Comparison of the Mechanical Properties of Early Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin versus PRGF/Endoret Membranes
- PMID: 26880919
- PMCID: PMC4736579
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/1849207
Comparison of the Mechanical Properties of Early Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin versus PRGF/Endoret Membranes
Abstract
Objectives. The mechanical properties of membranes are important factors in the success of treatment and clinical handling. The goal of this study was to compare the mechanical properties of early leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) versus PRGF/Endoret membrane. Materials and Methods. In this experimental study, membranes were obtained from 10 healthy male volunteers. After obtaining 20 cc venous blood from each volunteer, 10 cc was used to prepare early L-PRF (group 1) and the rest was used to get a membrane by PRGF-Endoret system (group 2). Tensile loads were applied to specimens using universal testing machine. Tensile strength, stiffness, and toughness of the two groups of membranes were calculated and compared by paired t-test. Results. The mean tensile strength and toughness were higher in group 1 with a significant difference (P < 0.05). The mean stiffness in group 1 was also higher but not statistically significant (P > 0.05). Conclusions. The results showed that early L-PRF membranes had stronger mechanical properties than membranes produced by PRGF-Endoret system. Early L-PRF membranes might have easier clinical handling and could be a more proper scaffold in periodontal regenerative procedures. The real results of the current L-PRF should be in fact much higher than what is reported here.
Figures









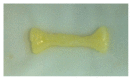
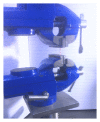
Similar articles
-
The impact of the centrifuge characteristics and centrifugation protocols on the cells, growth factors, and fibrin architecture of a leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) clot and membrane.Platelets. 2018 Mar;29(2):171-184. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2017.1293812. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Platelets. 2018. PMID: 28437133
-
Tensile strength assay comparing the resistance between two different autologous platelet concentrates (leucocyte-platelet rich fibrin versus advanced-platelet rich fibrin): a pilot study.Int J Implant Dent. 2021 Jan 15;7(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s40729-020-00284-w. Int J Implant Dent. 2021. PMID: 33447875 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical and structural properties of leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin membranes: An in vitro study on the impact of anticoagulant therapy.J Periodontal Res. 2020 Oct;55(5):686-693. doi: 10.1111/jre.12755. Epub 2020 May 14. J Periodontal Res. 2020. PMID: 32406545
-
Do the fibrin architecture and leukocyte content influence the growth factor release of platelet concentrates? An evidence-based answer comparing a pure platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) gel and a leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF).Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012 Jun;13(7):1145-52. doi: 10.2174/138920112800624382. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 21740377 Review.
-
Classification of platelet concentrates (Platelet-Rich Plasma-PRP, Platelet-Rich Fibrin-PRF) for topical and infiltrative use in orthopedic and sports medicine: current consensus, clinical implications and perspectives.Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014 May 8;4(1):3-9. eCollection 2014 Jan. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014. PMID: 24932440 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proliferation and differentiation of stem cells in contact with eluate from fibrin-rich plasma membrane.Rev Bras Ortop. 2017 Dec 12;53(1):45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.rboe.2017.12.004. eCollection 2018 Jan-Feb. Rev Bras Ortop. 2017. PMID: 29367906 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Low-Level Laser Therapy in Combination with Leukocyte- and Platelet- Rich Fibrin on Bone Regeneration in Rabbits' Calvarial Defects: Histologic and Histomorphometric Studies.Cell J. 2022 Jun;24(6):346-352. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2022.7864. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Cell J. 2022. PMID: 35892232 Free PMC article.
-
Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (L-PRF) Obtained from Smokers and Nonsmokers Shows a Similar Uniaxial Tensile Response In Vitro.Biomedicines. 2023 Dec 12;11(12):3286. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123286. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137506 Free PMC article.
-
Additive Effect of Platelet Rich Fibrin with Coronally Advanced Flap Procedure in Root Coverage of Miller's Class I and II Recession Defects-A PRISMA Compliant Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Materials (Basel). 2020 Sep 27;13(19):4314. doi: 10.3390/ma13194314. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32992613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological and Mechanical Properties of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Membranes after Thermal Manipulation and Preparation in a Single-Syringe Closed System.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 1;19(11):3433. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113433. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30388866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Newman M. G., Takei H., Klokkevold P. R., Carranza F. A. Carranza's Clinical Periodontology. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2011.
-
- Boyne P. J., Marx R. E., Nevins M., et al. A feasibility study evaluating rhBMP-2/absorbable collagen sponge for maxillary sinus floor augmentation. The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry. 1997;17(1):11–25. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz Z., Carnes D. L., Jr., Pulliam R., et al. Porcine fetal enamel matrix derivative stimulates proliferation but not differentiation of pre-osteoblastic 2T9 cells, inhibits proliferation and stimulates differentiation of osteoblast-like MG63 cells, and increases proliferation and differentiation of normal human osteoblast NHOst cells. Journal of Periodontology. 2000;71(8):1287–1296. doi: 10.1902/jop.2000.71.8.1287. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Marx R. E., Carlson E. R., Eichstaedt R. M., Schimmele S. R., Strauss J. E., Georgeff K. R. Platelet-rich plasma: growth factor enhancement for bone grafts. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontics. 1998;85(6):638–646. doi: 10.1016/s1079-2104(98)90029-4. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

