Discovery of Radioiodinated Monomeric Anthraquinones as a Novel Class of Necrosis Avid Agents for Early Imaging of Necrotic Myocardium
- PMID: 26878909
- PMCID: PMC4754898
- DOI: 10.1038/srep21341
Discovery of Radioiodinated Monomeric Anthraquinones as a Novel Class of Necrosis Avid Agents for Early Imaging of Necrotic Myocardium
Abstract
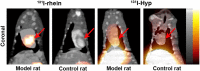
Assessment of myocardial viability is deemed necessary to aid in clinical decision making whether to recommend revascularization therapy for patients with myocardial infarction (MI). Dianthraquinones such as hypericin (Hyp) selectively accumulate in necrotic myocardium, but were unsuitable for early imaging after administration to assess myocardial viability. Since dianthraquinones can be composed by coupling two molecules of monomeric anthraquinone and the active center can be found by splitting chemical structure, we propose that monomeric anthraquinones may be effective functional groups for necrosis targetability. In this study, eight radioiodinated monomeric anthraquinones were evaluated as novel necrosis avid agents (NAAs) for imaging of necrotic myocardium. All (131)I-anthraquinones showed high affinity to necrotic tissues and (131)I-rhein emerged as the most promising compound. Infarcts were visualized on SPECT/CT images at 6 h after injection of (131)I-rhein, which was earlier than that with (131)I-Hyp. Moreover, (131)I-rhein showed satisfactory heart-to-blood, heart-to-liver and heart-to-lung ratios for obtaining images of good diagnostic quality. (131)I-rhein was a more promising "hot spot imaging" tracer for earlier visualization of necrotic myocardium than (131)I-Hyp, which supported further development of radiopharmaceuticals based on rhein for SPECT/CT ((123)I and (99m)Tc) or PET/CT imaging ((18)F and (124)I) of myocardial necrosis.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Synthesis and Preclinical Evaluation of Radioiodinated Hypericin Dicarboxylic Acid as a Necrosis Avid Agent in Rat Models of Induced Hepatic, Muscular, and Myocardial Necroses.Mol Pharm. 2016 Jan 4;13(1):232-40. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00686. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Mol Pharm. 2016. PMID: 26568406
-
Radiolabeled Rhein as Small-Molecule Necrosis Avid Agents for Imaging of Necrotic Myocardium.Anal Chem. 2017 Jan 17;89(2):1260-1266. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b03959. Epub 2016 Dec 28. Anal Chem. 2017. PMID: 27981843
-
Evaluation of Necrosis Avidity and Potential for Rapid Imaging of Necrotic Myocardium of Radioiodinated Hypocrellins.Mol Imaging Biol. 2018 Aug;20(4):551-561. doi: 10.1007/s11307-017-1157-8. Mol Imaging Biol. 2018. PMID: 29305726
-
Discovery of necrosis avidity of rhein and its applications in necrosis imaging.J Drug Target. 2020 Nov;28(9):904-912. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2020.1759079. Epub 2020 Apr 30. J Drug Target. 2020. PMID: 32314601 Review.
-
Mono-[123I]iodohypericine monocarboxylic acid.2008 Feb 21 [updated 2008 Jun 2]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2008 Feb 21 [updated 2008 Jun 2]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641782 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel 18F-Labeled 1-Hydroxyanthraquinone Derivatives for Necrotic Myocardium Imaging.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2016 Dec 28;8(2):191-195. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.6b00398. eCollection 2017 Feb 9. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 28197310 Free PMC article.
-
Avenues to molecular imaging of dying cells: Focus on cancer.Med Res Rev. 2018 Sep;38(6):1713-1768. doi: 10.1002/med.21495. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Med Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29528513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updated developments on molecular imaging and therapeutic strategies directed against necrosis.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2019 May;9(3):455-468. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.02.002. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2019. PMID: 31193829 Free PMC article.
-
Radiolabeled Angiogenesis-Targeting Croconaine Nanoparticles for Trimodality Imaging Guided Photothermal Therapy of Glioma.ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2018 Apr 27;1(4):1741-1749. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.8b00195. Epub 2018 Mar 20. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2018. PMID: 30506043 Free PMC article.
-
The evolving roles of radiolabeled quinones as small molecular probes in necrotic imaging.Br J Radiol. 2020 Jul;93(1111):20200034. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20200034. Epub 2020 May 21. Br J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32374626 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Harry R. P., Christopher M. O. & Joseph R. Revascularization for heart failure. Am. Heart J. 153, 65–73 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Samady H. et al. Failure to improve left ventricular function after coronary revascularization for ischemic cardiomyopathy is not associated with worse outcome. Circulation 100, 1298–1304 (1999). - PubMed
-
- White H. D. et al. Reinfarction after percutaneous coronary intervention or medical management using the universal definition in patients with total occlusion after myocardial infarction: Results from long-term follow-up of the Occluded Artery Trial (OAT) cohort. Am. Heart J. 163, 563–571 (2012). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ling L. F. et al. Identification of therapeutic benefit from revascularization in patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction: inducible ischemia versus hibernating myocardium. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 6, 363–372 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

