Transient inhibition of ROR-γt therapeutically limits intestinal inflammation by reducing TH17 cells and preserving group 3 innate lymphoid cells
- PMID: 26878233
- PMCID: PMC4948756
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.4046
Transient inhibition of ROR-γt therapeutically limits intestinal inflammation by reducing TH17 cells and preserving group 3 innate lymphoid cells
Abstract
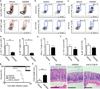
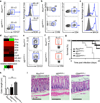
RAR-related orphan receptor-γt (ROR-γt) directs differentiation of proinflammatory T helper 17 (TH17) cells and is a potential therapeutic target in chronic autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. However, ROR-γt-dependent group 3 innate lymphoid cells ILC3s provide essential immunity and tissue protection in the intestine, suggesting that targeting ROR-γt could also result in impaired host defense after infection or enhanced tissue damage. Here, we demonstrate that transient chemical inhibition of ROR-γt in mice selectively reduces cytokine production from TH17 but not ILCs in the context of intestinal infection with Citrobacter rodentium, resulting in preserved innate immunity. Temporal deletion of Rorc (encoding ROR-γt) in mature ILCs also did not impair cytokine response in the steady state or during infection. Finally, pharmacologic inhibition of ROR-γt provided therapeutic benefit in mouse models of intestinal inflammation and reduced the frequency of TH17 cells but not ILCs isolated from primary intestinal samples of individuals with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Collectively, these results reveal differential requirements for ROR-γt in the maintenance of TH17 cell and ILC3 responses and suggest that transient inhibition of ROR-γt is a safe and effective therapeutic approach during intestinal inflammation.
Figures


References
-
- Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK. IL-17 and Th17 Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009;27:485–517. - PubMed
-
- Ivanov II, et al. The orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell. 2006;126:1121–1133. - PubMed
-
- Eberl G, Littman DR. The role of the nuclear hormone receptor RORgammat in the development of lymph nodes and Peyer's patches. Immunol Rev. 2003;195:81–90. - PubMed
-
- Sawa S, et al. RORgammat+ innate lymphoid cells regulate intestinal homeostasis by integrating negative signals from the symbiotic microbiota. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:320–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BBS/E/B/000C0409/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R56 AI114724/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56AI114724/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI123368/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- G9818340/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/E021638/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- UL1-RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 105644/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01AI123368/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DP5OD012116/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- DP5 OD012116/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

