The Effect of Pre-sowing Seed Treatment with Metal Nanoparticles on the Formation of the Defensive Reaction of Wheat Seedlings Infected with the Eyespot Causal Agent
- PMID: 26880729
- PMCID: PMC4754232
- DOI: 10.1186/s11671-016-1305-0
The Effect of Pre-sowing Seed Treatment with Metal Nanoparticles on the Formation of the Defensive Reaction of Wheat Seedlings Infected with the Eyespot Causal Agent
Abstract
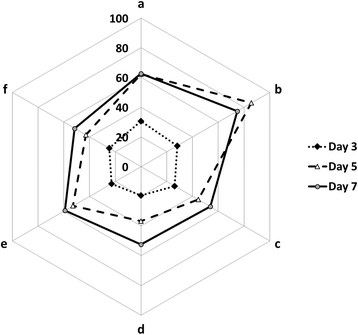
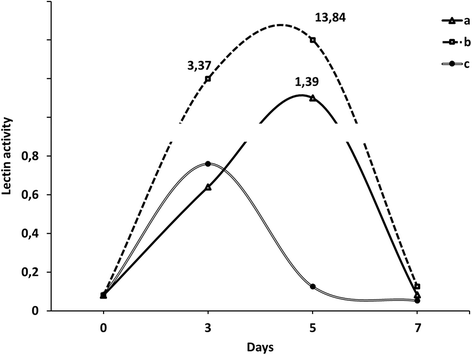
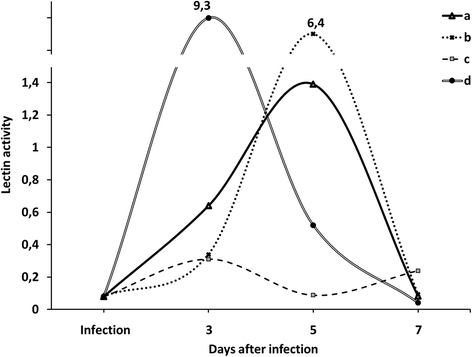
The paper presents research data of lipid peroxidation and lectin activity in wheat seedlings at seed treatment with solution of metal nanoparticles (Zn, Ag, Fe, Mn, Cu) and sole solution of copper nanoparticles under the high pathogen infection background of Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides (Fron) Deighton (synonym: Oculimacula yallundae (Wallwork & Sponer) Crous & W. Gams). It was shown that investigated nonionic colloidal solutions of biogenic metals have the antioxidant effect through the inhibition of the synthesis of lipid peroxidation products. The increase of lectin activity levels during the early plants ontogenesis stages was observed in wheat seedlings infected with pathogen pre-treated with the mixture of metal nanoparticles.
Keywords: Lectins; Lipid peroxidation; Metal nanoparticles; Oculimacula yallundae; Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides; Wheat.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effect of Silver and Copper Nanoparticles on the Wheat-Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides Pathosystem.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2017 Dec;12(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s11671-017-2028-6. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2017. PMID: 28381077 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association mapping of resistance to eyespot disease (Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides) in European winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and fine-mapping of Pch1.Theor Appl Genet. 2017 Mar;130(3):505-514. doi: 10.1007/s00122-016-2830-z. Epub 2016 Nov 19. Theor Appl Genet. 2017. PMID: 27866227
-
Redistribution of elements of metals in plant tissues under treatment by non-ionic colloidal solution of biogenic metal nanoparticles.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2014 Jul 15;9(1):354. doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-9-354. eCollection 2014. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2014. PMID: 25114646 Free PMC article.
-
Fungicide resistance status in French populations of the wheat eyespot fungi Oculimacula acuformis and Oculimacula yallundae.Pest Manag Sci. 2013 Jan;69(1):15-26. doi: 10.1002/ps.3408. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Pest Manag Sci. 2013. PMID: 23073993 Review.
-
Biogenic synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles by seed plants.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014 Feb;14(2):2024-37. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2014.8897. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24749471 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of seed coating with copper, iron and zinc nanoparticles on growth and yield of tomato.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2021 Oct;15(8):674-679. doi: 10.1049/nbt2.12064. Epub 2021 Jul 29. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34694722 Free PMC article.
-
Colloidal Nanomolybdenum Influence upon the Antioxidative Reaction of Chickpea Plants (Cicer arietinum L.).Nanoscale Res Lett. 2016 Dec;11(1):476. doi: 10.1186/s11671-016-1690-4. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2016. PMID: 27783378 Free PMC article.
-
Copper-Containing Bionanocomposites Based on Natural Raw Arabinogalactan as Effective Vegetation Stimulators and Agents against Phytopathogens.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Mar 6;16(5):716. doi: 10.3390/polym16050716. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475399 Free PMC article.
-
Nanopriming technology for enhancing germination and starch metabolism of aged rice seeds using phytosynthesized silver nanoparticles.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 15;7(1):8263. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08669-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28811584 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Bio-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles on Germination, Early Seedling Development, and Metabolome of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Molecules. 2022 Apr 1;27(7):2303. doi: 10.3390/molecules27072303. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35408702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamovskaya VG, Linchevskiy AA, Molodchenkova OO, Tsiselskaya LI. Lectins of the cell walls of barley seedlings at Fusarium culmorum infection and influence of salicylic acid. Physiol Biochem Cultivated Plants. 2005;3:267–274.
-
- Babosha AB. Lectins and the problem of plant pathogens recognition by host plant. J General Biology. 2008;69:5.379–96. - PubMed
-
- Batsmanova LM, Taran NYu (2010). Screening for adaptive capacity of plants based on the indicators of oxide stress. Avega, Kyiv. p.79.
-
- Belava VN, Panyuta OO, Taran NY. The infection model system and evaluation of the resistance level of winter wheat plants (Triticum aestivum L.) to pathogen Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides (Fron) Deighton. Quarantine and Protection Plants. 2008;7:25–28.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

