Holey graphene frameworks for highly selective post-combustion carbon capture
- PMID: 26879393
- PMCID: PMC4754909
- DOI: 10.1038/srep21537
Holey graphene frameworks for highly selective post-combustion carbon capture
Abstract
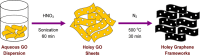
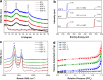
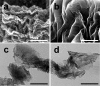
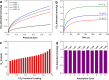
Atmospheric CO2 concentrations continue to rise rapidly in response to increased combustion of fossil fuels, contributing to global climate change. In order to mitigate the effects of global warming, development of new materials for cost-effective and energy-efficient CO2 capture is critically important. Graphene-based porous materials are an emerging class of solid adsorbents for selectively removing CO2 from flue gases. Herein, we report a simple and scalable approach to produce three-dimensional holey graphene frameworks with tunable porosity and pore geometry, and demonstrate their application as high-performance CO2 adsorbents. These holey graphene macrostructures exhibit a significantly improved specific surface area and pore volume compared to their pristine counterparts, and can be effectively used in post-combustion CO2 adsorption systems because of their intrinsic hydrophobicity together with good gravimetric storage capacities, rapid removal capabilities, superior cycling stabilities, and moderate initial isosteric heats. In addition, an exceptionally high CO2 over N2 selectivity can be achieved under conditions relevant to capture from the dry exhaust gas stream of a coal burning power plant, suggesting the possibility of recovering highly pure CO2 for long-term sequestration and/or utilization for downstream applications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development Trends in Porous Adsorbents for Carbon Capture.Environ Sci Technol. 2015 Nov 3;49(21):12641-61. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b03149. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Environ Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 26422294 Review.
-
Solution Processable Holey Graphene Oxide and Its Derived Macrostructures for High-Performance Supercapacitors.Nano Lett. 2015 Jul 8;15(7):4605-10. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b01212. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Nano Lett. 2015. PMID: 26056845
-
Gas adsorption properties of graphene-based materials.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017 May;243:46-59. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2017.03.007. Epub 2017 Mar 20. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017. PMID: 28347414 Review.
-
Hydroquinone and Quinone-Grafted Porous Carbons for Highly Selective CO2 Capture from Flue Gases and Natural Gas Upgrading.Environ Sci Technol. 2015 Aug 4;49(15):9364-73. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b01652. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Environ Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 26114815
-
A robust triphenylamine-based monolithic polymer network for selective sieving of CO2 and PM from flue gas.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Oct 10;946:174463. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.174463. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 38964385
Cited by
-
Synthesis of holey graphene for advanced nanotechnological applications.RSC Adv. 2021 Aug 12;11(44):27381-27405. doi: 10.1039/d1ra05157a. eCollection 2021 Aug 9. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35480691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resembling Graphene/Polymer Aerogel Morphology for Advancing the CO2/N2 Selectivity of the Postcombustion CO2 Capture Process.Ind Eng Chem Res. 2024 Apr 9;63(16):7073-7087. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.3c02989. eCollection 2024 Apr 24. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 38681868 Free PMC article.
-
S-nitrosocysteamine-functionalised porous graphene oxide nanosheets as nitric oxide delivery vehicles for cardiovascular applications.Redox Biol. 2024 Jun;72:103144. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103144. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38613920 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the capture and desorption of CO2 on graphene oxide foams supported by computational calculations.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 2;13(1):14476. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41683-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37660192 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental kinetics and thermodynamics investigation: Chemically activated carbon-enriched monolithic reduced graphene oxide for efficient CO2 capture.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 2;10(5):e27439. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27439. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38463862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leung D. Y. C., Caramanna G. & Maroto-Valer M. M. An overview of current status of carbon dioxide capture and storage technologies. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 39, 426–443 (2014).
-
- Wang J. et al.. Recent advances in solid sorbents for CO2 capture and new development trends. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 3478–3518 (2014).
-
- Kemper J. Biomass and carbon dioxide capture and storage: a review. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Con. 40, 401–430 (2015).
-
- Markewitz P. et al.. Worldwide innovations in the development of carbon capture technologies and the utilization of CO2. Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 7281–7305 (2012).
-
- von der Assen N., Voll P., Peters M. & Bardow A. Life cycle assessment of CO2 capture and utilization: a tutorial review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 7982–7994. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

