciculations and postoperative myalgias. JPMA. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association 2009;59(12):847‐50. [PUBMED: 20201179] - PubMed
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7:177‐88. [PUBMED: 3802833] - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(11):1539‐58. [PUBMED: 12111919] - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Kim 2008b
-
- Kim SK, Kwon MA, Park JS. The amount of 8.4% sodium bicarbonate needed to neutralize the acidity of rocuronium so as to prevent injection pain. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2008;20(8):629‐30. [PUBMED: 19100942] - PubMed
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Lockey 1995
-
- Lockey D, Coleman P. Pain on injection of rocuronium bromide. Anaesthesia 1995;50(5):474. [PUBMED: 7793569] - PubMed
Orebaugh 1999
-
- Orebaugh SL. Succinylcholine: adverse effects and alternatives in emergency medicine. American Journal of Emergency Medicine 1999;17(7):715‐21. [PUBMED: 10597098] - PubMed
RevMan 5.3 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
References to other published versions of this review
Prabhakar 2011
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

