Efficacy of covered and bare stent in TIPS for cirrhotic portal hypertension: A single-center randomized trial
- PMID: 26876503
- PMCID: PMC4753460
- DOI: 10.1038/srep21011
Efficacy of covered and bare stent in TIPS for cirrhotic portal hypertension: A single-center randomized trial
Abstract
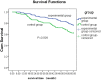
We conducted a single-center randomized trial to compare the efficacy of 8 mm Fluency covered stent and bare stent in transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) for cirrhotic portal hypertension. From January 2006 to December 2010, the covered (experimental group) or bare stent (control group) was used in 131 and 127 patients, respectively. The recurrence rates of gastrointestinal bleeding (18.3% vs. 33.9%, P = 0.004) and refractory hydrothorax/ascites (6.9% vs. 16.5%, P = 0.019) in the experimental group were significantly lower than those in the control group. The cumulative restenosis rates in 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5-years in the experimental group (6.9%, 11.5%, 19.1%, 26.0%, and 35.9%, respectively) were significantly lower (P < 0.001) than those in the control group (27.6%, 37.0%, 49.6%, 59.8%, 74.8%, respectively). Importantly, the 4 and 5-year survival rates in the experimental group (83.2% and 76.3%, respectively) were significantly higher (P = 0.001 and 0.02) than those in the control group (71.7% and 62.2%, respectively). The rate of secondary interventional therapy in the experimental group was significantly lower than that in the control group (20.6% vs. 49.6%; P < 0.001). Therefore, Fluency covered stent has advantages over the bare stent in terms of reducing the restenosis, recurrence, and secondary interventional therapy, whereas improving the long-term survival for post-TIPS patients.
Figures
References
-
- Rosch J., Hanafee W. N. & Snow H. Transjugular portal venography and radiologic portacaval shunt: an experimental study. Radiology 92, 1112–1124 (1969). - PubMed
-
- Colapinto R. F. et al. Formation of intrahepatic portosystemic shunts using a balloon dilatation catheter: preliminary clinical experience. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 140, 709–714 (1983). - PubMed
-
- Trover P. C. Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Stent Shunt: nonsurgical therapy for portal hypertension. J Ky Med Assoc 93, 95–100 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Dhanasekaran R. et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for symptomatic refractory hepatic hydrothorax in patients with cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 105, 635–641 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Darwish Murad S. et al. Etiology, management, and outcome of the Budd-Chiari syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 151, 167–175 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

