In vivo MR and Fluorescence Dual-modality Imaging of Atherosclerosis Characteristics in Mice Using Profilin-1 Targeted Magnetic Nanoparticles
- PMID: 26877785
- PMCID: PMC4729775
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.13350
In vivo MR and Fluorescence Dual-modality Imaging of Atherosclerosis Characteristics in Mice Using Profilin-1 Targeted Magnetic Nanoparticles
Abstract
Aims: This study aims to explore non-invasive imaging of atherosclerotic plaque through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF) by using profilin-1 targeted magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (PF1-Cy5.5-DMSA-Fe3O4-NPs, denoted as PC-NPs) as multimodality molecular imaging probe in murine model of atherosclerosis.
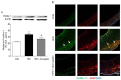
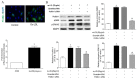
Methods and results: PC-NPs were constructed by conjugating polyclonal profilin-1 antibody and NHS-Cy5.5 fluorescent dye to the surface of DMSA-Fe3O4-nanoparticles via condensation reaction. Murine atherosclerosis model was induced in apoE(-/-) mice by high fat and cholesterol diet (HFD) for 16 weeks. The plaque areas in aortic artery were detected with Oil Red O staining. Immunofluorescent staining and Western blot analysis were applied respectively to investigate profilin-1 expression. CCK-8 assay and transwell migration experiment were performed to detect vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) proliferation. In vivo MRI and NIRF imaging of atherosclerotic plaque were carried out before and 36 h after intravenous injection of PC-NPs. Oil Red O staining showed that the plaque area was significantly increased in HFD group (p<0.05). Immunofluorescence staining revealed that profilin-1 protein was highly abundant within plaque in HFD group and co-localized with α-smooth muscle actin. Profilin-1 siRNA intervention could inhibit VSMCs proliferation and migration elicited by ox-LDL (p<0.05). In vivo MRI and NIRF imaging revealed that PC-NPs accumulated in atherosclerotic plaque of carotid artery. There was a good correlation between the signals of MRI and ex vivo fluorescence intensities of NIRF imaging in animals with PC-NPs injection.
Conclusion: PC-NPs is a promising dual modality imaging probe, which may improve molecular diagnosis of plaque characteristics and evaluation of pharmaceutical interventions for atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; DMSA-Fe3O4-nanoparticles; Molecular imaging; Profilin-1.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures









References
-
- Erbel R, Budoff M. Improvement of cardiovascular risk prediction using coronary imaging: subclinical atherosclerosis: the memory of lifetime risk factor exposure. European heart journal. 2012;33:1201–13. - PubMed
-
- Foin N, Evans P, Krams R. Atherosclerosis: cell biology and lipoproteins - new developments in imaging of inflammation of the vulnerable plaque. Current opinion in lipidology. 2008;19:98–100. - PubMed
-
- Chan JM, Monaco C, Wylezinska-Arridge M, Tremoleda JL, Gibbs RG. Imaging of the vulnerable carotid plaque: biological targeting of inflammation in atherosclerosis using iron oxide particles and MRI. European journal of vascular and endovascular surgery: the official journal of the European Society for Vascular Surgery. 2014;47:462–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

