Safety and efficacy of insulin glargine 300 u/mL compared with other basal insulin therapies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a network meta-analysis
- PMID: 26880669
- PMCID: PMC4762107
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009421
Safety and efficacy of insulin glargine 300 u/mL compared with other basal insulin therapies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a network meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To compare the efficacy and safety of a concentrated formulation of insulin glargine (Gla-300) with other basal insulin therapies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
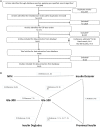
Design: This was a network meta-analysis (NMA) of randomised clinical trials of basal insulin therapy in T2DM identified via a systematic literature review of Cochrane library databases, MEDLINE and MEDLINE In-Process, EMBASE and PsycINFO.
Outcome measures: Changes in HbA1c (%) and body weight, and rates of nocturnal and documented symptomatic hypoglycaemia were assessed.
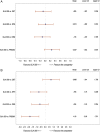
Results: 41 studies were included; 25 studies comprised the main analysis population: patients on basal insulin-supported oral therapy (BOT). Change in glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) was comparable between Gla-300 and detemir (difference: -0.08; 95% credible interval (CrI): -0.40 to 0.24), neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH; 0.01; -0.28 to 0.32), degludec (-0.12; -0.42 to 0.20) and premixed insulin (0.26; -0.04 to 0.58). Change in body weight was comparable between Gla-300 and detemir (0.69; -0.31 to 1.71), NPH (-0.76; -1.75 to 0.21) and degludec (-0.63; -1.63 to 0.35), but significantly lower compared with premixed insulin (-1.83; -2.85 to -0.75). Gla-300 was associated with a significantly lower nocturnal hypoglycaemia rate versus NPH (risk ratio: 0.18; 95% CrI: 0.05 to 0.55) and premixed insulin (0.36; 0.14 to 0.94); no significant differences were noted in Gla-300 versus detemir (0.52; 0.19 to 1.36) and degludec (0.66; 0.28 to 1.50). Differences in documented symptomatic hypoglycaemia rates of Gla-300 versus detemir (0.63; 0.19 to 2.00), NPH (0.66; 0.27 to 1.49) and degludec (0.55; 0.23 to 1.34) were not significant. Extensive sensitivity analyses supported the robustness of these findings.
Conclusions: NMA comparisons are useful in the absence of direct randomised controlled data. This NMA suggests that Gla-300 is also associated with a significantly lower risk of nocturnal hypoglycaemia compared with NPH and premixed insulin, with glycaemic control comparable to available basal insulin comparators.
Keywords: DIABETES & ENDOCRINOLOGY.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures

References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas: sixth edition. http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas (accessed 21 Mar 2014).
-
- World Health Organization. Diabetes Fact Sheet. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/ (accessed 1 May 2015).
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015;38:140–9. 10.2337/dc14-2441 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
