Analysis of midpalatal miniscrew-assisted maxillary molar distalization patterns with simultaneous use of fixed appliances: A preliminary study
- PMID: 26877983
- PMCID: PMC4751302
- DOI: 10.4041/kjod.2016.46.1.55
Analysis of midpalatal miniscrew-assisted maxillary molar distalization patterns with simultaneous use of fixed appliances: A preliminary study
Abstract
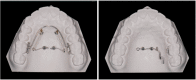
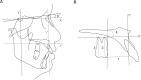
Skeletal anchorage-assisted upper molar distalization has become one of the standard treatment modalities for the correction of Class II malocclusion. The purpose of this study was to analyze maxillary molar movement patterns according to appliance design, with the simultaneous use of buccal fixed orthodontic appliances. The authors devised two distinct types of midpalatal miniscrew-assisted maxillary molar distalizers, a lingual arch type and a pendulum type. Fourteen patients treated with one of the two types of distalizers were enrolled in the study, and the patterns of tooth movement associated with each type were compared. Pre- and post-treatment lateral cephalograms were analyzed. The lingual arch type was associated with relatively bodily upper molar distalization, while the pendulum type was associated with distal tipping with intrusion of the upper molar. Clinicians should be aware of the expected tooth movement associated with each appliance design. Further well designed studies with larger sample sizes are required.
Keywords: Class II; Distalizing; Orthodontic mini-implant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no commercial, proprietary, or financial interest in the products or companies described in this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maxillary molar distalization with the indirect Palatal miniscrew for Anchorage and Distalization Appliance (iPANDA).Orthodontics (Chic.). 2013;14(1):e228-41. doi: 10.11607/ortho.982. Orthodontics (Chic.). 2013. PMID: 23646335
-
A comparison of two intraoral molar distalization appliances: distal jet versus pendulum.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2005 Sep;128(3):353-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2004.04.031. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2005. PMID: 16168332
-
Maxillary molar distalization or mandibular enhancement: a cephalometric comparison of comprehensive orthodontic treatment including the pendulum and the Herbst appliances.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003 Feb;123(2):108-16. doi: 10.1067/mod.2003.7. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003. PMID: 12594414
-
Treatment effects of intraoral appliances with conventional anchorage designs for non-compliance maxillary molar distalization: a literature review.Eur J Orthod. 2008 Dec;30(6):558-71. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjn047. Epub 2008 Sep 27. Eur J Orthod. 2008. PMID: 18820306 Review.
-
Time of maxillary molar distalization with non-compliance intraoral distalizing appliances: a meta-analysis.Eur J Orthod. 2019 Nov 15;41(6):652-660. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjz030. Eur J Orthod. 2019. PMID: 31107942
Cited by
-
Comparison of treatment effects between four premolar extraction and total arch distalization using the modified C-palatal plate.Korean J Orthod. 2018 Jul;48(4):224-235. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2018.48.4.224. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Korean J Orthod. 2018. PMID: 30003056 Free PMC article.
-
Distalization with a modified C-palatal plate for severe upper crowding and a missing lower incisor.Korean J Orthod. 2020 Jan;50(1):52-62. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2020.50.1.52. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Korean J Orthod. 2020. PMID: 32042720 Free PMC article.
-
Variations in the alveolar bone morphology in maxillary molar area: a retrospective CBCT study.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Aug 1;24(1):872. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04588-w. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39090625 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term stability of miniscrew anchored maxillary molar distalization in Class II treatment.Angle Orthod. 2020 May 1;90(3):362-368. doi: 10.2319/051619-335.1. Angle Orthod. 2020. PMID: 33378427 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional evaluation of tooth movement in Class II malocclusions treated without extraction by orthodontic mini-implant anchorage.Korean J Orthod. 2016 Sep;46(5):280-9. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2016.46.5.280. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Korean J Orthod. 2016. PMID: 27668191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bolla E, Muratore F, Carano A, Bowman SJ. Evaluation of maxillary molar distalization with the distal jet: a comparison with other contemporary methods. Angle Orthod. 2002;72:481–494. - PubMed
-
- Fuziy A, Rodrigues de Almeida R, Janson G, Angelieri F, Pinzan A. Sagittal, vertical, and transverse changes consequent to maxillary molar distalization with the pendulum appliance. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006;130:502–510. - PubMed
-
- Patel MP, Janson G, Henriques JF, de Almeida RR, de Freitas MR, Pinzan A, et al. Comparative distalization effects of Jones jig and pendulum appliances. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;135:336–342. - PubMed
-
- Sugawara J, Kanzaki R, Takahashi I, Nagasaka H, Nanda R. Distal movement of maxillary molars in nongrowing patients with the skeletal anchorage system. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006;129:723–733. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
