(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Enhances Hepatitis C Virus Double-Stranded RNA Intermediates-Triggered Innate Immune Responses in Hepatocytes
- PMID: 26879672
- PMCID: PMC4754899
- DOI: 10.1038/srep21595
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Enhances Hepatitis C Virus Double-Stranded RNA Intermediates-Triggered Innate Immune Responses in Hepatocytes
Abstract
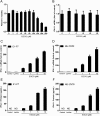
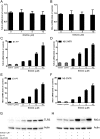
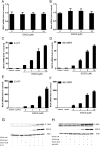
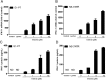
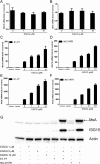
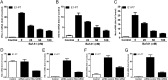
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), a major polyphenol component of green tea, has recently been identified as an inhibitor of hepatitis C virus (HCV) entry. Here, we examined whether EGCG can enhance hepatocyte-mediated intracellular innate immunity against HCV. HCV dsRNAs (Core, E1-P7, NS-3'NTR and NS5A) induced interferon-λ1 (IFN-λ1) expression in human hepatocytes. These HCV dsRNAs also induced the expression of Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3), retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) and several antiviral IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) expression. Although EGCG treatment of hepatocytes alone had little effect on TLR3 and RIG-I signaling pathways, EGCG significantly enhanced HCV dsRNAs-induced the expression of IFN-λ1, TLR3, RIG-I and antiviral ISGs in hepatocytes. Furthermore, treatment of HCV-infected hepatocytes with EGCG and HCV dsRNAs inhibited viral replication. Given that EGCG has the ability to enhance HCV dsRNAs-induced intracellular antiviral innate immunity against HCV, suggesting the potential application of EGCG as a new anti-HCV agent for HCV therapy.
Figures


References
-
- Alter M. J. Prevention of spread of hepatitis C. Hepatology 36, S93–98 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Battaglia A. M. & Hagmeyer K. O. Combination therapy with interferon and ribavirin in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C infection. Ann Pharmacother 34, 487–494 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Gale M. Jr. & Foy E. M. Evasion of intracellular host defence by hepatitis C virus. Nature 436, 939–945 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

