A Single CRISPR-Cas9 Deletion Strategy that Targets the Majority of DMD Patients Restores Dystrophin Function in hiPSC-Derived Muscle Cells
- PMID: 26877224
- PMCID: PMC4826286
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.01.021
A Single CRISPR-Cas9 Deletion Strategy that Targets the Majority of DMD Patients Restores Dystrophin Function in hiPSC-Derived Muscle Cells
Abstract
Mutations in DMD disrupt the reading frame, prevent dystrophin translation, and cause Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). Here we describe a CRISPR/Cas9 platform applicable to 60% of DMD patient mutations. We applied the platform to DMD-derived hiPSCs where successful deletion and non-homologous end joining of up to 725 kb reframed the DMD gene. This is the largest CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletion shown to date in DMD. Use of hiPSCs allowed evaluation of dystrophin in disease-relevant cell types. Cardiomyocytes and skeletal muscle myotubes derived from reframed hiPSC clonal lines had restored dystrophin protein. The internally deleted dystrophin was functional as demonstrated by improved membrane integrity and restoration of the dystrophin glycoprotein complex in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, miR31 was reduced upon reframing, similar to observations in Becker muscular dystrophy. This work demonstrates the feasibility of using a single CRISPR pair to correct the reading frame for the majority of DMD patients.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
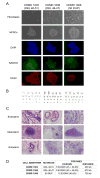
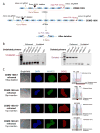
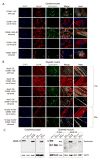
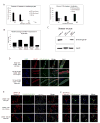
Comment in
-
Imprecision Medicine: A One-Size-Fits-Many Approach for Muscle Dystrophy.Cell Stem Cell. 2016 Apr 7;18(4):423-4. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.03.004. Cell Stem Cell. 2016. PMID: 27058929
References
-
- Arechavala-Gomeza V, Anthony K, Morgan J, Muntoni F. Antisense Oligonucleotide-Mediated Exon Skipping for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Progress and Challenges. Curr Gene Ther. 2012;12:152–160. - PubMed
-
- Beroud C, Tuffery-Giraud S, Matsuo M, Hamroun D, Calemard LM, Boisseau P, Blayau M, Philippe C, Cosse M, Page M, et al. Multiexon skipping leading to an artificial DMD protein lacking amino acids from exons 45 through 55 could rescue up to 63% of patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Hum Mutat. 2007;28:196–202. - PubMed
-
- Carsana A, Frisso G, Tremolaterra M, Lanzillo R, Vitale D, Santoro L, Salvatore F. Analysis of dystrophin gene deletions indicates that the hinge III region of the protein correlates with disease severity. Ann Hum Genet. 2005;69:253–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

