Practical Strategies and Concepts in GPCR Allosteric Modulator Discovery: Recent Advances with Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors
- PMID: 26882314
- PMCID: PMC4988345
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00656
Practical Strategies and Concepts in GPCR Allosteric Modulator Discovery: Recent Advances with Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors
Abstract
Allosteric modulation of GPCRs has initiated a new era of basic and translational discovery, filled with therapeutic promise yet fraught with caveats. Allosteric ligands stabilize unique conformations of the GPCR that afford fundamentally new receptors, capable of novel pharmacology, unprecedented subtype selectivity, and unique signal bias. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the basics of GPCR allosteric pharmacology, medicinal chemistry, drug metabolism, and validated approaches to address each of the major challenges and caveats. Then, the review narrows focus to highlight recent advances in the discovery of allosteric ligands for metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes 1-5 and 7 (mGlu1-5,7) highlighting key concepts ("molecular switches", signal bias, heterodimers) and practical solutions to enable the development of tool compounds and clinical candidates. The review closes with a section on late-breaking new advances with allosteric ligands for other GPCRs and emerging data for endogenous allosteric modulators.
Figures






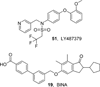





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH062646/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U19 MH106839/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD083211/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA023947/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH102548/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH074953/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM106232/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 MH097056/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS031373/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH082867/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH087965/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA037207/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

