Inhibition of WIP1 phosphatase sensitizes breast cancer cells to genotoxic stress and to MDM2 antagonist nutlin-3
- PMID: 26883108
- PMCID: PMC4924728
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7363
Inhibition of WIP1 phosphatase sensitizes breast cancer cells to genotoxic stress and to MDM2 antagonist nutlin-3
Abstract
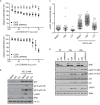
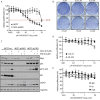
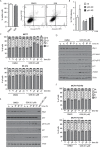
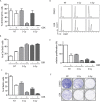
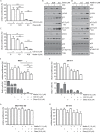
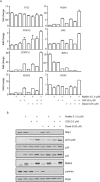
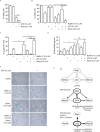
PP2C family serine/threonine phosphatase WIP1 acts as a negative regulator of the tumor suppressor p53 and is implicated in silencing of cellular responses to genotoxic stress. Chromosomal locus 17q23 carrying the PPM1D (coding for WIP1) is commonly amplified in breast carcinomas and WIP1 was proposed as potential pharmacological target. Here we employed a cellular model with knocked out PPM1D to validate the specificity and efficiency of GSK2830371, novel small molecule inhibitor of WIP1. We have found that GSK2830371 increased activation of the DNA damage response pathway to a comparable level as the loss of PPM1D. In addition, GSK2830371 did not affect proliferation of cells lacking PPM1D but significantly supressed proliferation of breast cancer cells with amplified PPM1D. Over time cells treated with GSK2830371 accumulated in G1 and G2 phases of the cell cycle in a p21-dependent manner and were prone to induction of senescence by a low dose of MDM2 antagonist nutlin-3. In addition, combined treatment with GSK2830371 and doxorubicin or nutlin-3 potentiated cell death through a strong induction of p53 pathway and activation of caspase 9. We conclude that efficient inhibition of WIP1 by GSK2830371 sensitizes breast cancer cells with amplified PPM1D and wild type p53 to chemotherapy.
Keywords: WIP1 inhibitor; breast cancer; checkpoint; nutlin-3; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemical Inhibition of Wild-Type p53-Induced Phosphatase 1 (WIP1/PPM1D) by GSK2830371 Potentiates the Sensitivity to MDM2 Inhibitors in a p53-Dependent Manner.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Mar;15(3):379-91. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0651. Epub 2016 Feb 1. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 26832796 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation of Nutlin-3a and a Wip1 inhibitor to induce p53 activity.Oncotarget. 2016 May 31;7(22):31623-38. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9302. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27183917 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting negative regulation of p53 by MDM2 and WIP1 as a therapeutic strategy in cutaneous melanoma.Br J Cancer. 2018 Feb 20;118(4):495-508. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.433. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Br J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29235570 Free PMC article.
-
WIP1 phosphatase as pharmacological target in cancer therapy.J Mol Med (Berl). 2017 Jun;95(6):589-599. doi: 10.1007/s00109-017-1536-2. Epub 2017 Apr 24. J Mol Med (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28439615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the Wip1 phosphatase and its effects on the stress response.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012 Jan 1;17(4):1480-98. doi: 10.2741/3999. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012. PMID: 22201816 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Truncated PPM1D Prevents Apoptosis in the Murine Thymus and Promotes Ionizing Radiation-Induced Lymphoma.Cells. 2020 Sep 10;9(9):2068. doi: 10.3390/cells9092068. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32927737 Free PMC article.
-
Wip1 is associated with tumorigenity and metastasis through MMP-2 in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 May 23;8(34):56672-56683. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18074. eCollection 2017 Aug 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28915621 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic WIP1 phosphatase attenuates the DNA damage response and sensitizes p53 mutant Jurkat cells to apoptosis.Oncol Lett. 2021 Jun;21(6):479. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12740. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33968195 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the adenovirus‑mediated Wip1 gene on lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in a rabbit model.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Dec;16(6):9487-9493. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7774. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 29039507 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Inhibition of WIP1 Sensitizes Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells to the MDM2 Inhibitor Nutlin-3a.Biomedicines. 2021 Apr 6;9(4):388. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9040388. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33917342 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

