Multi-functionalized carbon dots as theranostic nanoagent for gene delivery in lung cancer therapy
- PMID: 26880047
- PMCID: PMC4754752
- DOI: 10.1038/srep21170
Multi-functionalized carbon dots as theranostic nanoagent for gene delivery in lung cancer therapy
Abstract
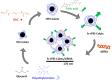
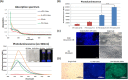
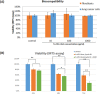
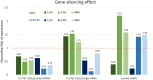
Theranostics, an integrated therapeutic and diagnostic system, can simultaneously monitor the real-time response of therapy. Different imaging modalities can combine with a variety of therapeutic moieties in theranostic nanoagents. In this study, a multi-functionalized, integrated theranostic nanoagent based on folate-conjugated reducible polyethylenimine passivated carbon dots (fc-rPEI-Cdots) is developed and characterized. These nanoagents emit visible blue photoluminescence under 360 nm excitation and can encapsulate multiple siRNAs (EGFR and cyclin B1) followed by releasing them in intracellular reductive environment. In vitro cell culture study demonstrates that fc-rPEI-Cdots is a highly biocompatible material and a good siRNA gene delivery carrier for targeted lung cancer treatment. Moreover, fc-rPEI-Cdots/pooled siRNAs can be selectively accumulated in lung cancer cells through receptor mediated endocytosis, resulting in better gene silencing and anti-cancer effect. Combining bioimaging of carbon dots, stimulus responsive property, gene silencing strategy, and active targeting motif, this multi-functionalized, integrated theranostic nanoagent may provide a useful tool and platform to benefit clinicians adjusting therapeutic strategy and administered drug dosage in real time response by monitoring the effect and tracking the development of carcinomatous tissues in diagnostic and therapeutic aspects.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Folic acid-functionalized polyethylenimine superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as theranostic agents for magnetic resonance imaging and PD-L1 siRNA delivery for gastric cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Jul 26;12:5331-5343. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S137245. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28794626 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering multifunctional bioactive citric acid-based nanovectors for intrinsical targeted tumor imaging and specific siRNA gene delivery in vitro/in vivo.Biomaterials. 2019 Apr;199:10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.01.045. Epub 2019 Feb 2. Biomaterials. 2019. PMID: 30731420
-
Fluorescent carbon dots as an efficient siRNA nanocarrier for its interference therapy in gastric cancer cells.J Nanobiotechnology. 2014 Dec 30;12:58. doi: 10.1186/s12951-014-0058-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2014. PMID: 25547381 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon Dots for In Vivo Bioimaging and Theranostics.Small. 2019 Aug;15(32):e1805087. doi: 10.1002/smll.201805087. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Small. 2019. PMID: 30779301 Review.
-
Multicolorful Carbon Dots for Tumor Theranostics.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(25):2894-2909. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170316110810. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28302015 Review.
Cited by
-
You Don't Learn That in School: An Updated Practical Guide to Carbon Quantum Dots.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Mar 1;11(3):611. doi: 10.3390/nano11030611. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33804394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of carbonization conditions on luminescence and gene delivery properties of nitrogen-doped carbon dots.RSC Adv. 2019 Jan 25;9(6):3493-3502. doi: 10.1039/c8ra09651a. eCollection 2019 Jan 22. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35518969 Free PMC article.
-
A Candidate for Multitopic Probes for Ligand Discovery in Dynamic Combinatorial Chemistry.Molecules. 2019 Jun 8;24(11):2166. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112166. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31181809 Free PMC article.
-
Triple conjugated carbon dots as a nano-drug delivery model for glioblastoma brain tumors.Nanoscale. 2019 Mar 28;11(13):6192-6205. doi: 10.1039/c8nr08970a. Nanoscale. 2019. PMID: 30874284 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon Dots-AS1411 Aptamer Nanoconjugate for Ultrasensitive Spectrofluorometric Detection of Cancer Cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 5;7(1):10513. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11087-2. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28874822 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pesic M. et al. Induced resistance in the human non small cell lung carcinoma (NCI-H460) cell line in vitro by anticancer drugs. J. Chemother. 18(1), 66–73 (2206). - PubMed
-
- Yan Y., Björnmalm M. & Caruso F. Particle carriers for combating multidrug-resistant cancer. ACS Nano 7, 9512–9517 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Xia W. et al. Bioreducible polyethylenimine-delivered siRNA targeting human telomerase reverse transcriptase inhibits HepG2 cell growth in vitro and in vivo. J Control Release 157, 427–436 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Park K. et al. Target specific systemic delivery of TGF-b siRNA/(PEI-SS)-g-HA complex for the treatment of liver cirrhosis. Biomaterials 32, 4951–4958 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

