Time course of pharmacokinetic and hormonal effects of inhaled high-dose salvinorin A in humans
- PMID: 26880225
- PMCID: PMC5289219
- DOI: 10.1177/0269881116629125
Time course of pharmacokinetic and hormonal effects of inhaled high-dose salvinorin A in humans
Abstract
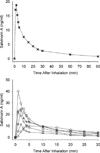
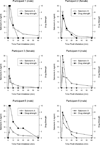
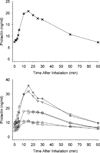
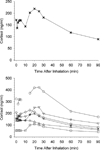
Salvinorin A is a kappa opioid agonist and the principal psychoactive constituent of the Salvia divinorum plant, which has been used for hallucinogenic effects. Previous research on salvinorin A pharmacokinetics likely underestimated plasma levels typically resulting from the doses administered due to inefficient vaporization and not collecting samples during peak drug effects. Six healthy adults inhaled a single high dose of vaporized salvinorin A (n = 4, 21 mcg/kg; n = 2, 18 mcg/kg). Participant- and monitor-rated effects were assessed every 2 min for 60 min post-inhalation. Blood samples were collected at 13 time points up to 90 min post-inhalation. Drug levels peaked at 2 min and then rapidly decreased. Drug levels were significantly, positively correlated with participant and monitor drug effect ratings. Significant elevations in prolactin were observed beginning 5 min post-inhalation and peaking at 15 min post-inhalation. Cortisol showed inconsistent increases across participants. Hormonal responses were not well correlated with drug levels. This is the first study to demonstrate a direct relationship between changes in plasma levels of salvinorin A and drug effects in humans. The results confirm the efficacy of an inhalation technique for salvinorin A.
Keywords: Salvia divinorum; cortisol; endocrine; pharmacokinetics; prolactin; salvinorin A.
© The Author(s) 2016.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial Disclosures All authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Addy PH. Acute and post-acute behavioral and psychological effects of salvinorin A in humans. Psychopharmacology. 2012;220:195–204. - PubMed
-
- Addy PH, Garcia-Romeu A, Metzger M, Wade J. The subjective experience of acute, experimentally-induced Salvia divinorum inebriation. Journal of Psychopharmacology. 2015;29(4):426–435. - PubMed
-
- Baggott MJ, Erowid E, Erowid F, Galloway GP, Mendelson J. Use patterns and self-reported effects of Salvia divinorum: an internet-based survey. Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 2010;111:250–256. - PubMed
-
- Baggott MJ, Erowid E, Erowid F, Mendelson JE. Use of Salvia divinorum, an unscheduled hallucinogenic plant: A web-based survey of 500 users. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2004;75:72.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

