Matrine Attenuates COX-2 and ICAM-1 Expressions in Human Lung Epithelial Cells and Prevents Acute Lung Injury in LPS-Induced Mice
- PMID: 26880863
- PMCID: PMC4736390
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/3630485
Matrine Attenuates COX-2 and ICAM-1 Expressions in Human Lung Epithelial Cells and Prevents Acute Lung Injury in LPS-Induced Mice
Abstract
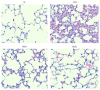
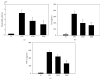
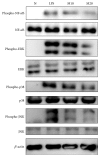
Matrine is isolated from Sophora flavescens and shows anti-inflammatory effects in macrophages. Here we evaluated matrine's suppressive effects on cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expressions in lipopolysaccharide- (LPS-) stimulated human lung epithelial A549 cells. Additionally, BALB/c mice were given various matrine doses by intraperitoneal injection, and then lung injury was induced via intratracheal instillation of LPS. In LPS-stimulated A549 cells, matrine inhibited the productions of interleukin-8 (IL-8), monocyte chemotactic protein-1, and IL-6 and decreased COX-2 expression. Matrine treatment also decreased ICAM-1 protein expression and suppressed the adhesion of neutrophil-like cells to inflammatory A549 cells. In vitro results demonstrated that matrine significantly inhibited mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation and decreased nuclear transcription factor kappa-B subunit p65 protein translocation into the nucleus. In vivo data indicated that matrine significantly inhibited neutrophil infiltration and suppressed productions of tumor necrosis factor-α and IL-6 in mouse bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and serum. Analysis of lung tissue showed that matrine decreased the gene expression of proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, COX-2, and ICAM-1. Our findings suggest that matrine improved lung injury in mice and decreased the inflammatory response in human lung epithelial cells.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Antiinflammatory effects of matrine in LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2011 Dec 18;44(5):573-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2011.09.020. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2011. PMID: 22019524
-
Matrine attenuates allergic airway inflammation and eosinophil infiltration by suppressing eotaxin and Th2 cytokine production in asthmatic mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151(1):470-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.10.065. Epub 2013 Nov 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24231072
-
Matrine alleviates Staphylococcus aureus-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting MLKL and NLRP3-mediated inflammatory activity.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 15;993:177385. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177385. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39956265
-
Synergistic protection of matrine and lycopene against lipopolysaccharide‑induced acute lung injury in mice.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Jul;20(1):455-462. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10278. Epub 2019 May 22. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31180535 Free PMC article.
-
Phloretin inhibits interleukin-1β-induced COX-2 and ICAM-1 expression through inhibition of MAPK, Akt, and NF-κB signaling in human lung epithelial cells.Food Funct. 2015 Jun;6(6):1960-7. doi: 10.1039/c5fo00149h. Food Funct. 2015. PMID: 25996641
Cited by
-
Natural product derived phytochemicals in managing acute lung injury by multiple mechanisms.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Jan;163:105224. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105224. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33007416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydroxytyrosol Exerts Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidant Activities in a Mouse Model of Systemic Inflammation.Molecules. 2018 Dec 5;23(12):3212. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123212. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30563131 Free PMC article.
-
Matrine protects PC12 cells from lipopolysaccharide-evoked inflammatory injury via upregulation of miR-9.Pharm Biol. 2020 Dec;58(1):314-320. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1719165. Pharm Biol. 2020. PMID: 32297823 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Diterpenes, Norditerpenes, and Sesquiterpenes from a Formosan Soft Coral Cespitularia sp.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Dec 1;14(12):1252. doi: 10.3390/ph14121252. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34959653 Free PMC article.
-
Casticin inhibits interleukin-1β-induced ICAM-1 and MUC5AC expression by blocking NF-κB, PI3K-Akt, and MAPK signaling in human lung epithelial cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 15;8(60):101175-101188. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20933. eCollection 2017 Nov 24. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29254155 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

