The C. elegans CCAAT-Enhancer-Binding Protein Gamma Is Required for Surveillance Immunity
- PMID: 26876169
- PMCID: PMC4767654
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.01.055
The C. elegans CCAAT-Enhancer-Binding Protein Gamma Is Required for Surveillance Immunity
Abstract
Pathogens attack host cells by deploying toxins that perturb core host processes. Recent findings from the nematode C. elegans and other metazoans indicate that surveillance or "effector-triggered" pathways monitor functioning of these core processes and mount protective responses when they are perturbed. Despite a growing number of examples of surveillance immunity, the signaling components remain poorly defined. Here, we show that CEBP-2, the C. elegans ortholog of mammalian CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein gamma, is a key player in surveillance immunity. We show that CEBP-2 acts together with the bZIP transcription factor ZIP-2 in the protective response to translational block by P. aeruginosa Exotoxin A as well as perturbations of other processes. CEBP-2 serves to limit pathogen burden, promote survival upon P. aeruginosa infection, and also promote survival upon Exotoxin A exposure. These findings may have broad implications for the mechanisms by which animals sense pathogenic attack and mount protective responses.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
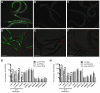
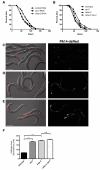
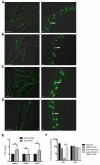
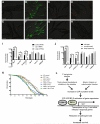
References
-
- Ausubel FM. Are innate immune signaling pathways in plants and animals conserved? Nature immunology. 2005;6:973–979. - PubMed
-
- Casas V, Miyake J, Balsley H, Roark J, Telles S, Leeds S, Zurita I, Breitbart M, Bartlett D, Azam F, et al. Widespread occurrence of phage-encoded exotoxin genes in terrestrial and aquatic environments in Southern California. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006;261:141–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

