(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Enhances Hepatitis C Virus Double-Stranded RNA Intermediates-Triggered Innate Immune Responses in Hepatocytes
- PMID: 26879672
- PMCID: PMC4754899
- DOI: 10.1038/srep21595
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Enhances Hepatitis C Virus Double-Stranded RNA Intermediates-Triggered Innate Immune Responses in Hepatocytes
Abstract
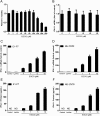
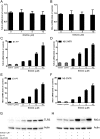
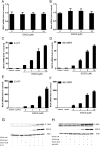
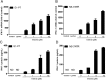
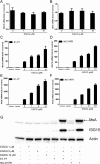
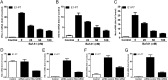
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), a major polyphenol component of green tea, has recently been identified as an inhibitor of hepatitis C virus (HCV) entry. Here, we examined whether EGCG can enhance hepatocyte-mediated intracellular innate immunity against HCV. HCV dsRNAs (Core, E1-P7, NS-3'NTR and NS5A) induced interferon-λ1 (IFN-λ1) expression in human hepatocytes. These HCV dsRNAs also induced the expression of Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3), retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) and several antiviral IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) expression. Although EGCG treatment of hepatocytes alone had little effect on TLR3 and RIG-I signaling pathways, EGCG significantly enhanced HCV dsRNAs-induced the expression of IFN-λ1, TLR3, RIG-I and antiviral ISGs in hepatocytes. Furthermore, treatment of HCV-infected hepatocytes with EGCG and HCV dsRNAs inhibited viral replication. Given that EGCG has the ability to enhance HCV dsRNAs-induced intracellular antiviral innate immunity against HCV, suggesting the potential application of EGCG as a new anti-HCV agent for HCV therapy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate enhances poly I:C-induced interferon-λ1 production and inhibits hepatitis C virus replication in hepatocytes.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug 28;23(32):5895-5903. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5895. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28932081 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid inducible gene-I (RIG-I) signaling of hepatic stellate cells inhibits hepatitis C virus replication in hepatocytes.Innate Immun. 2013;19(2):193-202. doi: 10.1177/1753425912460414. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Innate Immun. 2013. PMID: 23060457 Free PMC article.
-
DDX60L Is an Interferon-Stimulated Gene Product Restricting Hepatitis C Virus Replication in Cell Culture.J Virol. 2015 Oct;89(20):10548-68. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01297-15. Epub 2015 Aug 12. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26269178 Free PMC article.
-
[RIG-I mediated hepatic innate immune signaling that controls HCV infection].Uirusu. 2008 Dec;58(2):105-15. doi: 10.2222/jsv.58.105. Uirusu. 2008. PMID: 19374189 Review. Japanese.
-
Multi-step regulation of interferon induction by hepatitis C virus.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2013 Apr;61(2):127-38. doi: 10.1007/s00005-012-0214-x. Epub 2013 Jan 5. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2013. PMID: 23292079 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel combined single dose anti-hepatitis C therapy: a pilot study.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 25;11(1):4623. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84066-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33633233 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Epigallocatechin Gallate Nanodelivery Systems.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:5813793. doi: 10.1155/2017/5813793. Epub 2017 Jul 16. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28791306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of commitment to healthy daily habits and diets, preventive measures, and beliefs about natural products utilization during COVID-19 pandemic in certain population in Egypt and Saudi Arabia.Pharm Pract (Granada). 2022 Jul-Sep;20(3):2700. doi: 10.18549/PharmPract.2022.3.2700. Epub 2022 Aug 5. Pharm Pract (Granada). 2022. PMID: 36733518 Free PMC article.
-
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate enhances poly I:C-induced interferon-λ1 production and inhibits hepatitis C virus replication in hepatocytes.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug 28;23(32):5895-5903. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5895. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28932081 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on the Protective Effect of Green Tea Polyphenol (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) on the Liver.Nutrients. 2025 Mar 21;17(7):1101. doi: 10.3390/nu17071101. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40218859 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alter M. J. Prevention of spread of hepatitis C. Hepatology 36, S93–98 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Battaglia A. M. & Hagmeyer K. O. Combination therapy with interferon and ribavirin in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C infection. Ann Pharmacother 34, 487–494 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Gale M. Jr. & Foy E. M. Evasion of intracellular host defence by hepatitis C virus. Nature 436, 939–945 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

