Strategies to target long-lived plasma cells for treating hemophilia A inhibitors
- PMID: 26877251
- PMCID: PMC4844017
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2016.01.005
Strategies to target long-lived plasma cells for treating hemophilia A inhibitors
Abstract
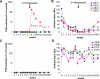
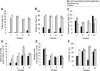
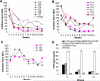
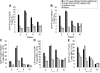
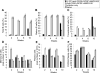
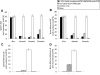
Long-lived plasma cells (LLPCs) can persistently produce anti-factor VIII (FVIII) antibodies which disrupt therapeutic effect of FVIII in hemophilia A patients with inhibitors. The migration of plasma cells to BM where they become LLPCs is largely controlled by an interaction between the chemokine ligand CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4. AMD3100 combined with G-CSF inhibit their interactions, thus facilitating the mobilization of CD34(+) cells and blocking the homing of LLPCs. These reagents were combined with anti-CD20 to reduce B-cells and the specific IL-2/IL-2mAb (JES6-1) complexes to induce Treg expansion for targeting anti-FVIII immune responses. Groups of mice primed with FVIII plasmid and protein respectively were treated with the combined regimen for six weeks, and a significant reduction of anti-FVIII inhibitor titers was observed, associated with the dramatic decrease of circulating and bone marrow CXCR4(+) plasma cells. The combination regimens are highly promising in modulating pre-existing anti-FVIII antibodies in FVIII primed subjects.
Keywords: AMD3100; Factor VIII; G-CSF; Hemophilia A; Immune tolerance; Immunomodulation; Inhibitors; Plasma cells.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
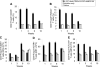
Similar articles
-
Long-term tolerance to factor VIII is achieved by administration of interleukin-2/interleukin-2 monoclonal antibody complexes and low dosages of factor VIII.J Thromb Haemost. 2014 Jun;12(6):921-31. doi: 10.1111/jth.12576. J Thromb Haemost. 2014. PMID: 24684505 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-CD20 as the B-Cell Targeting Agent in a Combined Therapy to Modulate Anti-Factor VIII Immune Responses in Hemophilia a Inhibitor Mice.Front Immunol. 2014 Jan 6;4:502. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00502. eCollection 2014 Jan 6. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24432019 Free PMC article.
-
The dataset from administration of single or combined immunomodulation agents to modulate anti-FVIII antibody responses in FVIII plasmid or protein primed hemophilia A mice.Data Brief. 2016 Mar 17;7:973-80. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2016.03.019. eCollection 2016 Jun. Data Brief. 2016. PMID: 27081675 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulation for inhibitors in hemophilia A: the important role of Treg cells.Expert Rev Hematol. 2010 Aug;3(4):469-83. doi: 10.1586/ehm.10.33. Expert Rev Hematol. 2010. PMID: 20976115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tolerating Factor VIII: Recent Progress.Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 10;10:2991. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02991. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31998296 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
B Cell Depletion Eliminates FVIII Memory B Cells and Enhances AAV8-coF8 Immune Tolerance Induction When Combined With Rapamycin.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 24;11:1293. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01293. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32670285 Free PMC article.
-
Hemophilia a patients with inhibitors: Mechanistic insights and novel therapeutic implications.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 8;13:1019275. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1019275. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36569839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevention of the anti-factor VIII memory B-cell response by inhibition of Bruton tyrosine kinase in experimental hemophilia A.Haematologica. 2019 May;104(5):1046-1054. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.200279. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Haematologica. 2019. PMID: 30545924 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma cells as an innovative target in autoimmune disease with renal manifestations.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016 Apr;12(4):232-40. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2016.20. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26923204 Review.
-
The regulatory functions of G protein-coupled receptors signaling pathways in B cell differentiation and development contributing to autoimmune diseases.Cell Biosci. 2025 Apr 30;15(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13578-025-01398-7. Cell Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40307944 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antonarakis SE, Youssoufian H, Kazazian HH., Jr. Molecular genetics of hemophilia A in man (factor VIII deficiency). Mol Biol Med. 1987;4:81–94. - PubMed
-
- Darby SC, Keeling DM, Spooner RJ, Wan Kan S, Giangrande PL, Collins PW, Hill FG, Hay CR, Organisation UKHCD The incidence of factor VIII and factor IX inhibitors in the hemophilia population of the UK and their effect on subsequent mortality, 1977-99. J Thromb Haemost. 2004;2:1047–54. - PubMed
-
- Lacroix-Desmazes S, Navarrete AM, Andre S, Bayry J, Kaveri SV, Dasgupta S. Dynamics of factor VIII interactions determine its immunologic fate in hemophilia A. Blood. 2008;112:240–9. - PubMed
-
- Ehrenforth S, Kreuz W, Scharrer I, Linde R, Funk M, Gungor T, Krackhardt B, Kornhuber B. Incidence of development of factor VIII and factor IX inhibitors in haemophiliacs. Lancet. 1992;339:594–8. - PubMed
-
- Lusher JM, Arkin S, Abildgaard CF, Schwartz RS. Recombinant factor VIII for the treatment of previously untreated patients with hemophilia A. Safety, efficacy, and development of inhibitors. Kogenate Previously Untreated Patient Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:453–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

