Efficacy and Toxicity of Mammalian Target Rapamycin Inhibitors in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma with Renal Insufficiency: The Korean Cancer Study Group GU 14-08
- PMID: 26875195
- PMCID: PMC5080820
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2016.018
Efficacy and Toxicity of Mammalian Target Rapamycin Inhibitors in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma with Renal Insufficiency: The Korean Cancer Study Group GU 14-08
Abstract
Purpose: We evaluated the efficacy and toxicity of mammalian target rapamycin inhibitors in Korean patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) with chronic renal insufficiency not requiring dialysis.
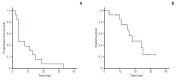
Materials and methods: Korean patients with mRCC and chronic renal insufficiency not requiring dialysis treated with everolimus or temsirolimus between January 2008 and December 2014 were included. Patient characteristics, clinical outcomes, and toxicities were evaluated. Overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) durations were evaluated according to the degree of renal impairment.
Results: Eighteen patients were considered eligible for the study (median age, 59 years). The median glomerular filtration rate was 51.5 mL/min/1.73 m2. The best response was partial response in six patients and stable disease in 11 patients. The median PFS and OS durations were 8 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 0 to 20.4) and 32 months (95% CI, 27.5 to 36.5), respectively. The most common non-hematologic and grade 3/4 adverse events included stomatitis, fatigue, flu-like symptoms, and anorexia as well as elevated creatinine level.
Conclusion: Mammalian target rapamycin inhibitors were efficacious and did not increase toxicity in Korean patients with mRCC and chronic renal insufficiency not requiring dialysis.
Keywords: Renal cell carcinoma; Renal insufficiency; TOR serine-threonine kinases.
Conflict of interest statement
relevant to this article was not reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and toxicity of sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma with renal insufficiency.Eur J Cancer. 2014 Mar;50(4):746-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.11.029. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Eur J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24332573
-
Biological toxicities as surrogate markers of efficacy in patients treated with mTOR inhibitors for metastatic renal cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2017 Jan 6;17(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2993-7. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28061764 Free PMC article.
-
First-Line and Sequential Use of Pazopanib Followed by Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Inhibitor Therapy Among Patients With Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma in a US Community Oncology Setting.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2015 Jun;13(3):210-7. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2014.11.001. Epub 2014 Nov 15. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25498215
-
Oral and intravenously administered mTOR inhibitors for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: pharmacokinetic considerations and clinical implications.Cancer Treat Rev. 2013 Nov;39(7):784-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2012.12.012. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Cancer Treat Rev. 2013. PMID: 23375248 Review.
-
Everolimus in renal cell carcinoma.Drugs Today (Barc). 2010 Aug;46(8):557-66. doi: 10.1358/dot.2010.46.8.1516824. Drugs Today (Barc). 2010. PMID: 20830316 Review.
Cited by
-
Renal toxicity with mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Oncol Rev. 2019 Nov 25;13(2):455. doi: 10.4081/oncol.2019.455. eCollection 2019 Jul 22. Oncol Rev. 2019. PMID: 31857859 Free PMC article.
-
Renal toxicity of targeted therapies for renal cell carcinoma in patients with normal and impaired kidney function.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2021 Jun;87(6):723-742. doi: 10.1007/s00280-021-04260-y. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33768301 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, et al. Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet. 2008;372:449–56. - PubMed
-
- Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P, Dutcher J, Figlin R, Kapoor A, et al. Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2271–81. - PubMed
-
- Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J, Szczylik C, Lee E, Wagstaff J, et al. Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1061–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

