Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF21) Protects against High Fat Diet Induced Inflammation and Islet Hyperplasia in Pancreas
- PMID: 26872145
- PMCID: PMC4752212
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148252
Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF21) Protects against High Fat Diet Induced Inflammation and Islet Hyperplasia in Pancreas
Abstract
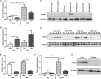
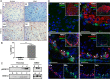
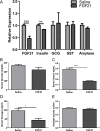
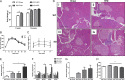
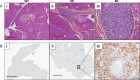
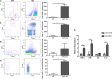
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is an important endocrine metabolic regulator expressed in multiple tissues including liver and adipose tissue. Although highest levels of expression are in pancreas, little is known about the function of FGF21 in this tissue. In order to understand the physiology of FGF21 in the pancreas, we analyzed its expression and regulation in both acinar and islet tissues. We found that acinar tissue express 20-fold higher levels than that observed in islets. We also observed that pancreatic FGF21 is nutritionally regulated; a marked reduction in FGF21 expression was noted with fasting while obesity is associated with 3-4 fold higher expression. Acinar and islet cells are targets of FGF21, which when systemically administered, leads to phosphorylation of the downstream target ERK 1/2 in about half of acinar cells and a small subset of islet cells. Chronic, systemic FGF21 infusion down-regulates its own expression in the pancreas. Mice lacking FGF21 develop significant islet hyperplasia and periductal lymphocytic inflammation when fed with a high fat obesogenic diet. Inflammatory infiltrates consist of TCRb+ Thy1+ T lymphocytes with increased levels of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Increased levels of inflammatory cells were coupled with elevated expression of cytokines such as TNFα, IFNγ and IL1β. We conclude that FGF21 acts to limit islet hyperplasia and may also prevent pancreatic inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oncogenic KRAS Reduces Expression of FGF21 in Acinar Cells to Promote Pancreatic Tumorigenesis in Mice on a High-Fat Diet.Gastroenterology. 2019 Nov;157(5):1413-1428.e11. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.030. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 31352001 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of the Fibroblast growth factor 21 gene is an underlying cause of acinar cell injury in mice lacking MIST1.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Apr 15;306(8):E916-28. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00559.2013. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24549397
-
Loss of fibroblast growth factor 21 action induces insulin resistance, pancreatic islet hyperplasia and dysfunction in mice.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Mar 26;6(3):e1707. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.80. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 25811804 Free PMC article.
-
FGF21 in obesity and cancer: New insights.Cancer Lett. 2021 Feb 28;499:5-13. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.11.026. Epub 2020 Nov 29. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 33264641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional regulation of fibroblast growth factor 21: from macronutrients to bioactive dietary compounds.Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2016 Sep 1;30(1):/j/hmbci.2017.30.issue-1/hmbci-2016-0034/hmbci-2016-0034.xml. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2016-0034. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2016. PMID: 27583468 Review.
Cited by
-
FGF21 Is an Exocrine Pancreas Secretagogue.Cell Metab. 2017 Feb 7;25(2):472-480. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.12.004. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Cell Metab. 2017. PMID: 28089565 Free PMC article.
-
FGF21 Mediates the Thermogenic and Insulin-Sensitizing Effects of Dietary Methionine Restriction but Not Its Effects on Hepatic Lipid Metabolism.Diabetes. 2017 Apr;66(4):858-867. doi: 10.2337/db16-1212. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 28096260 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring endocrine FGFs - structures, functions and biomedical applications.Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2024 Aug 25;15(4):68-99. doi: 10.62347/PALK2137. eCollection 2024. Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39309613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between Circulating Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and Aggressiveness in Thyroid Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 12;11(8):1154. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081154. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31408968 Free PMC article.
-
Adipokines, Hepatokines and Myokines: Focus on Their Role and Molecular Mechanisms in Adipose Tissue Inflammation.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 14;13:873699. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.873699. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35909571 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Badman MK, Pissios P, Kennedy AR, Koukos G, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E. Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARalpha and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell Metab. 2007;5: 426–437. - PubMed
-
- Inagaki T, Dutchak P, Zhao G, Ding X, Gautron L, Parameswara V, et al. Endocrine regulation of the fasting response by PPARalpha-mediated induction of fibroblast growth factor 21. Cell Metab. 2007;5: 415–425. - PubMed
-
- Fisher FM, Chui PC, Nasser IA, Popov Y, Cunniff JC, Lundasen T, et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Limits Lipotoxicity by Promoting Hepatic Fatty Acid Activation in Mice on Methionine and Choline-Deficient Diets. Gastroenterology. 2014;147: 1073–1083. 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.07.044 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

