Comparison of the Utility and Validity of Three Scoring Tools to Measure Skin Involvement in Patients With Juvenile Dermatomyositis
- PMID: 26881696
- PMCID: PMC5053292
- DOI: 10.1002/acr.22867
Comparison of the Utility and Validity of Three Scoring Tools to Measure Skin Involvement in Patients With Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Abstract
Objective: To compare the abbreviated Cutaneous Assessment Tool (CAT), Disease Activity Score (DAS), and Myositis Intention to Treat Activity Index (MITAX) and correlate them with the physician's 10-cm skin visual analog scale (VAS) in order to define which tool best assesses skin disease in patients with juvenile dermatomyositis.
Methods: A total of 71 patients recruited to the UK Juvenile Dermatomyositis Cohort and Biomarker Study were included and assessed for skin disease using the CAT, DAS, MITAX, and skin VAS. The Childhood Myositis Assessment Scale (CMAS), manual muscle testing of 8 groups (MMT8), muscle enzymes, inflammatory markers, and physician's global VAS were recorded. Relationships were evaluated using Spearman's correlations and predictors with linear regression. Interrater reliability was assessed using intraclass correlation coefficients.
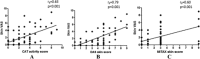
Results: All 3 tools showed correlation with the physician's global VAS and skin VAS, with DAS skin showing the strongest correlation with skin VAS. DAS skin and CAT activity were inversely correlated with CMAS and MMT8, but these correlations were moderate. No correlations were found between the skin tools and inflammatory markers or muscle enzymes. DAS skin and CAT were the quickest to complete (mean ± SD 0.68 ± 0.1 minutes and 0.63 ± 0.1 minutes, respectively).
Conclusion: The 3 skin tools were quick and easy to use. The DAS skin correlated best with the skin VAS. The addition of CAT in a bivariate model containing the physician's global VAS was a statistically significant estimator of skin VAS score. We propose that there is scope for a new skin tool to be devised and tested, which takes into account the strengths of the 3 existing tools.
© 2016, The Authors. Arthritis Care & Research published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

References
-
- Feldman BM, Rider LG, Reed AM, Pachman LM. Juvenile dermatomyositis and other idiopathic inflammatory myopathies of childhood. Lancet 2008;371:2201–12. - PubMed
-
- Martin N, Krol P, Smith S, Murray K, Pilkington CA, Davidson JE, et al. A national registry for juvenile dermatomyositis and other paediatric idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: 10 years' experience; the Juvenile Dermatomyositis National (UK and Ireland) Cohort Biomarker Study and Repository for Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2011;50:137–45. - PMC - PubMed
-
- McCann LJ, Juggins AD, Maillard SM, Wedderburn LR, Davidson JE, Murray KJ, et al. The Juvenile Dermatomyositis National Registry and Repository (UK and Ireland): clinical characteristics of children recruited within the first 5 yr. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006;45:1255–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

