Effects of cardiopulmonary bypass on lung nuclear factor-kappa B activity, cytokine release, and pulmonary function in dogs
- PMID: 26877854
- PMCID: PMC4744364
Effects of cardiopulmonary bypass on lung nuclear factor-kappa B activity, cytokine release, and pulmonary function in dogs
Abstract
Objectives: To study the effect of cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) on nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and cytokine expression and pulmonary function in dogs.
Materials and methods: Twelve male mongrel dogs were divided into a methylprednisolone group (group M) and a control group (group C). All animals underwent aortic and right atrial catheterization under general anesthesia. Changes in pulmonary function and hemodynamics were monitored and the injured site was histologically evaluated.
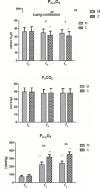
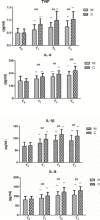
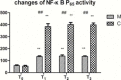
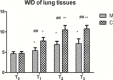
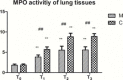
Results: The activity of NF-κB and myeloperoxidase (MPO), levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and IL-8, and the wet/dry (W/D) weight ratio were significantly higher after CPB than before CPB in both groups (P<0.01), with the lower values in group M than in group C, at different time points (P<0.01). Histological evaluation revealed neutrophilic infiltration and thickening of the alveolar interstitium in both groups; however, the degree of pathological changes was significantly lower in group M than in group C. The alveolar-arterial O2 tension difference (PA-aDO2) was significantly higher after CPB than before CBP (P<0.01), and lower in group M than in group C (P<0.01). The pulmonary compliance after removal of the aortic clamp obviously decreased in group C (P<0.05), with no significant change in group M.
Conclusion: CPB can significantly enhance the activation of NF-κB in lung tissues and increase the expression of inflammatory cytokines, thus inducing lung injury. Methylprednisolone can inhibit the NF-κB activation, thus inhibiting the release of cytokines and protecting the lung function.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Cardiopulmonary bypass Cytokines; Methyl-prednisolone; NF-κB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of aprotinin and steroids on generation of cytokines during coronary artery surgery.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2001 Oct;15(5):603-10. doi: 10.1053/jcan.2001.26539. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2001. PMID: 11688002 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of pulmonary artery perfusion with urinary trypsin inhibitor as a lung protective strategy under hypothermic low-flow cardiopulmonary bypass in an infant piglet model.Perfusion. 2014 Sep;29(5):434-42. doi: 10.1177/0267659113517286. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Perfusion. 2014. PMID: 24335190
-
[The impacts of regulating Toll-like receptor 2/nuclear factor-ΚB signal pathway on rats with ventilator-induced lung injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014 Dec;26(12):865-9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2014.12.004. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014. PMID: 25476077 Chinese.
-
[Inhibition of pulmonary nuclear factor -ΚB and tumor necrosis factor -α expression by diallyl sulfide in rats with paraquat poisoning].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015 Apr;27(4):274-9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2015.04.010. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015. PMID: 25891457 Chinese.
-
[SB203580 reduces proinflammatory cytokine production in rats after cardiopulmonary bypass].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2009 Nov;29(11):2168-70. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2009. PMID: 19923057 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Pulmonary Congestion Due to Right and Left Heart Output Mismatching: A Case Report and Literature Review.Front Physiol. 2021 Apr 13;12:665483. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.665483. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33927647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolated and Combined Valve Surgery in Elderly Patients: A Comparison of Mid-Term Results.Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017 Jun 20;23(3):123-127. doi: 10.5761/atcs.oa.16-00303. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017. PMID: 28302949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apostolakis E, Filos KS, Koletsis E, Dougenis D. Lung dysfunction following cardiopulmonary bypass. J Card Surg. 2010;25:47–55. - PubMed
-
- Onorati F, Rubino AS, Nucera S, Foti D, Sica V, Santini F, et al. Off-pump coronary artery bypass surgery versus standard linear or pulsatile cardiopulmonary bypass:endothelial activation and inflammatory response. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2010;37:897–904. - PubMed
-
- Ng CS, Hui CW, Wan S, Wan IY, Ho AM, Lau KM, et al. Lung ischaemia-reperfusion induced gene expression. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2010;37:1411–1420. - PubMed
-
- Larsen BM, Goonewardene LA, Joffe AR, Van Aerde JE, Field CJ, Olstad DL, et al. Pre-treatment with an intravenous lipid emulsion containing fish oil (eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acid) decreases inflammatory markers after open-heart surgery in infants:a randomized, controlled trial. Clin Nutr. 2012;31:322–329. - PubMed
-
- Pearl JM, Schwartz SM, Nelson DP, Wagner CJ, Lyons JM, Bauer SM, et al. Preoperative glucocorticoids decrease pulmonary hypertension in piglets after cardiopulmonary bypass and circulatory arrest. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004;77:994–1000. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
