Modelling severe Staphylococcus aureus sepsis in conscious pigs: are implications for animal welfare justified?
- PMID: 26879530
- PMCID: PMC4755015
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-016-1888-7
Modelling severe Staphylococcus aureus sepsis in conscious pigs: are implications for animal welfare justified?
Abstract
Background: A porcine model of haematogenous Staphylococcus aureus sepsis has previously been established in our research group. In these studies, pigs developed severe sepsis including liver dysfunction during a 48 h study period. As pigs were awake during the study, animal welfare was challenged by the severity of induced disease, which in some cases necessitated humane euthanasia. A pilot study was therefore performed in order to establish the sufficient inoculum concentration and application protocol needed to produce signs of liver dysfunction within limits of our pre-defined humane endpoints.
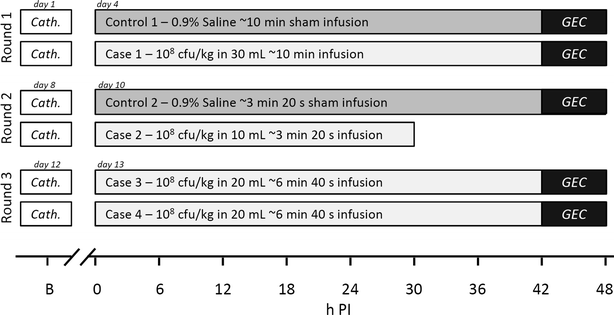
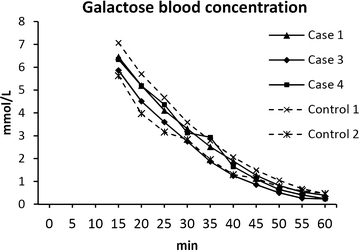
Methods: Four pigs received 1 × 10(8) cfu/kg BW of S. aureus, and two controls were sham inoculated with saline. A fixed infusion rate of 3 mL/min was used, while the inoculum concentration, i.e., the dose volume, was changed between the pigs. The following dose volumes were used: 10 mL (n = 1), 20 mL (n = 2), and 30 mL (n = 1), corresponding to infusion durations of 3.33, 6.66, and 10 min at dose rates of 3 × 10(7), 1.5 × 10(7), and 1 × 10(7) cfu/min/kg BW, respectively. Blood samples were drawn for complete blood count, clinical chemistry, and inflammatory markers before and every 6 h after inoculation. Prior to euthanasia, a galactose elimination capacity test was performed to assess liver function. Pigs were euthanised 48 h post inoculation for necropsy and histopathological evaluation.
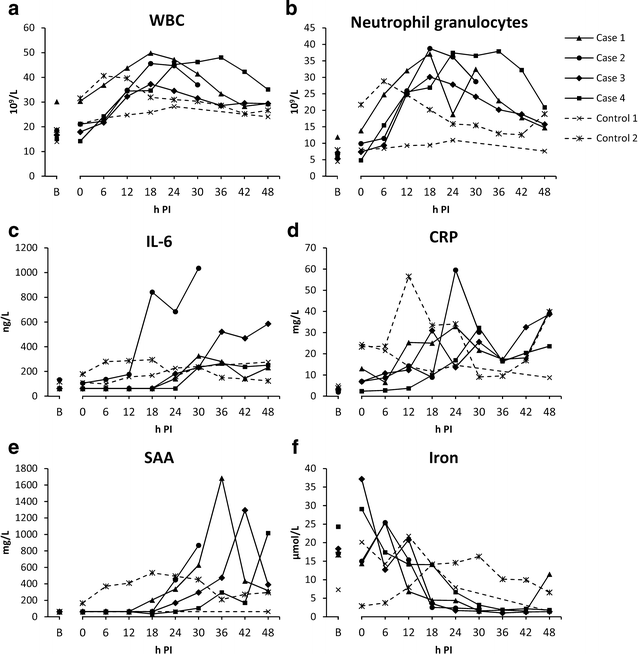
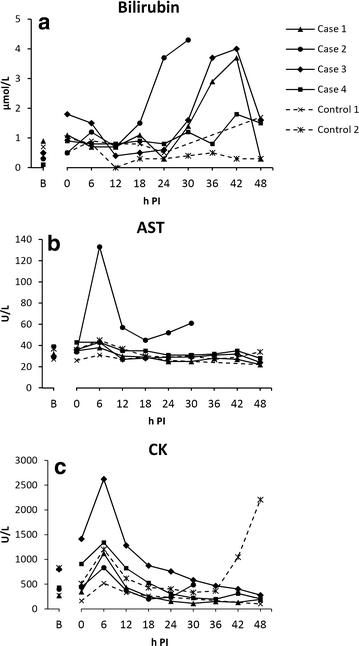
Results: While infusion times of 6.66 min, and higher, did not induce liver dysfunction (n = 3), the infusion time of 3.33 min (n = 1) caused alterations in parameters similar to what had been seen in our previous studies, i.e., increasing bilirubin and aspartate aminotransferase, as well as histopathological occurrence of intravascular fibrin split products in the liver. This pig was however euthanised after 30 h, according to humane endpoints.
Conclusions: A usable balance between scientific purpose and animal welfare could not be achieved, and we therefore find it hard to justify further use of this conscious porcine sepsis model. In order to make a model of translational relevance for human sepsis, we suggest that future model versions should use long-term anaesthesia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intravenous inoculation of Staphylococcus aureus in pigs induces severe sepsis as indicated by increased hypercoagulability and hepatic dysfunction.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010 Aug 1;309(2):208-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2010.02042.x. Epub 2010 Jun 17. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010. PMID: 20618862
