Granulocyte and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factors for newly diagnosed patients with myelodysplastic syndromes
- PMID: 26880256
- PMCID: PMC10405220
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009310.pub2
Granulocyte and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factors for newly diagnosed patients with myelodysplastic syndromes
Abstract
Background: Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are a heterogeneous group of haematological diseases which are characterised by a uni- or multilineage dysplasia of haematological stem cells. Standard treatment is supportive care of the arising symptoms including red blood cell transfusions or the administration of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) in the case of anaemia or the treatment with granulocyte (G-CSF) and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factors (GM-CSF) in cases of neutropenia.
Objectives: The objective of this review is to assess the evidence for the treatment of patients with MDS with G-CSF and GM-CSF in addition to standard therapy in comparison to the same standard therapy or the same standard therapy and placebo.
Search methods: We searched MEDLINE (from 1950 to 3 December 2015) and CENTRAL (Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials until 3 December 2015), as well as conference proceedings (American Society of Hematology, American Society of Clinical Oncology, European Hematology Association, European Society of Medical Oncology) for randomised controlled trials (RCTs). Two review authors independently screened search results.
Selection criteria: We included RCTs examining G-CSF or GM-CSF in addition to standard therapy in patients with newly diagnosed MDS.
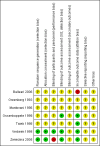
Data collection and analysis: We used hazard ratios (HR) as effect measure for overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS) and time to progression, and risk ratios for response rates, adverse events, antibiotic use and hospitalisation. Two independent review authors extracted data and assessed risk of bias. Investigators of two trials were contacted for subgroup information, however, no further data were provided. G-CSF and GM-CSF were analysed separately.
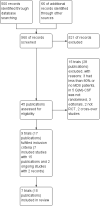
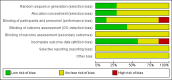
Main results: We screened a total of 566 records. Seven RCTs involving 486 patients were identified, but we could only meta-analyse the two evaluating GM-CSF. We judged the potential risk of bias of these trials as unclear, mostly due to missing information. All trials were randomised and open-label studies. However, three trials were published as abstracts only, therefore we were not able to assess the potential risk of bias for these trials in detail. Overall, data were not reported in a comparable way and patient-related outcomes like survival, time to progression to acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) or the incidence of infections was reported in two trials only.Five RCTs (N = 337) assessed the efficacy of G-CSF in combination with standard therapy (supportive care, chemotherapy or erythropoietin). We were not able to perform meta-analyses for any of the pre-planned outcomes due to inconsistent and insufficient reporting of data. There is no evidence for a difference for overall survival (hazard ratio (HR) 0.80, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.44 to 1.47), progression-free survival (only P value provided), progression to AML, incidence of infections and number of red blood transfusions (average number of 12 red blood cell transfusions in each arm). We judged the quality of evidence for all these outcomes as very low, due to very high imprecision and potential publication bias, as three trials were published as abstracts only. Data about quality of life and serious adverse events were not reported in any of the included trials.Two RCTs (N = 149) evaluated GM-CSF in addition to standard therapy (chemotherapy). For mortality (two RCTs; HR 0.88, 95% CI 0.62 to 1.26), we found no evidence for a difference (low-quality evidence). Data for progression-free survival and serious adverse events were not comparable across both studies, without evidence for a difference between both arms (low-quality evidence). For infections, red blood cell and platelet transfusions, we found no evidence for a difference, however, these outcomes were reported by one trial only (low-quality evidence). Time to progression to AML and quality of life were not reported at all.Moreover, we identified two cross-over trials, including 244 patients and evaluating GM-CSF versus placebo, without publishing results for each arm before crossing over. In addition, we identified two ongoing studies, one of which was discontinued due to withdrawal of pharmaceutical support, the other was terminated early, both without publishing results.
Authors' conclusions: Although we identified seven trials with a total number of 486 patients, and two unpublished, prematurely finished studies, this systematic review mainly shows that there is a substantial lack of data, which might inform the use of G-CSF and GM-CSF for the prevention of infections, prolonging of survival and improvement of quality of life. The impact on progression to AML remains unclear.
