Trends in publication on evidence-based antioxidative herbal medicines in management of diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 26877997
- PMCID: PMC4752788
- DOI: 10.1186/s40200-016-0221-2
Trends in publication on evidence-based antioxidative herbal medicines in management of diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
Background: Recently, popularity and use of herbal medicine in treatment of diabetes have been increased. Since, oxidative stress is known as the main underlying pathophysiology of diabetes and its complications, the purpose of this bibliometric study is to assess the global scientific production analysis and developing its trend in field of antioxidative hypoglycemic herbal medicines and diabetic nephropathy focusing on the scientific publication numbers, citations, geographical distribution in the world and determining the main journal (source) in the field.
Methods: Our search terms were "diabetes", "renal", "nephropathy", "herb", "Chinese medicine", "traditional medicine", and "antioxidant" from Scopus database until January 2015 and analysis of the distribution of words in the publication year, main journal (source) in the field, geographical distribution, documents' type and language, subject area, and h-index of citations were crried out. The Scopus analysis tools and VOSviewer software version 1.6.3 have been used for analysis.
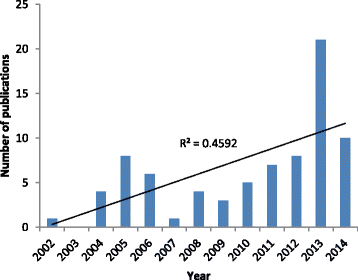
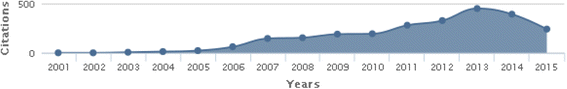
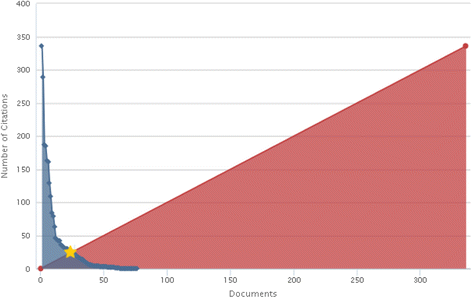
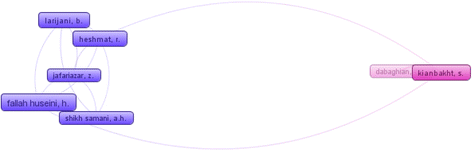
Results: Within 1166 papers were published until year 2015, 78 studies were related to this topic in human. Increasing trend in number of related researches was shown. Fifty eight percent of the published papers were original articles, and the highest number was produced in 2013 with 21 documents. Top subject areas were medicine with global publication share of 71.8 %, and pharmacology was ranked the second (39.7 %). Iran was the first country with global publication. The total citation of the documents were 2518 times and h-index was 24. The highest cited paper was a review article with 336 citation number, and top source was "Journal of Medicinal Plants". Both of top authors and affiliation were from Iran; "Tehran University of Medical Sciences". Also, top author in the co-authorship mapping and clustering assessment was from Iran.
Conclusions: Although, we found an ascending trend of scientific publications in field of antioxidative herbal medicine and diabetic nephropathy with a good position for Iran, the number of publications is insufficient and more researches in this topic is necessary.
Keywords: Antioxidative; Diabetic nephropathy; Herbal medicine; Scientometric analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Scientometric study of academic publications on antioxidative herbal medicines in type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2016 Oct 21;15:48. doi: 10.1186/s40200-016-0273-3. eCollection 2016. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2016. PMID: 27785446 Free PMC article.
-
Worldwide trends in scientific publications on association of gut microbiota with obesity.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019 Jan;22(1):65-71. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2018.30203.7281. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30944710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scientometric study of academic publications on herbal medicines in Endocrinology & Metabolism Research Institute (EMRI) of Tehran University of Medical Sciences.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020 Aug 28;23(2):1783-1791. doi: 10.1007/s40200-020-00622-0. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020. PMID: 39610507 Free PMC article.
-
Study of Scientific Production of Community Medicines' Department Indexed in ISI Citation Databases.Acta Inform Med. 2016 Oct;24(5):370-374. doi: 10.5455/aim.2016.24.370-374. Epub 2016 Nov 1. Acta Inform Med. 2016. PMID: 28077896 Free PMC article.
-
Research Performance in Stem Cell Science and Regenerative Medicine in Iran: A National Comprehensive Observation.Arch Iran Med. 2019 Jun 1;22(6):318-327. Arch Iran Med. 2019. PMID: 31356098
Cited by
-
Scientometric Study on Non-communicable Diseases in Iran: A Review Article.Iran J Public Health. 2018 Jul;47(7):936-943. Iran J Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30181990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scientometric study of academic publications on antioxidative herbal medicines in type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2016 Oct 21;15:48. doi: 10.1186/s40200-016-0273-3. eCollection 2016. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2016. PMID: 27785446 Free PMC article.
-
Worldwide trends in scientific publications on association of gut microbiota with obesity.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019 Jan;22(1):65-71. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2018.30203.7281. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30944710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for Prevention and Treatment of Peritoneal Fibrosis: A Scientometric Study.Int J Prev Med. 2019 May 17;10:60. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_549_17. eCollection 2019. Int J Prev Med. 2019. PMID: 31198495 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of publication activity in the field of familial Mediterranean fever in 2010-2019: a Scopus-based study.Rheumatol Int. 2021 Nov;41(11):2015-2023. doi: 10.1007/s00296-021-04988-z. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Rheumatol Int. 2021. PMID: 34499195
References
-
- Marinac JS, Buchinger CL, Godfrey LA, Wooten JM, Sun C, Willsie SK. Herbal products and dietary supplements: a survey of use, attitudes, and knowledge among older adults. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2007;107(1):13–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

