Nephrotic syndrome complicated with portal, splenic, and superior mesenteric vein thrombosis
- PMID: 26877968
- PMCID: PMC4714169
- DOI: 10.1016/j.krcp.2014.07.001
Nephrotic syndrome complicated with portal, splenic, and superior mesenteric vein thrombosis
Abstract
Thromboembolism is a major complication of nephrotic syndrome. Renal vein thrombosis and deep vein thrombosis are relatively common, especially in membranous nephropathy. However, the incidence of portal vein and superior mesenteric vein (SMV) thrombosis in patients with nephrotic syndrome is very rare. To date, several cases of portal vein thrombosis treated by anticoagulation therapy, not by thrombolytic therapy, have been reported as a complication of nephrotic syndrome. Here, we report a case of portal, splenic, and SMV thrombosis in a patient with a relapsed steroid dependent minimal change disease who was treated successfully with anticoagulation and thrombolytic therapy using urokinase. Radiologic findings and his clinical conditions gradually improved. Six months later, a complete remission of the nephrotic syndrome was observed and the follow-up computed tomography scan showed the disappearance of all portal vein, splenic vein, and SMV thrombi.
Keywords: Complications; Nephrotic syndrome; Thrombolytic therapy; Venous thrombosis.
Figures
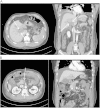
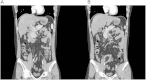
References
-
- Harris RC, Ismail N. Extrarenal complications of the nephrotic syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis. 1994;23:477–497. - PubMed
-
- Llach F. Hypercoagulability, renal vein thrombosis, and other thrombotic complications of nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 1985;28:429–439. - PubMed
-
- Sagripanti A, Barsotti G. Hypercoagulability, intraglomerular coagulation, and thromboembolism in nephrotic syndrome. Nephron. 1995;70:271–281. - PubMed
-
- Kumar S, Sarr MG, Kamath PS. Mesenteric venous thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1683–1688. - PubMed
-
- Brunaud L, Antunes L, Collinet-Adler S, Marchal F, Ayav A, Bresler L, Boissel P. Acute mesenteric venous thrombosis: case for nonoperative management. J Vasc Surg. 2001;34:673–679. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

