Mogat1 deletion does not ameliorate hepatic steatosis in lipodystrophic (Agpat2-/-) or obese (ob/ob) mice
- PMID: 26880786
- PMCID: PMC4808770
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M065896
Mogat1 deletion does not ameliorate hepatic steatosis in lipodystrophic (Agpat2-/-) or obese (ob/ob) mice
Abstract
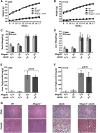
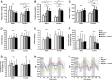
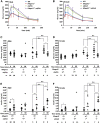
Reducing triacylglycerol (TAG) in the liver continues to pose a challenge in states of nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis. MonoacylglycerolO-acyltransferase (MOGAT) enzymes convert monoacylglycerol (MAG) to diacylglycerol, a precursor for TAG synthesis, and are involved in a major pathway of TAG synthesis in selected tissues, such as small intestine. MOGAT1 possesses MGAT activity in in vitro assays, but its physiological function in TAG metabolism is unknown. Recent studies suggest a role for MOGAT1 in hepatic steatosis in lipodystrophic [1-acylglycerol-3-phosphateO-acyltransferase (Agpat)2(-/-)] and obese (ob/ob) mice. To test this, we deletedMogat1in theAgpat2(-/-)andob/obgenetic background to generateMogat1(-/-);Agpat2(-/-)andMogat1(-/-);ob/obdouble knockout (DKO) mice. Here we report that, despite the absence ofMogat1in either DKO mouse model, we did not find any decrease in liver TAG by 16 weeks of age. Additionally, there were no measureable changes in plasma glucose (diabetes) and insulin resistance. Our data indicate a minimal role, if any, of MOGAT1 in liver TAG synthesis, and that TAG synthesis in steatosis associated with lipodystrophy and obesity is independent of MOGAT1. Our findings suggest that MOGAT1 likely has an alternative function in vivo.
Keywords: 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 2; diabetes; fatty liver; lipodystrophy; monoacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1; ob/ob.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Agarwal A. K., and Garg A.. 2006. Genetic basis of lipodystrophies and management of metabolic complications. Annu. Rev. Med. 57: 297–311. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal A. K., and Garg A.. 2006. Genetic disorders of adipose tissue development, differentiation, and death. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 7: 175–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

