Genomic sequencing of a dyslexia susceptibility haplotype encompassing ROBO1
- PMID: 26877820
- PMCID: PMC4751651
- DOI: 10.1186/s11689-016-9136-y
Genomic sequencing of a dyslexia susceptibility haplotype encompassing ROBO1
Abstract
Background: The DYX5 locus for developmental dyslexia was mapped to chromosome 3 by linkage study of a large Finnish family, and later, roundabout guidance receptor 1 (ROBO1) was implicated as a candidate gene at DYX5 with suppressed expression from the segregating rare haplotype. A functional magnetoencephalographic study of several family members revealed abnormal auditory processing of interaural interaction, supporting a defect in midline crossing of auditory pathways. In the current study, we have characterized genetic variation in the broad ROBO1 gene region in the DYX5-linked family, aiming to identify variants that would increase our understanding of the altered expression of ROBO1.
Methods: We have used a whole genome sequencing strategy on a pooled sample of 19 individuals in combination with two individually sequenced genomes. The discovered genetic variants were annotated and filtered. Subsequently, the most interesting variants were functionally tested using relevant methods, including electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA), luciferase assay, and gene knockdown by lentiviral small hairpin RNA (shRNA) in lymphoblasts.
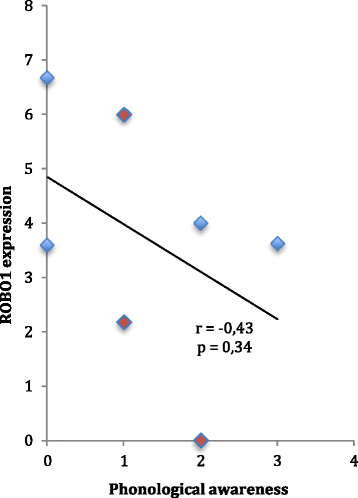
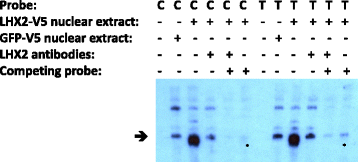
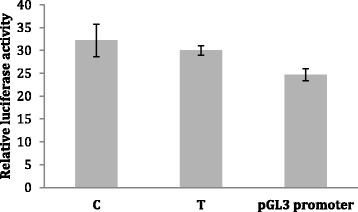
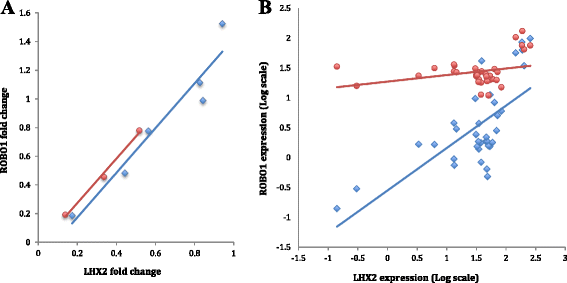
Results: We found one novel intronic single nucleotide variant (SNV) and three novel intergenic SNVs in the broad region of ROBO1 that were specific to the dyslexia susceptibility haplotype. Functional testing by EMSA did not support the binding of transcription factors to three of the SNVs, but one of the SNVs was bound by the LIM homeobox 2 (LHX2) protein, with increased binding affinity for the non-reference allele. Knockdown of LHX2 in lymphoblast cell lines extracted from subjects from the DYX5-linked family showed decreasing expression of ROBO1, supporting the idea that LHX2 regulates ROBO1 also in human.
Conclusions: The discovered variants may explain the segregation of dyslexia in this family, but the effect appears subtle in the experimental settings. Their impact on the developing human brain remains suggestive based on the association and subtle experimental support.
Keywords: Dyslexia; ROBO1; Whole genome sequencing.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The axon guidance receptor gene ROBO1 is a candidate gene for developmental dyslexia.PLoS Genet. 2005 Oct;1(4):e50. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0010050. Epub 2005 Oct 28. PLoS Genet. 2005. PMID: 16254601 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing identifies functional noncoding variation in SEMA3C that cosegregates with dyslexia in a multigenerational family.Hum Genet. 2021 Aug;140(8):1183-1200. doi: 10.1007/s00439-021-02289-w. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 34076780 Free PMC article.
-
Human ROBO1 regulates interaural interaction in auditory pathways.J Neurosci. 2012 Jan 18;32(3):966-71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4007-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22262894 Free PMC article.
-
The genetics of reading disability.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2009 Apr;11(2):149-55. doi: 10.1007/s11920-009-0023-z. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2009. PMID: 19302769 Review.
-
[Genetics of dyslexia].Z Kinder Jugendpsychiatr Psychother. 2006 Nov;34(6):435-44. doi: 10.1024/1422-4917.34.6.435. Z Kinder Jugendpsychiatr Psychother. 2006. PMID: 17094062 Review. German.
Cited by
-
The Mediation Role of Dynamic Multisensory Processing Using Molecular Genetic Data in Dyslexia.Brain Sci. 2020 Dec 16;10(12):993. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10120993. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 33339203 Free PMC article.
-
Dyslexia-Related Hearing Loss Occurs Mainly through the Abnormal Spontaneous Electrical Activity of Spiral Ganglion Neurons.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Jun;10(16):e2205754. doi: 10.1002/advs.202205754. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37068190 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Modifications of Developmental Dyslexia and Its Representation Using In Vivo, In Vitro Model.Glob Med Genet. 2024 Feb 27;11(1):76-85. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1781456. eCollection 2024 Jan. Glob Med Genet. 2024. PMID: 38414980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurogenetics of developmental dyslexia: from genes to behavior through brain neuroimaging and cognitive and sensorial mechanisms.Transl Psychiatry. 2017 Jan 3;7(1):e987. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.240. Transl Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28045463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroimaging genetics studies of specific reading disability and developmental language disorder: A review.Lang Linguist Compass. 2019 Sep;13(9):e12349. doi: 10.1111/lnc3.12349. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Lang Linguist Compass. 2019. PMID: 31844423 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

