FGF23 signaling impairs neutrophil recruitment and host defense during CKD
- PMID: 26878171
- PMCID: PMC4767336
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI83470
FGF23 signaling impairs neutrophil recruitment and host defense during CKD
Abstract
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has been associated with impaired host response and increased susceptibility to infections. Leukocyte recruitment during inflammation must be tightly regulated to protect the host against pathogens. FGF23 levels are increased in blood during CKD, and levels of this hormone have been associated with a variety of adverse effects in CKD patients. Here, we have shown that CKD impairs leukocyte recruitment into inflamed tissue and host defense in mice and humans. FGF23 neutralization during CKD in murine models restored leukocyte recruitment and host defense. Intravital microscopy of animals with chronic kidney failure showed that FGF23 inhibits chemokine-activated leukocyte arrest on the endothelium, and downregulation of FGF receptor 2 (FGFR2) on PMNs rescued host defense in these mice. In vitro, FGF23 inhibited PMN adhesion, arrest under flow, and transendothelial migration. Mechanistically, FGF23 binding to FGFR2 counteracted selectin- and chemokine-triggered β2 integrin activation on PMNs by activating protein kinase A (PKA) and inhibiting activation of the small GTPase Rap1. Moreover, knockdown of PKA abolished the inhibitory effect of FGF23 on integrin activation. Together, our data reveal that FGF23 acts directly on PMNs and dampens host defense by direct interference with chemokine signaling and integrin activation.
Figures

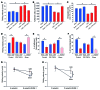

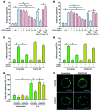


Comment in
-
Chronic kidney disease: FGF-23 inhibits neutrophil activation.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016 Apr;12(4):198. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2016.28. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26923203 No abstract available.
-
More trouble with FGF23: a novel role in systemic immunosuppression.Kidney Int. 2016 Jun;89(6):1176-7. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.04.002. Kidney Int. 2016. PMID: 27181769
References
-
- Recio-Mayoral A, Banerjee D, Streather C, Kaski JC. Endothelial dysfunction, inflammation and atherosclerosis in chronic kidney disease — a cross-sectional study of predialysis, dialysis and kidney-transplantation patients. Atherosclerosis. 2011;216(2):446–451. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.02.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ley K. Arrest chemokines. Microcirculation. 2003;10(3–4):289–295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

