Deciphering the biological effects of acupuncture treatment modulating multiple metabolism pathways
- PMID: 26879284
- PMCID: PMC4754631
- DOI: 10.1038/srep19942
Deciphering the biological effects of acupuncture treatment modulating multiple metabolism pathways
Abstract
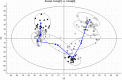
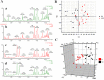
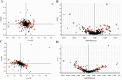
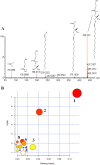
Acupuncture is an alternative therapy that is widely used to treat various diseases. However, detailed biological interpretation of the acupuncture stimulations is limited. We here used metabolomics and proteomics technology, thereby identifying the serum small molecular metabolites into the effect and mechanism pathways of standardized acupuncture treatments at 'Zusanli' acupoint which was the most often used acupoint in previous reports. Comprehensive overview of serum metabolic profiles during acupuncture stimulation was investigated. Thirty-four differential metabolites were identified in serum metabolome and associated with ten metabolism pathways. Importantly, we have found that high impact glycerophospholipid metabolism, fatty acid metabolism, ether lipid metabolism were acutely perturbed by acupuncture stimulation. As such, these alterations may be useful to clarify the biological mechanism of acupuncture stimulation. A series of differentially expressed proteins were identified and such effects of acupuncture stimulation were found to play a role in transport, enzymatic activity, signaling pathway or receptor interaction. Pathway analysis further revealed that most of these proteins were found to play a pivotal role in the regulation of multiple metabolism pathways. It demonstrated that the metabolomics coupled with proteomics as a powerful approach for potential applications in understanding the biological effects of acupuncture stimulation.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang A. et al. Systems biology approach opens door to essence of acupuncture. Complement Ther Med 21, 253–259 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Xiong J. et al. De-qi, not psychological factors, determines the therapeutic efficacy of acupuncture treatment for primary dysmenorrhea. Chin J Integr Med 18, 7–15 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Jia J. et al. A review of Omics research in acupuncture: the relevance and future prospects for understanding the nature of meridians and acupoints. J Ethnopharmacol. 140, 594–603 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Cheung F. Modern TCM: Enter the clinic. Nature 480, S94–5 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

