Dynamic changes in protein interaction between AKAP95 and Cx43 during cell cycle progression of A549 cells
- PMID: 26880274
- PMCID: PMC4754773
- DOI: 10.1038/srep21224
Dynamic changes in protein interaction between AKAP95 and Cx43 during cell cycle progression of A549 cells
Abstract
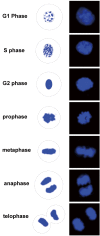
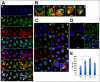
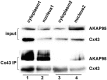
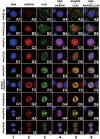
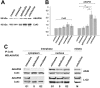
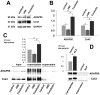
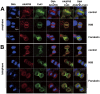
Here we show that A-kinase anchoring protein 95 (AKAP95) and connexin 43 (Cx43) dynamically interact during cell cycle progression of lung cancer A549 cells. Interaction between AKAP95 and Cx43 at different cell cycle phases was examined by tandem mass spectrometry(MS/MS), confocal immunofluorescence microscopy, Western blot, and co-immunoprecipitation(Co-IP). Over the course of a complete cell cycle, interaction between AKAP95 and Cx43 occurred in two stages: binding stage from late G1 to metaphase, and separating stage from anaphase to late G1. The binding stage was further subdivided into complex binding to DNA in interphase and complex separating from DNA in metaphase. In late G1, Cx43 translocated to the nucleus via AKAP95; in anaphase, Cx43 separated from AKAP95 and aggregated between two daughter nuclei. In telophase, Cx43 aggregated at the membrane of the cleavage furrow. After mitosis, Cx43 was absent from the furrow membrane and was located in the cytoplasm. Binding between AKAP95 and Cx43 was reduced by N-(2-[P-Bromocinnamylamino]-ethyl)-5-isoquinolinesulfonmide (H89) treatment and enhanced by Forskolin. dynamic interaction between AKAP95 and Cx43 varies with cell cycle progression to regulate multiple biological processes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cx43 and AKAP95 regulate G1/S conversion by competitively binding to cyclin E1/E2 in lung cancer cells.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Jun;11(6):1594-1602. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13435. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32338437 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning, chromosomal localization, and cell cycle-dependent subcellular distribution of the A-kinase anchoring protein, AKAP95.Exp Cell Res. 1998 Feb 1;238(2):305-16. doi: 10.1006/excr.1997.3855. Exp Cell Res. 1998. PMID: 9473338
-
AKAP95 regulates ubiquitination and degradation of cyclin Ds/Es, influencing the G1/S transition of lung cancer cells.Mol Carcinog. 2024 Oct;63(10):1907-1921. doi: 10.1002/mc.23781. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Mol Carcinog. 2024. PMID: 38923703
-
[Expression of A-kinase anchor protein 95, cyclin E2, and connexin 43 in lung cancer tissue, clinical significance of their expression, and their expression correlation].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2012 Oct;30(10):725-9. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23256994 Chinese.
-
Roles of Cx43 and AKAP95 in ovarian cancer tissues in G1/S phase.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Nov 1;8(11):14315-24. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26823747 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A unique biomimetic modification endows polyetherketoneketone scaffold with osteoinductivity by activating cAMP/PKA signaling pathway.Sci Adv. 2022 Oct 7;8(40):eabq7116. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abq7116. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36197987 Free PMC article.
-
Cx43 and AKAP95 regulate G1/S conversion by competitively binding to cyclin E1/E2 in lung cancer cells.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Jun;11(6):1594-1602. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13435. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32338437 Free PMC article.
-
A-Kinase Anchor Protein 95 Is Involved in ERK1/2-Elk-1 Signal Transduction in Colon Cancer.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2023 Jan 14;2023:8242646. doi: 10.1155/2023/8242646. eCollection 2023. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2023. PMID: 36691407 Free PMC article.
-
Shuttling of cellular proteins between the plasma membrane and nucleus (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2022 Jan;25(1):14. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12530. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 34779504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein⁻Protein Interactions with Connexin 43: Regulation and Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 10;19(5):1428. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051428. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29748463 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

