Six-minute walk test in children and adolescents with renal diseases: tolerance, reproducibility and comparison with healthy subjects
- PMID: 26872080
- PMCID: PMC4737086
- DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2016(01)05
Six-minute walk test in children and adolescents with renal diseases: tolerance, reproducibility and comparison with healthy subjects
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate exercise tolerance and the reproducibility of the six-minute walk test in Brazilian children and adolescents with chronic kidney disease and to compare their functional exercise capacities with reference values for healthy children.
Methods: This cross-sectional study assessed the use of the six-minute walk test in children and adolescents aged 6-16 with stage V chronic kidney disease. For statistical analysis of exercise tolerance, including examinations of correlations and comparisons with reference values, the longest walked distances were considered. The reproducibility of the six-minute walk test was assessed using intraclass correlation coefficients.
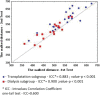
Results: A total of 38 patients (14 females and 24 males) were evaluated, including 5 on peritoneal dialysis, 12 on hemodialysis and 21 who had undergone renal transplantation, with a median age of 11.2 years (6.5-16). The median walked distance was 538.5 meters (413-685) and the six-minute walk test was found to be reproducible. The walked distance was significantly correlated with age (r=0.66), weight (r=0.76), height (r=0.82), the height Z score (r=0.41), hemoglobin (r=0.46), hematocrit (r=0.47) and post-test systolic blood pressure (r=0.39). The chronic kidney disease patients predicted walked distance was 84.1% of the reference value according to age, 90.6% according to age-corrected height and 87.4% according to a predictive equation.
Conclusions: The stage V chronic kidney disease patients had a significantly decreased functional exercise capacity, as measured by the six-minute walk test, compared with the healthy pediatric reference values. In addition, the six-minute walk test was shown to be well tolerated, reliable and applicable as a low-cost tool to monitor functional exercise capacity in patients with renal disease.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reference values for the 6-minute walk test in healthy children and adolescents in Switzerland.BMC Pulm Med. 2013 Aug 5;13:49. doi: 10.1186/1471-2466-13-49. BMC Pulm Med. 2013. PMID: 23915140 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical correlates and prognostic significance of six-minute walk test in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Comparison with cardiopulmonary exercise testing.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000 Feb;161(2 Pt 1):487-92. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.161.2.9906015. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. PMID: 10673190
-
Reference Equation for the Incremental Shuttle Walk Test in Children and Adolescents.J Pediatr. 2015 Nov;167(5):1057-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2015.07.068. Epub 2015 Aug 29. J Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 26323195
-
Six-minute walk test: a valuable tool for assessing pulmonary impairment.J Bras Pneumol. 2011 Jan-Feb;37(1):110-7. doi: 10.1590/s1806-37132011000100016. J Bras Pneumol. 2011. PMID: 21390439 Review. English, Portuguese.
-
Submaximal Field Walking Tests Applied in the Cardiopulmonary Assessment in Congenital Heart Diseases: A Systematic Review.Curr Pediatr Rev. 2024;21(1):56-66. doi: 10.2174/0115733963263592231127042702. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2024. PMID: 38251699
Cited by
-
Reduced peripheral and respiratory muscle strength in pediatric patients after kidney transplantation.J Bras Nefrol. 2023 Jul-Sep;45(3):318-325. doi: 10.1590/2175-8239-JBN-2022-0096en. J Bras Nefrol. 2023. PMID: 37058682 Free PMC article.
-
REPRODUCIBILITY OF PHYSIOLOGICAL VARIABLES OF THE SIX-MINUTE WALK TEST IN HEALTHY STUDENTS.Rev Paul Pediatr. 2021;39:e2019326. doi: 10.1590/1984-0462/2021/39/2019326. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Rev Paul Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 32876306 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiopulmonary fitness in children/adolescents with chronic kidney disease and the impact of exercise training: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational study and randomized controlled trials.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2458197. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2458197. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 39908064 Free PMC article.
-
Physical performance capacity after pediatric kidney transplant and clinical parameters associated with physical performance capacity.Pediatr Nephrol. 2023 May;38(5):1633-1642. doi: 10.1007/s00467-022-05758-0. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Pediatr Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36315277 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of progressive resistance exercises on quality of life and functional capacity in pediatric patients with chronic kidney disease: a randomized trail.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2019 Jun 1;19(2):187-195. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2019. PMID: 31186389 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Solway S, Brooks D, Lacasse Y, Thomas S. A qualitative systematic overview of the measurement properties of functional walk tests used in the cardiorespiratory domain. Chest. 2001;119((1)):256–70. 10.1378/chest.119.1.256 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Enright PL. The six-minute walk test. Respir Care. 2003;48((8)):783–5. - PubMed
-
- Lammers AE, Hislop AA, Flynn Y, Haworth SG. The 6-minute walk test: normal values for children of 4-11 years of age. Arch Dis Child. 2008;93((6)):464–8. 10.1136/adc.2007.123653 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Guillén MAJ, Posadas AS, Asensi JRV, Moreno RMG, Rodríguez MAN, González AS. Reproductibilidad del test de la marcha (walking test) en pacientes afectos de fibrosis quística. An Esp Pediatr. 1999;51((5)):475–8. - PubMed
-
- Cunha MT, Rozov T, de Oliveira RC, Jardim JR. Six-minute walk test in children and adolescents with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2006;41((7)):618–22. 10.1002/ppul.20308 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical