Nanoscale dynamics of synaptic vesicle trafficking and fusion at the presynaptic active zone
- PMID: 26880547
- PMCID: PMC4786419
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.13245
Nanoscale dynamics of synaptic vesicle trafficking and fusion at the presynaptic active zone
Abstract
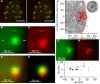
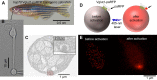
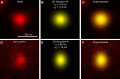
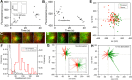
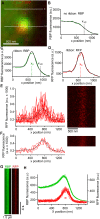
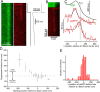
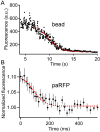
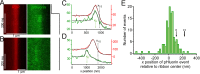
The cytomatrix at the active zone (CAZ) is a macromolecular complex that facilitates the supply of release-ready synaptic vesicles to support neurotransmitter release at synapses. To reveal the dynamics of this supply process in living synapses, we used super-resolution imaging to track single vesicles at voltage-clamped presynaptic terminals of retinal bipolar neurons, whose CAZ contains a specialized structure-the synaptic ribbon-that supports both fast, transient and slow, sustained modes of transmission. We find that the synaptic ribbon serves a dual function as a conduit for diffusion of synaptic vesicles and a platform for vesicles to fuse distal to the plasma membrane itself, via compound fusion. The combination of these functions allows the ribbon-type CAZ to achieve the continuous transmitter release required by synapses of neurons that carry tonic, graded visual signals in the retina.
Keywords: neuroscience; presynaptic mechanisms; retina; synaptic transmission; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Visualizing synaptic vesicle turnover and pool refilling driven by calcium nanodomains at presynaptic active zones of ribbon synapses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jun 10;111(23):8655-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323962111. Epub 2014 May 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24912160 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular organization and assembly of the presynaptic active zone of neurotransmitter release.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006;43:49-68. doi: 10.1007/400_012. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006. PMID: 17068967 Review.
-
Molecular organization of the presynaptic active zone.Cell Tissue Res. 2006 Nov;326(2):379-91. doi: 10.1007/s00441-006-0244-y. Epub 2006 Jul 25. Cell Tissue Res. 2006. PMID: 16865347 Review.
-
Stabilization of spontaneous neurotransmitter release at ribbon synapses by ribbon-specific subtypes of complexin.J Neurosci. 2013 May 8;33(19):8216-26. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1280-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23658160 Free PMC article.
-
Passive diffusion as a mechanism underlying ribbon synapse vesicle release and resupply.J Neurosci. 2014 Jul 2;34(27):8948-62. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1022-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24990916 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Spatial patterns of noise-induced inner hair cell ribbon loss in the mouse mid-cochlea.iScience. 2024 Jan 8;27(2):108825. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.108825. eCollection 2024 Feb 16. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38313060 Free PMC article.
-
Resolving the molecular architecture of the photoreceptor active zone with 3D-MINFLUX.Sci Adv. 2022 Jul 15;8(28):eabl7560. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abl7560. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35857490 Free PMC article.
-
Transmission at rod and cone ribbon synapses in the retina.Pflugers Arch. 2021 Sep;473(9):1469-1491. doi: 10.1007/s00424-021-02548-9. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Pflugers Arch. 2021. PMID: 33779813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into cochlear sound encoding.F1000Res. 2016 Aug 26;5:F1000 Faculty Rev-2081. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.8924.1. eCollection 2016. F1000Res. 2016. PMID: 27635230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resting and stimulated mouse rod photoreceptors show distinct patterns of vesicle release at ribbon synapses.J Gen Physiol. 2020 Dec 7;152(12):e202012716. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202012716. J Gen Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33175961 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

