An Overview of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) 3CL Protease Inhibitors: Peptidomimetics and Small Molecule Chemotherapy
- PMID: 26878082
- PMCID: PMC7075650
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01461
An Overview of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) 3CL Protease Inhibitors: Peptidomimetics and Small Molecule Chemotherapy
Abstract
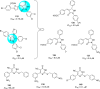
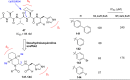
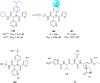
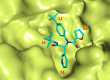
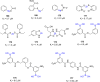
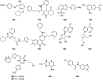
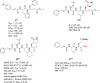
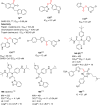
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is caused by a newly emerged coronavirus that infected more than 8000 individuals and resulted in more than 800 (10-15%) fatalities in 2003. The causative agent of SARS has been identified as a novel human coronavirus (SARS-CoV), and its viral protease, SARS-CoV 3CL(pro), has been shown to be essential for replication and has hence been recognized as a potent drug target for SARS infection. Currently, there is no effective treatment for this epidemic despite the intensive research that has been undertaken since 2003 (over 3500 publications). This perspective focuses on the status of various efficacious anti-SARS-CoV 3CL(pro) chemotherapies discovered during the last 12 years (2003-2015) from all sources, including laboratory synthetic methods, natural products, and virtual screening. We describe here mainly peptidomimetic and small molecule inhibitors of SARS-CoV 3CL(pro). Attempts have been made to provide a complete description of the structural features and binding modes of these inhibitors under many conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 Mpro: A Potential Target for Peptidomimetics and Small-Molecule Inhibitors.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 19;11(4):607. doi: 10.3390/biom11040607. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33921886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and synthesis of a series of serine derivatives as small molecule inhibitors of the SARS coronavirus 3CL protease.Bioorg Med Chem. 2016 Mar 15;24(6):1241-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.01.052. Epub 2016 Jan 29. Bioorg Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26879854 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-induced Dimerization of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) Coronavirus nsp5 Protease (3CLpro): IMPLICATIONS FOR nsp5 REGULATION AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF ANTIVIRALS.J Biol Chem. 2015 Aug 7;290(32):19403-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.651463. Epub 2015 Jun 8. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26055715 Free PMC article.
-
The structure-based design of peptidomimetic inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 3C like protease as Potent anti-viral drug candidate.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Aug 5;238:114458. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114458. Epub 2022 May 13. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35635946 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Evaluation of Anti-SARS-Coronavirus Agents Based on Molecular Interactions with the Viral Protease.Molecules. 2020 Aug 27;25(17):3920. doi: 10.3390/molecules25173920. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32867349 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The 2019-2020 Novel Coronavirus (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2) Pandemic: A Joint American College of Academic International Medicine-World Academic Council of Emergency Medicine Multidisciplinary COVID-19 Working Group Consensus Paper.J Glob Infect Dis. 2020 May 22;12(2):47-93. doi: 10.4103/jgid.jgid_86_20. eCollection 2020 Apr-Jun. J Glob Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32773996 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Mpro: A Potential Target for Peptidomimetics and Small-Molecule Inhibitors.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 19;11(4):607. doi: 10.3390/biom11040607. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33921886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Room-temperature neutron and X-ray data collection of 3CL Mpro from SARS-CoV-2.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2020 Oct 1;76(Pt 10):483-487. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X20011814. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2020. PMID: 33006576 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the molecular mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibition from 137 crystal structures using algebraic topology and deep learning.Chem Sci. 2020 Sep 30;11(44):12036-12046. doi: 10.1039/d0sc04641h. Chem Sci. 2020. PMID: 34123218 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual Double-System Single-Box: A Nonequilibrium Alchemical Technique for Absolute Binding Free Energy Calculations: Application to Ligands of the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease.J Chem Theory Comput. 2020 Nov 10;16(11):7160-7172. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.0c00634. Epub 2020 Oct 22. J Chem Theory Comput. 2020. PMID: 33090785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rota P. A.; Oberste M. S.; Monroe S. S.; Nix W. A.; Campagnoli R.; Icenogle J. P.; Penaranda S.; Bankamp B.; Maher K.; Chen M. H.; Tong S.; Tamin A.; Lowe L.; Frace M.; DeRisi J. L.; Chen Q.; Wang D.; Erdman D. D.; Peret T. C.; Burns C.; Ksiazek T. G.; Rollin P. E.; Sanchez A.; Liffick S.; Holloway B.; Limor J.; McCaustland K.; Olsen-Rasmussen M.; Fouchier R.; Gunther S.; Osterhaus A. D.; Drosten C.; Pallansch M. A.; Anderson L. J.; Bellini W. J. Characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Science 2003, 300, 1394–1399. 10.1126/science.1085952. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Drosten C.; Gunther S.; Preiser W.; van der Werf S.; Brodt H. R.; Becker S.; Rabenau H.; Panning M.; Kolesnikova L.; Fouchier R. A.; Berger A.; Burguiere A. M.; Cinatl J.; Eickmann M.; Escriou N.; Grywna K.; Kramme S.; Manuguerra J. C.; Muller S.; Rickerts V.; Sturmer M.; Vieth S.; Klenk H. D.; Osterhaus A. D.; Schmitz H.; Doerr H. W. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1967–1976. 10.1056/NEJMoa030747. - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Groot R. J.; Baker S. C.; Baric R.; Enjuanes L.; Gorbalenya A. E.; Holmes K. V.; Perlman S.; Poon L.; Rottier P. J. M.; Talbot P. J.; Woo P. C. Y.; Ziebuhr J.. Family Coronaviridae. In Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; King A. M. Q., Lefkowitz E., Adams M. J., Carstens E. B., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, 2011; pp 806–828.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

