Endovascular repair or open repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: a Cochrane systematic review
- PMID: 26873043
- PMCID: PMC4762122
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008391
Endovascular repair or open repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: a Cochrane systematic review
Abstract
Objectives: Emergency endovascular aneurysm repair (eEVAR) may improve outcomes for patients with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm (RAAA). The study aim was to compare the outcomes for eEVAR with conventional open surgical repair for the treatment of RAAA.
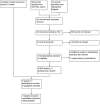
Setting: A systematic review of relevant publications was performed. Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing eEVAR with open surgical repair for RAAA were included.
Participants: 3 RCTs were included, with a total of 761 patients with RAAA.
Interventions: Meta-analysis was performed with fixed-effects models with ORs and 95% CIs for dichotomous data and mean differences with 95% CIs for continuous data.
Primary and secondary outcome measures: Primary outcome was short-term mortality. Secondary outcome measures included aneurysm-specific and general complication rates, quality of life and economic analysis.
Results: Overall risk of bias was low. There was no difference between the 2 interventions on 30-day (or in-hospital) mortality, OR 0.91 (95% CI 0.67 to 1.22; p=0.52). 30-day complications included myocardial infarction, stroke, composite cardiac complications, renal complications, severe bowel ischaemia, spinal cord ischaemia, reoperation, amputation and respiratory failure. Reporting was incomplete, and no robust conclusion was drawn. For complication outcomes that did include at least 2 studies in the meta-analysis, there was no clear evidence to support a difference between eEVAR and open repair. Longer term outcomes and cost per patient were evaluated in only a single study, thus precluding definite conclusions.
Conclusions: Outcomes between eEVAR and open repair, specifically 30-day mortality, are similar. However, further high-quality trials are required, as the paucity of data currently limits the conclusions.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures
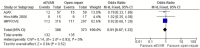
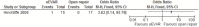

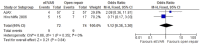
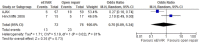


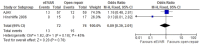
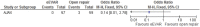
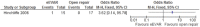
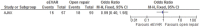

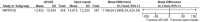
Similar articles
-
Endovascular treatment for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 26;5(5):CD005261. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005261.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28548204 Free PMC article.
-
Endovascular treatment for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jul 21;(7):CD005261. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005261.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 26;5:CD005261. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005261.pub4. PMID: 25042123 Updated.
-
Endovascular treatment for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD005261. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005261.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jul 21;(7):CD005261. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005261.pub3. PMID: 17253551 Updated.
-
Totally percutaneous versus surgical cut-down femoral artery access for elective bifurcated abdominal endovascular aneurysm repair.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 21;2(2):CD010185. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010185.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 11;1:CD010185. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010185.pub4. PMID: 28221665 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Totally percutaneous versus surgical cut-down femoral artery access for elective bifurcated abdominal endovascular aneurysm repair.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 11;1(1):CD010185. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010185.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36629152 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Aortic Neck IFU Violations During EVAR for Ruptured Infrarenal Aortic Aneurysms are Associated with Increased In-Hospital Mortality.Ann Vasc Surg. 2021 Aug;75:12-21. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2021.04.019. Epub 2021 May 2. Ann Vasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 33951521 Free PMC article.
-
Activated clotting time-guided heparinization during open AAA surgery: a pilot study.Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2024 May 8;10(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s40814-024-01500-9. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2024. PMID: 38720378 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the use of resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta in the management of major exsanguination.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2018 Aug;44(4):535-550. doi: 10.1007/s00068-018-0959-y. Epub 2018 May 21. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2018. PMID: 29785654 Free PMC article.
-
Immediate outcome of endovascular treatment of ruptured juxtarenal aneurysm with parallel stents.J Vasc Bras. 2021 Mar 15;20:e20200120. doi: 10.1590/1677-5449.200120. J Vasc Bras. 2021. PMID: 34093683 Free PMC article.
-
Early experiences of endovascular aneurysm repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms.Ann Surg Treat Res. 2019 Mar;96(3):138-145. doi: 10.4174/astr.2019.96.3.138. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2019. PMID: 30838186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anon. NHS Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Screening Programme 2013. http://aaa.screening.nhs.uk
-
- Alsac JM, Kobeiter H, Becquemin JP et al. . Endovascular repair for ruptured AAA: a literature review. Acta Chir Belg 2005;105:134–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
