Eosinophil resistance to glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis is mediated by the transcription factor NFIL3
- PMID: 26880402
- PMCID: PMC4769953
- DOI: 10.1007/s10495-016-1226-5
Eosinophil resistance to glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis is mediated by the transcription factor NFIL3
Abstract
The mainstay of asthma therapy, glucocorticoids (GCs) exert their therapeutic effects through the inhibition of inflammatory signaling and induction of eosinophil apoptosis. However, laboratory and clinical observations of GC-resistant asthma suggest that GCs' effects on eosinophil viability may depend on the state of eosinophil activation. In the present study we demonstrate that eosinophils stimulated with IL-5 show impaired pro-apoptotic response to GCs. We sought to determine the contribution of GC-mediated transactivating (TA) and transrepressing (TR) pathways in modulation of activated eosinophils' response to GC by comparing their response to the selective GC receptor (GR) agonist Compound A (CpdA) devoid of TA activity to that upon treatment with Dexamethasone (Dex). IL-5-activated eosinophils showed contrasting responses to CpdA and Dex, as IL-5-treated eosinophils showed no increase in apoptosis compared to cells treated with Dex alone, while CpdA elicited an apoptotic response regardless of IL-5 stimulation. Proteomic analysis revealed that both Nuclear Factor IL-3 (NFIL3) and Map Kinase Phosphatase 1 (MKP1) were inducible by IL-5 and enhanced by Dex; however, CpdA had no effect on NFIL3 and MKP1 expression. We found that inhibiting NFIL3 with specific siRNA or by blocking the IL-5-inducible Pim-1 kinase abrogated the protective effect of IL-5 on Dex-induced apoptosis, indicating crosstalk between IL-5 anti-apoptotic pathways and GR-mediated TA signaling occurring via the NFIL3 molecule. Collectively, these results indicate that (1) GCs' TA pathway may support eosinophil viability in IL-5-stimulated cells through synergistic upregulation of NFIL3; and (2) functional inhibition of IL-5 signaling (anti-Pim1) or the use of selective GR agonists that don't upregulate NFIL3 may be effective strategies for the restoring pro-apoptotic effect of GCs on IL-5-activated eosinophils.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Eosinophils; Glucocorticoid receptor; Signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



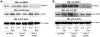
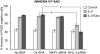

References
-
- Hagan JB, Kita H, Gleich GJ. Inhibition of interleukin-5 mediated eosinophil viability by fluticasone 17-propionate: comparison with other glucocorticoids. Clin Exp Allergy. 1998;28(8):999–1006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