Conflict of interest statement
Franz Hutzschenreuter: none known.
Ina Monsef: none known.
Karl‐Anton Kreuzer: Grants, consulting fee or honoraria, support for travel to meetings from: AbbVie, Alexion, Amgen, Ariad, Baxter, Bayer Health Care, Biotest, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Chugai, Gilead, Glaxo‐SmithKline, Grifols, Hexal, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Leo, Mundipharma, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Shire, Teva. None of the above‐mentioned relationships has a direct influence on my activities within the Cochrane group.
Andreas Engert: none known.
Nicole Skoetz: none known.
Figures



















Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009310
Similar articles
-
Prophylactic antibiotics or G(M)-CSF for the prevention of infections and improvement of survival in cancer patients receiving myelotoxic chemotherapy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 21;2015(12):CD007107. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007107.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26687844 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombopoietin mimetics for patients with myelodysplastic syndromes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 30;9(9):CD009883. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009883.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28962071 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of first-line chemotherapy including escalated BEACOPP versus chemotherapy including ABVD for people with early unfavourable or advanced stage Hodgkin lymphoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 25;5(5):CD007941. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007941.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28541603 Free PMC article.
-
Optimisation of chemotherapy and radiotherapy for untreated Hodgkin lymphoma patients with respect to second malignant neoplasms, overall and progression-free survival: individual participant data analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 13;9(9):CD008814. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008814.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28901021 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Infections in Myelodysplastic Syndrome in Relation to Stage and Therapy.Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2018 Jul 1;10(1):e2018039. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2018.039. eCollection 2018. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30002795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deregulation of New Cell Death Mechanisms in Leukemia.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 25;16(9):1657. doi: 10.3390/cancers16091657. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38730609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired formation of neutrophil extracellular traps in patients with MDS.Blood Adv. 2022 Jan 11;6(1):129-137. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021005721. Blood Adv. 2022. PMID: 34653237 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Patients with Lower-Risk Myelodysplastic Neoplasms (MDS).Curr Oncol. 2023 Jun 27;30(7):6177-6196. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30070459. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37504319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of low-risk myelodysplastic syndromes.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2016 Dec 2;2016(1):462-469. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2016.1.462. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2016. PMID: 27913517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
References to studies included in this review
Balleari 2006 {published data only}
-
- Balleari E, Rossi E, Clavio M, Congiu A, Gobbi M, Grosso M, et al. Erythropoietin plus granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor is better than erythropoietin alone to treat anemia in low‐risk myelodysplastic syndromes: results from a randomized single‐centre study. Annals of Hematology 2006;85(3):174‐80. - PubMed
Greenberg 1993 {published data only}
-
- Greenberg P, Taylor K, Lardon R, Koeffler P, Negrin R, Saba H, et al. Phase III randomized multicenter trial of G‐CSF vs. observation for myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Blood 1993;Suppl:196a.
Mantovani 1996 {published data only}
-
- Mantovani L, Lentini G, Hentschel B, Ko Y D, Tesch H, Wickramanayake P, et al. Long term treatment of intermediate risk myelodysplastic syndromes with rhG‐CSF and rhEPO: interim report of an ongoing randomized phase III trial. Annals of Hematology 1996;73(Suppl 2):A28.
Ossenkoppele 1999 {published data only}
-
- Ossenkoppele GJ, Verhoef GE, Holt B, Verdonck LF, Vellenga E, Sonneveld P, et al. Randomized Phase II study on the value of G‐CSF (Filgrastim) in combination with standard induction chemotherapy in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Blood 1995;86(10 Suppl 1):338a.