-
The impact of Staphylococcus aureus concentration on the development of pulmonary lesions and cytokine expression after intravenous inoculation of pigs.Vet Pathol. 2012 Nov;49(6):950-62. doi: 10.1177/0300985812439726. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Vet Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22461225
-
Disseminated intravascular coagulation in a novel porcine model of severe Staphylococcus aureus sepsis fulfills human clinical criteria.J Comp Pathol. 2013 Nov;149(4):463-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2013.04.003. Epub 2013 Jun 6. J Comp Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23746745
-
Refining humane endpoints in mouse models of disease by systematic review and machine learning-based endpoint definition.ALTEX. 2019;36(4):555-571. doi: 10.14573/altex.1812231. Epub 2019 Apr 18. ALTEX. 2019. PMID: 31026040
-
The Influence of Pain and Analgesia in Rodent Models of Sepsis.Comp Med. 2019 Dec 1;69(6):546-554. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-CM-19-000004. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Comp Med. 2019. PMID: 31213216 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Part I: Minimum Quality Threshold in Preclinical Sepsis Studies (MQTiPSS) for Study Design and Humane Modeling Endpoints.Shock. 2019 Jan;51(1):10-22. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001243. Shock. 2019. PMID: 30106874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pediatric Swine Model of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy, Disseminated Microvascular Thrombosis, and Organ Injuries.Crit Care Explor. 2023 May 26;5(6):e0916. doi: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000916. eCollection 2023 Jun. Crit Care Explor. 2023. PMID: 37255626 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Testing of Radiopharmaceuticals for the Detection and Characterization of Osteomyelitis: Experiences from a Porcine Model.Molecules. 2021 Jul 12;26(14):4221. doi: 10.3390/molecules26144221. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34299496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fitness of animals for transport to slaughter.Can Vet J. 2019 Apr;60(4):423-429. Can Vet J. 2019. PMID: 30992599 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jenniskens M, Langouche L, Vanwijngaerden YM, Mesotten D, Van den Berghe G. Cholestatic liver (dys) function during sepsis and other critical illnesses. Intensive Care Med. 2015 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

