Requirement of interleukin 7 signaling for anti-tumor immune response under lymphopenic conditions in a murine lung carcinoma model
- PMID: 26880265
- PMCID: PMC11028809
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-016-1808-7
Requirement of interleukin 7 signaling for anti-tumor immune response under lymphopenic conditions in a murine lung carcinoma model
Abstract
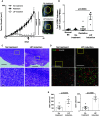
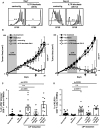
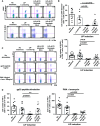
Induction of lymphopenia before adoptive transfer of T cells was followed by lymphopenia-induced proliferation (LIP) and generated a potent anti-tumor immune response in rodents and in a clinical setting. Previously, we reported that CD28 signaling is essential for the differentiation of functional effector cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) under lymphopenic conditions and sequential LIP of T cells. In this study, to clarify the correlation between LIP and the anti-tumor effect, LIP was inhibited with interleukin 7 (IL7) receptor blockade at various stages, and the anti-tumor effect then assessed. We confirmed that IL7 signaling at the start of LIP is crucial for the anti-tumor immune response. In contrast, continuous IL7 signaling was not required for tumor regression, although LIP of naïve CD8+ T cells is usually regulated by IL7. The expansion and migration of CTLs in lymphopenic hosts depend on IL7 signaling during the induction phase. Here, we propose that IL7 signaling and subsequent LIP of T cells have distinct roles in the induction of T cell immunity during lymphopenia.
Keywords: Anti-tumor immune response; CD28; Interleukin 7; Lymphopenia-induced proliferation; Priming and induction of CTLs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
IL7-Fc Enhances the Efficacy of Adoptive T Cell Therapy under Lymphopenic Conditions in a Murine Melanoma Model.Cells. 2021 Aug 7;10(8):2018. doi: 10.3390/cells10082018. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440787 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated IL-7 availability does not account for T cell proliferation in moderate lymphopenia.J Immunol. 2011 Feb 15;186(4):1981-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002224. Epub 2011 Jan 14. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21239710
-
IL-18 synergizes with IL-7 to drive slow proliferation of naive CD8 T cells by costimulating self-peptide-mediated TCR signals.J Immunol. 2014 Oct 15;193(8):3992-4001. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400396. Epub 2014 Sep 8. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25200954 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the biology of IL-7 for therapeutic application.Nat Rev Immunol. 2011 May;11(5):330-42. doi: 10.1038/nri2970. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21508983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine signals in T-cell homeostasis.J Immunother. 2005 Jul-Aug;28(4):289-94. doi: 10.1097/01.cji.0000165356.03924.e7. J Immunother. 2005. PMID: 16000945 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of antigen-prediction algorithm for personalized neoantigen vaccine using human leukocyte antigen transgenic mouse.Cancer Sci. 2022 Apr;113(4):1113-1124. doi: 10.1111/cas.15291. Epub 2022 Mar 2. Cancer Sci. 2022. PMID: 35122353 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-infiltrating CD62L+PD-1-CD8 T cells retain proliferative potential via Bcl6 expression and replenish effector T cells within the tumor.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 26;15(8):e0237646. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237646. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32845913 Free PMC article.
-
Combining all-trans retinoid acid treatment targeting myeloid-derived suppressive cells with cryo-thermal therapy enhances antitumor immunity in breast cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 1;13:1016776. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1016776. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389684 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotherapy and immunotherapy: A close interplay to fight cancer?Oncoimmunology. 2016 Jun 21;5(7):e1190061. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1190061. eCollection 2016 Jul. Oncoimmunology. 2016. PMID: 27622046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic polymorphisms in IL-7 and IL-7R are correlated with lung cancer risk in the Chinese Han population.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Jun 11;11:5393-5401. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S202839. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31354347 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