-
- Ossenkoppele GJ, Holt B, Verhoef GE, Daenen SM, Verdonck LF, Sonneveld P, et al. A randomized study of granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor applied during and after chemotherapy in patients with poor risk myelodysplastic syndromes: a report from the HOVON Cooperative Group. Dutch‐Belgian Hemato‐Oncology Cooperative Group. Leukemia 1999;13(8):1207‐13. - PubMed
-
- Ossenkoppele GJ, Holt B, Verhoef GE, Daenen SM, Verdonck LF, Sonneveld P, et al. A randomized study of granulocyte‐colony stimulating factor applied during and after chemotherapy in patients with poor risk myelodysplastic syndromes: A final report from the HOVON Co‐operative Group. Blood 1998;92(10 Suppl 1 Pt 1):630‐1a. - PubMed
Taieb 1998 {published data only}
-
- Taieb O, Chevret S, Fenaux P, Guerci A, Bordessoule D, Solary E, et al. Evaluation of lenograstim in patients with poor prognosis refractory anaemia with excess of blasts (RAEB) treated with ARA‐C(3mg/m2 x 2). Blood 1998;92(10 Suppl 1 Pt 1):633a.
Verbeek 1999 {published data only}
-
- Hiddemann W, Buchner T, Wormann B, Koch P, Aul C, Balleisen L, et al. Treatment of high‐risk myelodysplastic syndromes with sequential intermediate dose cytosine‐arabinoside and mitoxantrone (S‐HAM) with or without GM‐CSF: a prospective double blinded randomized study. Annals of Hematology 1993;67(Suppl):A51.
-
- Hiddemann W, Buchner Th, Wormann B, Koch P, Aul C, Balleisen L, et al. Intensive therapy of high risk myelodysplastic syndromes with sequential intermediate dose cytosine arabinoside and mitoxantrone with or without GM‐CSF. Annals of Hematology 1995;70 Suppl 1:A109.
-
- Verbeek W, Wormann B, Koch P, Aul C, Hinrichs H F, Balleisen L, et al. Results of a randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial evaluating sequential high‐dose cytosine arabinoside/mitoxantrone chemotherapy with or without granulocyte/macrophage‐colony‐stimulating factor in high‐risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Research & Clinical Oncology 1999;125(6):369‐74. - PubMed
-
- Verbeek W, Wormann B, Koch P, Aul C, Hinrichs H, Balleisen L, et al. S‐HAM induction chemotherapy with or without GM‐CSF in patients with high‐risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Annals of Hematology 1997;74(5):205‐8. - PubMed
Zwierzina 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gerhartz HH, Walther J, Neuwirtova R, Fenaux P, Harousseau JL, Beksac M. Randomized‐3 armed phase III study of interleukin 3 (IL‐3) or granulocyte/macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (GM‐CSF) as an adjuvant to low doses of cytosine arabinoside (LD‐AraC) for the treatment of high‐risk myelodysplastic syndromes (HR‐MDS). Blood 1996;88(10):580a.
-
- Gerhartz HH, Zwierzina H, Suciu S, Walther J, Dardenne M, Neuwirtova R, et al. Randomized 3 arm phase III study of interleukin 3 (IL‐3) or granulocyte/macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (GM‐CSF) as an adjuvant to low doses of cytosine arabinoside (LD‐AraC) for the treatment of high‐risk myelodysplastic syndrome (HR‐MDS). Blood 1997;90(10 Suppl 1 Pt 1):85a.
-
- Schmetzer HM, Poleck B, Mittermuller J, Duell T, Wilmanns W, Gerhartz HH. Clonality analysis as a tool to study the biology and response to therapy in myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 1997;11(5):660‐6. - PubMed
-
- Zwierzina H, Suciu S, Loeffler‐Ragg J, Neuwirtova R, Fenaux P, Beksac M, et al. Low‐dose cytosine arabinoside (LD‐AraC) vs LD‐AraC plus granulocyte/macrophage colony stimulating factor vs LD‐AraC plus Interleukin‐3 for myelodysplastic syndrome patients with a high risk of developing acute leukemia: final results of a randomized phase III study (06903) of the EORTC Leukemia Cooperative Group. Leukemia 2005;19(11):1929‐33. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Bernasconi 1998 {published data only}
-
- Bernasconi C, Alessandrino EP, Bernasconi P, Bonfichi M, Lazzarino M, Canevari A, et al. Randomized clinical study comparing aggressive chemotherapy with or without G‐CSF support for high‐risk myelodysplastic syndromes or secondary acute myeloid leukaemia evolving from MDS. British Journal of Haematology 1998;102(3):678‐83. - PubMed
Bowen 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bowen D, Hyslop A, Keenan N, Groves M, Culligan D, Johnson P, et al. Prediction of response to recombinant erythropoietin plus granulocyte‐colony stimulating factor following a single subcutaneous bolus in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes; a randomised placebo controlled study. Blood 2004; Vol. 104:402a.
