Skeletal manifestations of Marfan syndrome associated to heterozygous R2726W FBN1 variant: sibling case report and literature review
- PMID: 26875674
- PMCID: PMC4753669
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-016-0935-9
Skeletal manifestations of Marfan syndrome associated to heterozygous R2726W FBN1 variant: sibling case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: FBN1 (15q21.1) encodes fibrillin-1, a large glycoprotein which is a major component of microfibrils that are widely distributed in structural elements of elastic and non-elastic tissues. FBN1 variants are responsible for the related connective tissue disorders, grouped under the generic term of type-1 fibrillinopathies, which include Marfan syndrome (MFS), MASS syndrome (Mitral valve prolapse, Aortic enlargement, Skin and Skeletal findings, Acromicric dysplasia, Familial ectopia lentis, Geleophysic dysplasia 2, Stiff skin syndrome, and dominant Weill-Marchesani syndrome.
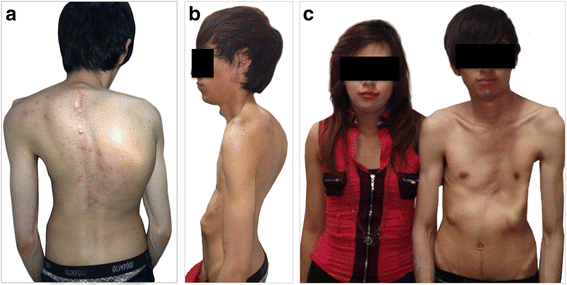
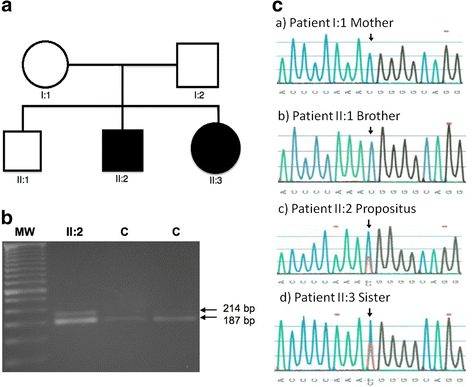
Case presentation: Two siblings presented with isolated skeletal manifestations of MFS, including severe pectus excavatum, elongated face, scoliosis in one case, and absence of other clinical features according to Ghent criteria diagnosis, were screened for detection of variants in whole FBN1 gene (65 exons). Both individuals were heterozygous for the R2726W variant. This variant has been previously reported in association with some skeletal features of Marfan syndrome in the absence of both tall stature and non-skeletal features. These features are consistent with the presentation of the siblings reported here.
Conclusion: The presented cases confirm that the R2726W FBN1 variant is associated with skeletal features of MFS in the absence of cardiac or ocular findings. These findings confirm that FBN1 variants are associated with a broad phenotypic spectrum and the value of sequencing in atypical cases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Missense mutations in FBN1 exons 41 and 42 cause Weill-Marchesani syndrome with thoracic aortic disease and Marfan syndrome.Am J Med Genet A. 2013 Sep;161A(9):2305-10. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36044. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Am J Med Genet A. 2013. PMID: 23897642 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype and phenotype analysis of 171 patients referred for molecular study of the fibrillin-1 gene FBN1 because of suspected Marfan syndrome.Arch Intern Med. 2001 Nov 12;161(20):2447-54. doi: 10.1001/archinte.161.20.2447. Arch Intern Med. 2001. PMID: 11700157
-
Fibrillin-1 mutations in Marfan syndrome and other type-1 fibrillinopathies.Hum Mutat. 1997;10(6):415-23. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1997)10:6<415::AID-HUMU1>3.0.CO;2-C. Hum Mutat. 1997. PMID: 9401003 Review.
-
A mutation in FBN1 disrupts profibrillin processing and results in isolated skeletal features of the Marfan syndrome.J Clin Invest. 1995 May;95(5):2373-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI117930. J Clin Invest. 1995. PMID: 7738200 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular characteristics in Marfan syndrome and their relation to the genotype.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2009;71(6):335-71. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2009. PMID: 20232788 Review.
Cited by
-
Case report: Biochemical and clinical phenotypes caused by cysteine substitutions in the epidermal growth factor-like domains of fibrillin-1.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 11;13:928683. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.928683. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36035136 Free PMC article.
-
An enormous Italian pedigree of Marfan syndrome with a novel mutation in the FBN1 gene.Clin Case Rep. 2020 Jun 2;8(8):1445-1451. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.2881. eCollection 2020 Aug. Clin Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32884772 Free PMC article.
-
Association of FBN1 polymorphism with susceptibility of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a case-control study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 May 7;23(1):430. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05370-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022. PMID: 35526034 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Exome Sequencing Identifies Three Candidate Homozygous Variants in a Consanguineous Iranian Family with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Skeletal Problems.Mol Syndromol. 2020 Jun;11(2):62-72. doi: 10.1159/000506530. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Mol Syndromol. 2020. PMID: 32655337 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly assay identifies a critical region of human fibrillin-1 required for 10-12 nm diameter microfibril biogenesis.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 18;16(3):e0248532. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248532. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33735269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gao LG, Yao XP, Zhang L, Hui RT, Zhou XL. Molecular analysis for diagnosis of Marfan syndrome and Marfan-associated disorders. Chin Med J (Engl) 2011;124:930–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

