Nailfold videocapillaroscopy and serum VEGF levels in scleroderma are associated with internal organ involvement
- PMID: 26878864
- PMCID: PMC4754208
- DOI: 10.1007/s13317-016-0077-y
Nailfold videocapillaroscopy and serum VEGF levels in scleroderma are associated with internal organ involvement
Abstract
Purpose: Nailfold videocapillaroscopy (NVC) identifies the microvascular hallmarks of systemic sclerosis (SSc) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and may play a pivotal role in the associated vasculopathy. The aim of the present study was to compare NVC alterations with clinical subsets, internal organ involvement, and serum VEGF levels in a cohort of selected SSc cases.
Methods: We studied 44 patients with SSc who were evaluated within 3 months from enrollment by NVC, skin score, severity index, pulmonary function tests, carbon monoxide diffusing capacity (DLCO), echocardiography, pulmonary high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT), gastroesophageal (GE) endoscopy or manometry or X-ray, and serum autoantibodies. Serum VEGF-A levels were determined by ELISA in 72 SSc patients and 31 healthy controls.
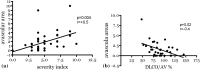
Results: Giant capillaries were inversely correlated with age (p = 0.034, r = -0.34) and to the extent of reticular pattern at HRCT (p = 0.04, r = -0.5). Avascular areas were directly correlated with capillaroscopy skin ulcer risk index (CSURI) (p = 0.006, r = +0.4) and severity index (p = 0.004, r = +0.5). The mean capillary density was directly correlated to the ulcer number (p = 0.02, r = +0.4) and to DLCO/alveolar volume (p = 0.02, r = +0.4) and inversely correlated with severity index (p = 0.01, r = -0.4) and skin score (p = 0.02, r = -0.4). Serum VEGF levels were higher in the SSc population vs controls (p = 0.03) and inversely correlated with DLCO (p = 0.01, r =-0.4) and directly with ground-glass and reticular pattern at HRCT (p = 0.04, r = +0.4 for both).
Conclusions: Our data suggest the importance of NVC not only for the diagnosis, but also for the global evaluation of SSc patients. Of note, serum VEGF levels may act as a biomarker of interstitial lung involvement.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Biomarkers; Endothelium; Personalized medicine; Systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
MDS and AC received travel support from Actelion. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Ethical approval All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent All subjects enrolled signed a written informed consent for serum samples and data analysis after approval from the local ethical committee.
Figures



References
-
- De Santis M, Selmi C. The autoinflammatory side of systemic sclerosis. Isr Med Assoc J. 2015;17(1):47–49. - PubMed
-
- Selmi C, Feghali-Bostwick CA, Lleo A, Lombardi SA, De Santis M, Cavaciocchi F, Zammataro L, Mitchell MM, Lasalle JM, Medsger T, Jr, Gershwin ME. X chromosome gene methylation in peripheral lymphocytes from monozygotic twins discordant for scleroderma. Clin Exp Immunol. 2012;169(3):253–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2012.04621.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