Bowen 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bowen D, Hyslop A, Keenan N, Groves M, Culligan D, Johnson P, et al. Predicting erythroid response to recombinant erythropoietin plus granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor therapy following a single subcutaneous bolus in patients with myelodysplasia. Haematologica 2006;91:709‐10. - PubMed
Estey 1999 {published data only}
-
- Estey EH, Thall PF, Pierce S, Cortes J, Beran M, Kantarjian H, et al. Randomized phase II study of fludarabine + cytosine arabinoside + idarubicin +/‐ all‐trans retinoic acid +/‐ granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor in poor prognosis newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 1999;93(8):2478‐84. - PubMed
Gerhartz 1994 {published data only}
-
- Gerhartz HH. Randomized phase II study LD‐ARAC plus rhGM‐CSF in advanced myelodysplasia [abstract no: 249]. European Journal of Cancer 1993;29A:S51.
-
- Gerhartz HH, Delmer A, Jacobs A, Zwierzina H, Ribeiro M, Lowenberg B, et al. Randomized phase II trial of low‐dose ARA‐C and human recombinant GM‐CSF in refractory anemia with excess of blasts. Blut 1989;59:255.
-
- Gerhartz HH, Marcus R, Delmer A, Zwierzina H, Suciu S, Dardenne M, et al. A randomized phase II study of low‐dose cytosine arabinoside (LD‐AraC) plus granulocyte‐macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (rhGM‐CSF) in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) with a high risk of developing leukemia. EORTC Leukemia Cooperative Group. Leukemia 1994;8:16‐23. - PubMed
-
- Gerhartz HH, Marcus R, Delmer A, Zwierzina H, Witte T, Jacobs A. Randomized phase II study with GM‐CSF and low‐dose Ara‐C in patients with "high risk" myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Blood 1990;76:274a.
-
- Gerhartz HH, Marcus R, Delmer A, Zwierzina H, Witte T, Jacobs A, et al. Randomized phase II study with GM‐CSF and low‐dose ARAC in patients with "high risk" myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Annals of Hematology 1991;62 Suppl 1:A95.
Gotlib 2009 {published data only}
Greenberg 2009 {published data only}
-
- Greenberg PL, Sun Z, Miller KB, Bennett JM, Tallman MS, Dewald G, et al. Treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome patients with erythropoietin with or without granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor: results of a prospective randomized phase 3 trial by the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (E1996). Blood 2009;114:2393‐400. - PMC - PubMed
Hast 2003 {published data only}
-
- Bernell P, Hast R, Hellstrom Lindberg E, Celsing F, Linder O, Lafvenberg E, et al. GM‐CSF in combination with chemotherapy does not improve the remission rate in acute leukaemia after myelodysplastic syndromes ‐ A randomized study. Blood 1998;92(10 Suppl 1 Pt 1):615a.
-
- Hast R, Hellstrom‐Lindberg E, Ohm L, Bjorkholm M, Celsing F, Dahl IM, et al. No benefit from adding GM‐CSF to induction chemotherapy in transforming myelodysplastic syndromes: better outcome in patients with less proliferative disease. Leukemia 2003;17(9):1827‐33. - PubMed
-
- Ohm AC, Hast R, Bernell P, Celsing F, Dahl IM, Dybedal I. Randomized study comparing chemotherapy plus GM‐CSF in high‐risk MDS and AML following MDS (MDS‐AML). Blood 2000;96(11):148a.
