EGCG prevents PCB-126-induced endothelial cell inflammation via epigenetic modifications of NF-κB target genes in human endothelial cells
- PMID: 26878794
- PMCID: PMC4757812
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.10.003
EGCG prevents PCB-126-induced endothelial cell inflammation via epigenetic modifications of NF-κB target genes in human endothelial cells
Abstract
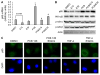
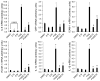
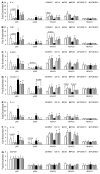
Anti-inflammatory polyphenols, such as epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), have been shown to protect against the toxicity of environmental pollutants. It is well known that bioactive food compounds such as polyphenols may exert their protection by modulating inflammatory pathways regulated through nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling. EGCG has been reported to inhibit NF-κB activation. We hypothesize that EGCG can protect against polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB)-induced endothelial inflammation in part through epigenetic regulation of NF-κB-regulated inflammatory genes. In order to test this hypothesis, human endothelial cells (EA.hy926) were exposed to physiologically relevant levels of coplanar PCB 126 and/or 15 or 30 μM of EGCG, followed by quantification of NF-κB subunit p65, histone acetyltransferase p300 and histone deacetylases (HDACs) accumulation through chromatin immunoprecipitation assay in the promoter region of inflammatory genes. In addition, the enrichment of the acetylated H3 was also quantified. PCB 126 exposure increased the expression of vascular inflammatory mediators, including interleukin (IL)-6, C-reactive protein, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and IL-1α/β, which were prevented by pretreatment with EGCG. This inhibitory effect by EGCG correlated with abolished nuclear import of p65, decreased chromatin binding of p65 and p300, as well as increased chromatin binding of HDAC 1/2. Furthermore, EGCG induced hypoacetylation of H3, which accounts for deactivation of downstream genes. These data suggest that EGCG-induced epigenetic modifications can decrease PCB-induced vascular toxicity.
Keywords: EGCG; HDACs; PCB 126; Vascular inflammation; p300; p65.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of nutrition on pollutant toxicity: an update with new insights into epigenetic regulation.Rev Environ Health. 2017 Mar 1;32(1-2):65-72. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2016-0041. Rev Environ Health. 2017. PMID: 28076319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exposure to coplanar PCBs induces endothelial cell inflammation through epigenetic regulation of NF-κB subunit p65.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015 Dec 15;289(3):457-65. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.10.015. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26519613 Free PMC article.
-
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, inhibits EBV-induced B lymphocyte transformation via suppression of RelA acetylation.Cancer Res. 2009 Jan 15;69(2):583-92. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2442. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19147572
-
EGCG protects endothelial cells against PCB 126-induced inflammation through inhibition of AhR and induction of Nrf2-regulated genes.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012 Jun 1;261(2):181-8. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2012.03.024. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22521609 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Epigallocatechin Gallate on Endothelial Disorders in Atherosclerosis.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020 Apr;75(4):292-298. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000792. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31895874 Review.
Cited by
-
Low-dose green tea intake reduces incidence of atrial fibrillation in a Chinese population.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):85592-85602. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12243. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27683043 Free PMC article.
-
Catechins: Protective mechanism of antioxidant stress in atherosclerosis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 24;14:1144878. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1144878. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37033663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of nutrition on pollutant toxicity: an update with new insights into epigenetic regulation.Rev Environ Health. 2017 Mar 1;32(1-2):65-72. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2016-0041. Rev Environ Health. 2017. PMID: 28076319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective influence of healthful nutrition on mechanisms of environmental pollutant toxicity and disease risks.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017 Jun;1398(1):99-107. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13365. Epub 2017 Jun 2. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017. PMID: 28574588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function of Green Tea Catechins in the Brain: Epigallocatechin Gallate and its Metabolites.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 25;20(15):3630. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153630. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31349535 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hansson GK, et al. Innate and adaptive immunity in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2002;91(4):281–91. - PubMed
-
- Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2002;105(9):1135–43. - PubMed
-
- Nakashima Y, et al. Upregulation of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 at atherosclerosis-prone sites on the endothelium in the ApoE-deficient mouse. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998;18(5):842–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

