Effects of Toll-like receptor antagonist 4,5-dihydro-3-phenyl-5-isoxasole acetic acid on the progression of kidney disease in mice on a high-fat diet
- PMID: 26877948
- PMCID: PMC4714156
- DOI: 10.1016/j.krcp.2013.11.002
Effects of Toll-like receptor antagonist 4,5-dihydro-3-phenyl-5-isoxasole acetic acid on the progression of kidney disease in mice on a high-fat diet
Abstract
Background: Obesity-related metabolic disorders are closely associated with inflammation induced by innate immunity. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play a pivotal role in the innate immune system by activating proinflammatory signaling pathways. GIT27 (4,5-dihydro-3-phenyl-5-isoxasole acetic acid) is an active immunomodulatory agent that primarily targets macrophages and inhibits secretion of tumor necrosis factor α [as well as interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-10, and interferon γ]. However, the effect of TLR antagonist on kidney diseases has rarely been reported. We investigated whether the TLR antagonist GIT27 has beneficial effects on the progression of kidney disease in obese mice on a high-fat diet (HFD).
Methods: Six-week-old male C57BL/6 mice were divided into three groups: mice fed with normal chow diet (N=4); mice fed with a HFD (60% of total calories from fat, 5.5% from soybean oil, and 54.5% from lard, N=4); and GIT27-treated mice fed with a HFD (N=7).
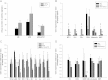
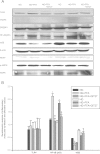
Results: Glucose intolerance, oxidative stress, and lipid abnormalities in HFD mice were improved by GIT27 treatment. In addition, GIT27 treatment decreased the urinary excretion of albumin and protein in obesity-related kidney disease, urinary oxidative stress markers, and inflammatory cytokine levels. This treatment inhibited the expression of proinflammatory cytokines in the kidneys and adipose tissue, and improved extracellular matrix expansion and tubulointerstitial fibrosis in obesity-related kidney disease.
Conclusion: TLR inhibition by administering GIT27 improved metabolic parameters. GIT27 ameliorates abnormalities of lipid metabolism and may have renoprotective effects on obesity-related kidney disease through its anti-inflammatory properties.
Keywords: Kidney disease; Metabolic syndrome; Obesity; Toll-like receptors.
Figures







References
-
- Cignarelli M., Lamacchia O. Obesity and kidney disease. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2007;17:757–762. - PubMed
-
- Kang Y.S., Cha J.J., Hyun Y.Y., Cha D.R., Novel C.–C. chemokine receptor 2 antagonists in metabolic disease: a review of recent developments. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2011;20:745–756. - PubMed
-
- Wickman C., Kramer H. Obesity and kidney disease: potential mechanisms. Semin Nephrol. 2013;33:14–22. - PubMed
-
- Amann K., Benz K. Structural renal changes in obesity and diabetes. Semin Nephrol. 2013;33:23–33. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