Miller 1998 {published data only}
-
- Miller K. Erythropoietin, with and without granulocyte‐colony stimulating factor (G‐CSF), in the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) patients. [Review] [16 refs]. Leukemia Research 1998;22:Suppl‐6. - PubMed
Schuster 1989 {published data only}
-
- Schuster MW, Allen SL, Lichtman SM, Schulman P, DeMarco LC, Budman DR, et al. The efficacy of GM‐CSF in the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome and aplastic anemia. Blood 1989;74(7 Suppl 1):332a.
-
- Schuster MW, Thompson JA, Larson R, Allen SL, O'Laughlin R, Israel R, et al. Randomized trial of subcutaneous granulocyte‐macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (GM‐CSF) versus observation in patients (PTS) with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) or aplastic anemia (AA) [abstract]. Journal of Clinical Oncology 1990;9:205, Abstract.
-
- Schuster, MW, Thompson JA, Larson, R, Allen SL, O'Laughlin R, Israel R, et al. Randomized trial of subcutaneous granulocyte‐macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (GM‐CSF) versus observation in patients (PTS) with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) or aplastic anemia (AA) [abstract]. Journal of Cancer Research & Clinical Oncology 1990; Vol. 116(Suppl):1079.
Schuster 1995 {published data only}
-
- Coiffier B, Bastion Y, Felman P, Tigaud JD, Bryon PA. GM‐CSF treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes: personal experience and preliminary results of a randomized international study. Pathologie Biologie 1992;39(9):957‐8. - PubMed
-
- Schuster MW, Larson RA, Thompson JA, Coiffier B, Bennett JM, Israel RJ. Granulocyte‐macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (GM‐CSF) for myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS): results of a multi‐center randomized controlled trial. Blood 1990;76(10 Suppl 1):318a.
-
- Schuster MW, Thompson JA, Larson R, Coiffier V, Bennett J, Dugan M. Randomized Phase II study of recombinant granulocyte macrophage‐colony stimulating factor (rGM‐CSF) in patients with neutropenia secondary to myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Blood 1995;86(10 Suppl 1):338a.
Stasi 2004 {published data only}
-
- Stasi R, Amadori S, Newland AC, Provan D. Comparison of rHuEpo plus rHuG‐CSF and supportive care: apples to oranges. Blood 2004;104:2201‐2. - PubMed
Terpos 2000 {published data only}
-
- Terpos E, Mougiou A, Stavroyianni N, Kouraklis A, Giannakoulas N, Zoumbos NC. Treatment of anemia in myelodysplastic syndromes with prolonged administration of erythropoietin or erythropoietin and granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor. Blood 2000;96:147a.
Thompson 1995 {published data only}
-
- Thompson J, Gilliland G, Prchal J, Bennett J, Larholt K, Nelson R, et al. The use of GM‐CSF ± r‐HuEPO for the treatment of cytopenias associated with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) [he use of GM‐CSF ± r‐HuEPO for the treatment of cytopenias associated with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS).]. Blood 1995;86(10 Suppl 1):337a, Abstract 1337.
Willemze 1992 {published data only}
-
- Willemze R, Lely N, Zwierzina H, Gerhartz H, Suciu S, Solbu G, et al. GM‐CSF and IL‐3 in myelodysplastic syndromes at low risk of developing acute leukemia (MDS‐LR) [abstract]. Leukemia & Lymphoma 1992;7 Suppl 2:64.
References to ongoing studies
04/Q1907/94 {published data only}
-
- Erythropoietin and GCSF for lowrisk MDS (NCT00234143). Ongoing study October 2004.
REGIME {published data only}
-
- Comparison study of standard care against combination of growth factors agents for low‐risk MDS (NCT01196715). Ongoing study November 2010.
