CADA-computer-aided DaTSCAN analysis
- PMID: 26879864
- PMCID: PMC4754234
- DOI: 10.1186/s40658-016-0140-9
CADA-computer-aided DaTSCAN analysis
Abstract
Background: Dopamine transporter (DaT) imaging (DaTSCAN) is useful for the differential diagnosis of parkinsonian syndromes. Visual evaluation of DaTSCAN images represents the generally accepted diagnostic method, but it is strongly dependent on the observer's experience and shows inter- and intra-observer variability. A reliable and automatic method for DaTSCAN evaluation can provide objective quantification; it is desirable for longitudinal studies, and it allows for a better follow-up control. Moreover, it is crucial for an automated method to produce coherent measures related to the severity of motor symptoms.
Methods: In this work, we propose a novel fully automated technique for DaTSCAN analysis that generates quantitative measures based on striatal intensity, shape, symmetry and extent. We tested these measures using a support vector machine (SVM) classifier.
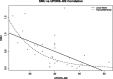
Results: The proposed measures reached 100 % accuracy in distinguishing between patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) and control subjects. We also demonstrate the existence of a linear relationship and an exponential trend between pooled structural and functional striatal characteristics and the Unified Parkinson's disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) motor score.
Conclusions: We present a novel, highly reproducible, user-independent technique for DaTSCAN analysis producing quantitative measures directly connected to striatum uptake and shape. In our method, no a priori assumption is required on the spatial conformation and localization of striatum, and both uptake and symmetry contribute to the index quantification. These measures can reliably support a computer-assisted decision system.
Keywords: Computer-aided diagnosis; DaTSCAN; Parkinson’s disease.
Figures
References
-
- Bhidayasiri R. How useful is (123I) beta-CIT SPECT in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease? Rev Neurol Dis. 2006;3(1):19–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources