A hypothesis of couplet molecules and couplet cells in gastric function and an association with Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 26879837
- PMCID: PMC4754955
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-016-0429-0
A hypothesis of couplet molecules and couplet cells in gastric function and an association with Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
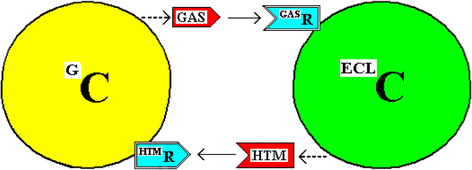
Background: Gastrin, from G-cells, and histamine, from enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells, are two of the hormones that regulate gastric activity.
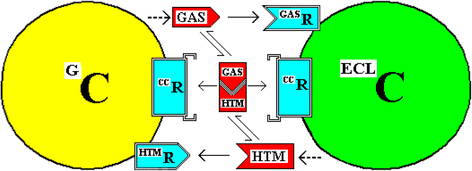
Discussion: It is proposed that the G-cells and the ECL cells are coupled by the couplet molecules gastrin and histamine and by a prior asymmetrical cell division. The gastrin (from G-cells) stimulates the ECL cells to produce and secrete histamine while, in a reciprocal way, this histamine (from ECL cells), stimulates the G-cells to produce and secrete gastrin. These molecules would also stimulate cell division - the gastrin would stimulate cell division of ECL cells while histamine would stimulate that of G-cells. A chemical complex of gastrin and histamine is postulated as is also the asymmetric cell divisions of precursor cells to produce the coupled G-cells and ECL cells.
Conclusion: There is sufficient evidence to support the feasibility of the model in general, but more direct experimental evidence is required to validate the model as applied here to gastric function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide stimulates histamine release and DNA synthesis in rat enterochromaffin-like cells.Gastroenterology. 1997 Oct;113(4):1110-7. doi: 10.1053/gast.1997.v113.pm9322505. Gastroenterology. 1997. PMID: 9322505
-
The vagus regulates histamine mobilization from rat stomach ECL cells by controlling their sensitivity to gastrin.J Physiol. 2005 May 1;564(Pt 3):895-905. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.082677. Epub 2005 Mar 3. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15746169 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric submucosal microdialysis: a method to study gastrin- and food-evoked mobilization of ECL-cell histamine in conscious rats.Regul Pept. 2000 Jan 29;86(1-3):113-23. doi: 10.1016/s0167-0115(99)00096-8. Regul Pept. 2000. PMID: 10672910
-
Physiological significance of ECL-cell histamine.Yale J Biol Med. 1998 May-Aug;71(3-4):183-93. Yale J Biol Med. 1998. PMID: 10461351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship of ECL cells and gastric neoplasia.Yale J Biol Med. 1998 May-Aug;71(3-4):325-35. Yale J Biol Med. 1998. PMID: 10461363 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer Stem Cells in Tumor Microenvironment of Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach, Colon, and Rectum.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 16;14(16):3948. doi: 10.3390/cancers14163948. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36010940 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Craven CJ. Alpha- and beta-cell proliferation and extracellular signaling - a hypothesis. Int J Diabetes Clin Res. 2015;2(2):6.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