Additional references
Beekman 2010
-
- Beekman R, Touw IP. G‐CSF and its receptor in myeloid malignancy. Blood 2010;115(25):5131‐6. - PubMed
Bernasconi 1998a
-
- Bernasconi C, Alessandrino EP, Bernasconi P, Bonfichi M, Lazzarino M, Canevari A. Randomized clinical study comparing aggressive chemotherapy with or without G‐CSF support for high‐risk myelodysplastic syndromes or secondary acute myeloid leukaemia evolving from MDS. British Journal of Haematology 1998;102:678‐83. - PubMed
Bohlius 2003
-
- Bohlius J, Reiser M, Schwarzer G, Engert A. Impact of granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor (CSF) and granulocyte‐macrophage CSF in patients with malignant lymphoma: a systematic review. British Journal of Haematology 2003;122(3):413‐23. - PubMed
Bowen 2003
-
- Bowen D, Culligan D, Jowitt S, Kelsey S, Mufti G, Oscier D, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and therapy of adult myelodysplastic syndromes. British Journal of Haematology 2003;120(2):187‐200. - PubMed
Buckstein 2011
-
- Buckstein R, Yee K, Wells RA. 5‐Azacytidine in myelodysplastic syndromes: A clinical practice guideline. Cancer Treatment Reviews 2011;37:160‐7. - PubMed
Casadevall 2004
-
- Casadevall N, Durieux P, Dubois S, Hemery F, Lepage E, Quarré MC, et al. for the Groupe Français des Myélodysplasies. Health, economic, and quality‐of‐life effects of erythropoietin and granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes: a randomized, controlled trial. Blood 2004;104:321‐7. - PubMed
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org, 2011.
Economopoulos 1999
-
- Economopoulos T, Mellou S, Papageorgiou E, Pappa V, Kokkinou V, Stathopoulou E. Treatment of anemia in low risk myelodysplastic syndromes with granulocyte‐macrophage colony‐stimulating factor plus recombinant human erythropoietin. Leukemia 1999;13:1009‐12. - PubMed
Ferrini 1998
-
- Ferrini PR, Grossi A, Vannucchi AM, Barosi G, Guarnone R, Piva N, et al. A randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled study with subcutaneous recombinant human erythropoietin in patients with low‐risk myelodysplastic syndromes. British Journal of Haematology 1998;103(4):1070‐4. - PubMed
Fey 2010
-
- Fey MF, Dreyling M. Acute myeloblastic leukaemias and myelodysplastic syndromes in adult patients: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow‐up. Annals of Oncology 2010;21 Suppl 5:158‐61. - PubMed
Gerhartz 1992a
-
- Gerhartz HH, Marcus R, Delmer A, Zwierzina H, Witte T, Jacobs A, et al. Treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and high leukaemic risk with low‐dose cytosine arabinoside (LD‐AraC) plus granulocyte‐macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (rh GM‐CSF). The EORTC Leukaemia Group. Infection 1992; Vol. 20 Suppl 2:116‐23. - PubMed
Gerhartz 1994a
-
- Gerhartz HH, Marcus R, Delmer A, Zwierzina H, Suciu S, Dardenne M, et al. A randomized phase II study of low‐dose cytosine arabinoside (LD‐AraC) plus granulocyte‐macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (rhGM‐CSF) in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) with a high risk of developing leukemia. EORTC Leukemia Cooperative Group. Leukemia 1994; Vol. 8, issue 1:16‐23. - PubMed
Gotze 2010
-
- Gotze K, Platzbecker U, Giagounidis A, Haase D, Lubbert M, Aul C, et al. Azacitidine for treatment of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS): practical recommendations of the German MDS Study Group. Annals of Hematology 2010;89:841‐50. - PubMed
Greenberg 1997
-
- Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G, et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997;89(6):2079‐88. - PubMed
Hansen 1993
-
- Hansen PB, Johnsen HE, Hippe E, Hellstrom‐Lindberg E, Ralfkiaer E. Recombinant human granulocyte‐macrophage colony‐stimulating factor plus recombinant human erythropoietin may improve anemia in selected patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. American Journal of Hematology 1993;44:229‐36. - PubMed
Hellstrom‐Lindberg 1995
-
- Hellstrom‐Lindberg E. Efficacy of erythropoietin in the myelodysplastic syndromes: a meta‐analysis of 205 patients from 17 studies. British Journal of Haematology 1995;89(1):67‐71. - PubMed
Hellstrom‐Lindberg 1997
-
- Hellstrom‐Lindberg E, Negrin R, Stein R, Krantz S, Lindberg G, Vardiman J, et al. Erythroid response to treatment with G‐CSF plus erythropoietin for the anaemia of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: proposal for a predictive model. British Journal of Haematology 1997;99(2):344‐51. - PubMed
Hellstrom‐Lindberg 1998
-
- Hellstrom‐Lindberg E, Ahlgren T, Beguin Y, Carlsson M, Carneskog J, Dahl IM, et al. Treatment of anemia in myelodysplastic syndromes with granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor plus erythropoietin: results from a randomized phase II study and long‐term follow‐up of 71 patients. Blood 1998;92(1):68‐75. - PubMed
Hellström‐Lindberg 2003
-
- Hellström‐Lindberg E, Gulbrandsen N, Lindberg G, Ahlgren T, Dahl IM, Dybedal I, et al. Scandinavian MDS Group. A validated decision model for treating the anaemia of myelodysplastic syndromes with erythropoietin + granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor: significant effects on quality of life. British Journal of Haematology 2003; Vol. 120(6):1037‐46. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org, 2011.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ. Chapter 7: Selecting studies and collecting data. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org, 2011.
Higgins 2011c
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org, 2011.
Jadersten 2008
-
- Jadersten M, Malcovati L, Dybedal I, Della Porta MG, Invernizzi R, Montgomery SM, et al. Erythropoietin and granulocyte‐colony stimulating factor treatment associated with improved survival in myelodysplastic syndrome. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2008;26(21):3607‐13. - PubMed
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org, 2011.
Lieschke 1992
-
- Lieschke GJ, Burgess AW. Granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor and granulocyte‐macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (1). New England Journal of Medicine 1992;327:28‐35. - PubMed
Lieschke 1994
-
- Lieschke GJ, Grail D, Hodgson G, Metcalf D, Stanley E, Cheers C, et al. Mice lacking granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor have chronic neutropenia, granulocyte and macrophage progenitor cell deficiency, and impaired neutrophil mobilization. Blood 1994;84(6):1737‐46. - PubMed
Mantovani 2000
-
- Mantovani L, Lentini G, Hentschel B, Wickramanayake PD, Loeffler M, Diehl V. Treatment of anaemia in myelodysplastic syndromes with prolonged administration of recombinant human granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor and erythropoietin. British Journal of Haematology 2000;109:367‐75. - PubMed
Moher 2009
-
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta‐Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2009;62(10):1006‐12. - PubMed
Mundle 2009
-
- Mundle S, Lefebvre P, Vekeman F, Duh MS, Rastogi R, Moyo V. An assessment of erythroid response to epoetin alpha as a single agent versus in combination with granulocyte‐ or granulocyte‐macrophage‐colony‐stimulating factor in myelodysplastic syndromes using a meta‐analysis approach. Cancer 2009;115(4):706‐15. - PubMed
NCCN 2012
-
- Greenberg PL, Attar E, Battiwalla M, Bennett JM, Bloomfield CD, DeCastro CM, et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes. NCCN clinical practice guidlines in oncology.V.1.2012. www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/mds.pdf.
Negrin 1996
-
- Negrin RS, Stein R, Doherty K, Cornwell J, Vardiman J, Krantz S, et al. Maintenance treatment of the anemia of myelodysplastic syndromes with recombinant human granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor and erythropoietin: evidence for in vivo synergy. Blood 1996;87(10):4076‐81. - PubMed
O'Connor 2011
-
- O'Connor D, Green S, Higgins JPT. Chapter 5: Defining the review question and developing criteria for including studies. In: Higgins JPT Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org, 2011.
