An expanded sequence context model broadly explains variability in polymorphism levels across the human genome
- PMID: 26878723
- PMCID: PMC4811712
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3511
An expanded sequence context model broadly explains variability in polymorphism levels across the human genome
Abstract
The rate of single-nucleotide polymorphism varies substantially across the human genome and fundamentally influences evolution and incidence of genetic disease. Previous studies have only considered the immediately flanking nucleotides around a polymorphic site--the site's trinucleotide sequence context--to study polymorphism levels across the genome. Moreover, the impact of larger sequence contexts has not been fully clarified, even though context substantially influences rates of polymorphism. Using a new statistical framework and data from the 1000 Genomes Project, we demonstrate that a heptanucleotide context explains >81% of variability in substitution probabilities, highlighting new mutation-promoting motifs at ApT dinucleotide, CAAT and TACG sequences. Our approach also identifies previously undocumented variability in C-to-T substitutions at CpG sites, which is not immediately explained by differential methylation intensity. Using our model, we present informative substitution intolerance scores for genes and a new intolerance score for amino acids, and we demonstrate clinical use of the model in neuropsychiatric diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

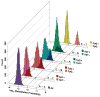
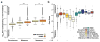

References
-
- Hodgkinson A, Eyre-Walker A. Variation in the mutation rate across mammalian genomes. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:756–66. - PubMed
-
- Ehrlich M, Wang RY. 5-Methylcytosine in eukaryotic DNA. Science. 1981;212:1350–7. - PubMed
-
- Rideout WM, Coetzee GA, Olumi AF, Jones PA. 5-Methylcytosine as an endogenous mutagen in the human LDL receptor and p53 genes. Science. 1990;249:1288–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

