The Wnt Antagonist Dickkopf-1 Promotes Pathological Type 2 Cell-Mediated Inflammation
- PMID: 26872695
- PMCID: PMC4758884
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.01.008
The Wnt Antagonist Dickkopf-1 Promotes Pathological Type 2 Cell-Mediated Inflammation
Abstract
Exposure to a plethora of environmental challenges commonly triggers pathological type 2 cell-mediated inflammation. Here we report the pathological role of the Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1 (Dkk-1) upon allergen challenge or non-healing parasitic infection. The increased circulating amounts of Dkk-1 polarized T cells to T helper 2 (Th2) cells, stimulating a marked simultaneous induction of the transcription factors c-Maf and Gata-3, mediated by the kinases p38 MAPK and SGK-1, resulting in Th2 cell cytokine production. Circulating Dkk-1 was primarily from platelets, and the increase of Dkk-1 resulted in formation of leukocyte-platelet aggregates (LPA) that facilitated leukocyte infiltration to the affected tissue. Functional inhibition of Dkk-1 impaired Th2 cell cytokine production and leukocyte infiltration, protecting mice from house dust mite (HDM)-induced asthma or Leishmania major infection. These results highlight that Dkk-1 from thrombocytes is an important regulator of leukocyte infiltration and polarization of immune responses in pathological type 2 cell-mediated inflammation.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
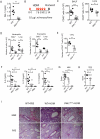

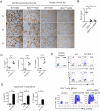
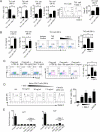

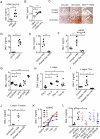
References
-
- Abbas AK, Janeway CA., Jr. Immunology: improving on nature in the twenty-first century. Cell. 2000;100:129–138. - PubMed
-
- Belkaid Y, Hoffmann KF, Mendez S, Kamhawi S, Udey MC, Wynn TA, Sacks DL. The role of interleukin (IL)-10 in the persistence of Leishmania major in the skin after healing and the therapeutic potential of anti-IL-10 receptor antibody for sterile cure. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2001;194:1497–1506. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Butler J. Shear stress platelet activation. Lancet. 1995;346:841. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL115247/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007019/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI107957/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1R21AI107957-01/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA168670/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01CA168670-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR053495/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR026526/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122815/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1S10-RR-026526-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI089824/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016359/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI093775/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI093775/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

