Hepatitis C virus relies on lipoproteins for its life cycle
- PMID: 26877603
- PMCID: PMC4726671
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.1953
Hepatitis C virus relies on lipoproteins for its life cycle
Abstract
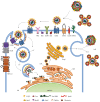
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infects over 150 million people worldwide. In most cases, HCV infection becomes chronic causing liver disease ranging from fibrosis to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Viral persistence and pathogenesis are due to the ability of HCV to deregulate specific host processes, mainly lipid metabolism and innate immunity. In particular, HCV exploits the lipoprotein machineries for almost all steps of its life cycle. The aim of this review is to summarize current knowledge concerning the interplay between HCV and lipoprotein metabolism. We discuss the role played by members of lipoproteins in HCV entry, replication and virion production.
Keywords: Apolipoproteins; Hepatitis C virus; Lipid metabolism; Lipoproteins; Review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic hepatitis C virus infection and lipoprotein metabolism.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Sep 28;21(36):10299-313. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i36.10299. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26420957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipids: a key for hepatitis C virus entry and a potential target for antiviral strategies.Biochimie. 2013 Jan;95(1):96-102. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2012.07.016. Epub 2012 Aug 1. Biochimie. 2013. PMID: 22884392 Review.
-
HCV Interplay with Lipoproteins: Inside or Outside the Cells?Viruses. 2020 Apr 12;12(4):434. doi: 10.3390/v12040434. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32290553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Lipoproteins and Apolipoproteins in Particle Formation of Hepatitis C Virus.Trends Microbiol. 2015 Oct;23(10):618-629. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2015.07.007. Trends Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26433694 Review.
-
Hepatitis C virus-apolipoprotein interactions: molecular mechanisms and clinical impact.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2017 Jul;14(7):593-606. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2017.1344102. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28625086 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vectorial Release of Human RNA Viruses from Epithelial Cells.Viruses. 2022 Jan 25;14(2):231. doi: 10.3390/v14020231. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Mevastatin on HCV Replication and Autophagy of Non-Transformed HCV Replicon Hepatocytes Is Influenced by the Extracellular Lipid Uptake.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jun 26;10:718. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00718. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31316383 Free PMC article.
-
Cure or curd: Modification of lipid profiles and cardio-cerebrovascular events after hepatitis C virus eradication.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020 Nov;36(11):920-928. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12275. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32643842 Free PMC article.
-
HCV Assembly and Egress via Modifications in Host Lipid Metabolic Systems.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021 Jan 4;11(1):a036814. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a036814. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021. PMID: 32122916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular pathways in viral hepatitis-associated liver carcinogenesis: An update.World J Clin Cases. 2021 Jul 6;9(19):4890-4917. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.4890. World J Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 34307543 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hajarizadeh B, Grebely J, Dore GJ. Epidemiology and natural history of HCV infection. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:553–562. - PubMed
-
- Mohd Hanafiah K, Groeger J, Flaxman AD, Wiersma ST. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection: new estimates of age-specific antibody to HCV seroprevalence. Hepatology. 2013;57:1333–1342. - PubMed
-
- Bruggmann P, Berg T, Øvrehus AL, Moreno C, Brandão Mello CE, Roudot-Thoraval F, Marinho RT, Sherman M, Ryder SD, Sperl J, et al. Historical epidemiology of hepatitis C virus (HCV) in selected countries. J Viral Hepat. 2014;21 Suppl 1:5–33. - PubMed
-
- European Association for Study of Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: management of hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol. 2014;60:392–420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

