Neurotensin Changes Propulsive Activity into a Segmental Motor Pattern in the Rat Colon
- PMID: 26882114
- PMCID: PMC4930308
- DOI: 10.5056/jnm15181
Neurotensin Changes Propulsive Activity into a Segmental Motor Pattern in the Rat Colon
Abstract
Background/aims: Neurotensin is a gut-brain peptide with both inhibitory and excitatory actions on the colonic musculature; our objective was to understand the implications of this for motor patterns occurring in the intact colon of the rat.
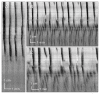
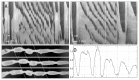
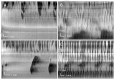
Methods: The effects of neurotensin with concentrations ranging from 0.1-100 nM were studied in the intact rat colon in vitro, by investigating spatio-temporal maps created from video recordings of colonic motility before and after neurotensin.
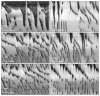
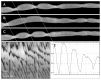
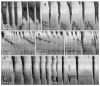
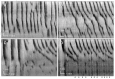
Results: Low concentration of neurotensin (0.1-1 nM) inhibited propagating long distance contractions and rhythmic propagating motor complexes; in its place a slow propagating rhythmic segmental motor pattern developed. The neurotensin receptor 1 antagonist SR-48692 prevented the development of the segmental motor pattern. Higher concentrations of neurotensin (10 nM and 100 nM) were capable of restoring long distance contraction activity and inhibiting the segmental activity. The slow propagating segmental contraction showed a rhythmic contraction-- relaxation cycle at the slow wave frequency originating from the interstitial cells of Cajal associated with the myenteric plexus pacemaker. High concentrations given without prior additions of low concentrations did not evoke the segmental motor pattern. These actions occurred when neurotensin was given in the bath solution or intraluminally. The segmental motor pattern evoked by neurotensin was inhibited by the neural conduction blocker lidocaine.
Conclusions: Neurotensin (0.1-1 nM) inhibits the dominant propulsive motor patterns of the colon and a distinct motor pattern of rhythmic slow propagating segmental contractions develops. This motor pattern has the hallmarks of haustral boundary contractions.
Keywords: Absorption; Colonic motility; Neurotensin; Peristalsis; Propulsion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two independent networks of interstitial cells of cajal work cooperatively with the enteric nervous system to create colonic motor patterns.Front Neurosci. 2011 Aug 5;5:93. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2011.00093. eCollection 2011. Front Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21833164 Free PMC article.
-
Neurogenic and myogenic properties of pan-colonic motor patterns and their spatiotemporal organization in rats.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060474. Epub 2013 Apr 5. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23577116 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of hydrogen sulphide on motility patterns in the rat colon.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 May;169(1):34-50. doi: 10.1111/bph.12100. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23297830 Free PMC article.
-
Colonic motility in humans--a growing understanding.Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1991 Jun;5(2):453-78. doi: 10.1016/0950-3528(91)90037-2. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1991. PMID: 1912659 Review.
-
Physiology and pathophysiology of colonic motor activity (2).Dig Dis Sci. 1991 Jul;36(7):998-1018. doi: 10.1007/BF01297155. Dig Dis Sci. 1991. PMID: 2070711 Review.
Cited by
-
Colonic Transit Time and Gut Peptides in Adult Patients with Slow and Normal Colonic Transit Constipation.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:3178263. doi: 10.1155/2017/3178263. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 29082242 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships Between Distention-, Butyrate- and Pellet-Induced Stimulation of Peristalsis in the Mouse Colon.Front Physiol. 2020 Feb 18;11:109. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00109. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32132933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carraway R, Leeman SE. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem. 1973;248:6854–6861. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