Ossenkoppele 1999a
-
- Ossenkoppele GJ, Holt B, Verhoef GE, Daenen SM, Verdonck LF, Sonneveld P, et al. A randomized study of granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor applied during and after chemotherapy in patients with poor risk myelodysplastic syndromes: a report from the HOVON Cooperative Group. Dutch‐Belgian Hemato‐Oncology Cooperative Group. Leukemia 1999; Vol. 13, issue 8:1207‐13. - PubMed
Park 2008
-
- Park S, Grabar S, Kelaidi C, Beyne‐Rauzy O, Picard F, Bardet V, et al. GFM group (Groupe Francophone des Myélodysplasies). Predictive factors of response and survival in myelodysplastic syndrome treated with erythropoietin and G‐CSF: the GFM experience. Blood 2008;111(2):574‐82. - PubMed
Parmar 1998
-
- Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L. Extracting summary statistics to perform meta‐analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Statistics in Medicine 1998;17(24):2815‐34. - PubMed
Rapoport 1992
-
- Rapoport AP, Abboud CN, DiPersio JF. Granulocyte‐macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (GM‐CSF) and granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor (G‐CSF): receptor biology, signal transduction, and neutrophil activation. Blood Reviews 1992;6(1):43‐57. - PubMed
RevMan 5.3 [Computer program]
-
- Cochrane. Review Manager (RevMan) Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre: Cochrane, 2014.
Santini 2010
-
- Santini V, Alessandrino PE, Angelucci E, Barosi G, Billio A, Maio M, et al. Clinical management of myelodysplastic syndromes: update of SIE, SIES, GITMO practice guidelines. Leukemia Research 2010;34:1576‐88. - PubMed
Schuster 1995a
-
- Schuster MW, Thompson JA, Larson R, Coiffier V, Bennett J, Dugan M, et al. Randomized phase II study of recombinant granulocyte macrophage‐colony stimulating factor (rGM‐CSF) in patients with neutropenia secondary to myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Blood, Abstract 1341. 1995:338a.
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org, 2011.
Scott 2008
SEER 2010
-
- Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Krapcho M, Neyman N, Aminou R, Waldron W, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review , 1975‐2007, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD. http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2007/, based on November 2009 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER website 2010.
Smith 2006
-
- Smith TJ, Khatcheressian J, Lyman GH, Ozer H, Armitage JO, Balducci L, et al. 2006 update of recommendations for the use of white blood cell growth factors: an evidence‐based clinical practice guideline. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2006;24(19):3187‐205. - PubMed
Steensma 2006
-
- Steensma DP, Bennett JM. The myelodysplastic syndromes: diagnosis and treatment. Mayo Clinic proceedings. Mayo Clinic 2006;81(1):104‐30. - PubMed
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Moher D. Chapter 10: Addressing reporting biases. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org, 2011.
Tefferi 2009
-
- Tefferi A, Vardiman JW. Myelodysplastic syndromes. New England Journal of Medicine 2009;361(19):1872‐85. - PubMed
Tierney 2007
Vardiman 2008
-
- Vardiman JW, Brunning RD, Arber DA, et al. Introduction and overview of the classification of myeloid neoplasms. In: Swerdlow, SH, Campo, E, Harris, NL, et al. editor(s). WHO classification of tumors of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4. WHO Press, 2008:18.
Verbeek 1999a
-
- Verbeek W, Wörmann B, Koch P, Aul C, Hinrichs HF, Balleisen L, et al. Results of a randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial evaluating sequential high‐dose cytosine arabinoside/mitoxantrone chemotherapy with or without granulocyte/macrophage‐colony‐stimulating factor in high‐risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology 1999; Vol. 6:369‐74. - PubMed
Williamson 1989
Zwierzina 2005a
-
- Zwierzina H, Suciu S, Loeffler‐Ragg J, Neuwirtova R, Fenaux P, Beksac M, et al. Low‐dose cytosine arabinoside (LD‐AraC) vs LD‐AraC plus granulocyte/macrophage colony stimulating factor vs LD‐AraC plus Interleukin‐3 for myelodysplastic syndrome patients with a high risk of developing acute leukemia: final results of a randomized phase III study (06903) of the EORTC Leukemia Cooperative Group. Leukemia 2005; Vol. 19, issue 11:1929‐33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

